标签:student and 操作 编号 分析 create group _id manage
(题目来自力扣)
1、编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第二高的薪水(Salary) 。
+----+--------+
| Id | Salary |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
+----+--------+
例如上述 Employee 表,SQL查询应该返回 200 作为第二高的薪水。如果不存在第二高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
+---------------------+
| SecondHighestSalary |
+---------------------+
| 200 |
+---------------------+
解答:使用mysql 中limit
1)查询结果为null需要在外在次查一次
select (select distinct Salary from Employee order by Salary desc limit 1,1) as SecondHighestSalary
2)使用isnull
select ifnull((select distinct Salary from Employee order by Salary desc limit 1,1),null) as SecondHighestSalary
2、获取第n高的薪水。
create function getNthHighestSalary(N int) returns int begin declare P int default N-1; if (P<0) then return null; else return ( select ifnull( ( select distinct Salary from Employee order by Salary desc limit P,1 ),null) as getNthHighestSalary ); end if; end
3、排序
编写一个 SQL 查询来实现分数排名。如果两个分数相同,则两个分数排名(Rank)相同。请注意,平分后的下一个名次应该是下一个连续的整数值。换句话说,名次之间不应该有“间隔”。
+----+-------+
| Id | Score |
+----+-------+
| 1 | 3.50 |
| 2 | 3.65 |
| 3 | 4.00 |
| 4 | 3.85 |
| 5 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 3.65 |
+----+-------+
例如,根据上述给定的 Scores 表,你的查询应该返回(按分数从高到低排列):
+-------+------+
| Score | Rank |
+-------+------+
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 3.85 | 2 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.50 | 4 |
+-------+------+
解答:
1)mysql 思路 count(distinct b.score) 、自连接、b.score >= a.score
select a.Score , count(distinct b.Score) rank from Scores a ,Scores b where b.Score >= a.Score group by a.id order by a.Score desc;
2) sql 设想b表中比a表那一列大的数量再计数。
select a.Score ,(
select count(distinct b.Score) from Scores b
where b.Score >= a.Score
)rank from Scores a order by a.Score desc
4、Employee 表包含所有员工,他们的经理也属于员工。每个员工都有一个 Id,此外还有一列对应员工的经理的 Id。
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| Id | Name | Salary | ManagerId |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 3 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 4 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | NULL |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | NULL |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
给定 Employee 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,该查询可以获取收入超过他们经理的员工的姓名。在上面的表格中,Joe 是唯一一个收入超过他的经理的员工。
+----------+
| Employee |
+----------+
| Joe |
+----------+
解答:笛卡尔积
select a.Name Employee from Employee a,Employee b where a.ManagerId = b.Id and a.Salary > b.Salary group by a.Id
**5、Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的 Id, salary 和 department Id。
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
+----+----------+
| Id | Name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
+----+----------+
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门工资最高的员工。例如,根据上述给定的表格,Max 在 IT 部门有最高工资,Henry 在 Sales 部门有最高工资。
+------------+----------+--------+
| Department | Employee | Salary |
+------------+----------+--------+
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
+------------+----------+--------+
解答思路:内连接和in
select b.Name Department , a.Name Employee , a.Salary Salary
from Employee a join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id
where (a.DepartmentId,a.Salary) in (
select DepartmentId , max(Salary) from Employee group by DepartmentId
)
6、排序(前三高)
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的工号 Id,姓名 Name,工资 Salary 和部门编号 DepartmentId 。
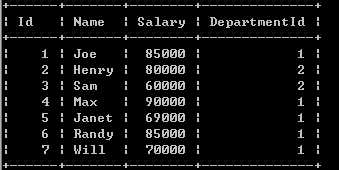
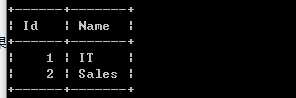
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
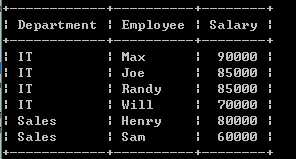
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门获得前三高工资的所有员工。例如,根据上述给定的表,查询结果应返回:
解释:
IT 部门中,Max 获得了最高的工资,Randy 和 Joe 都拿到了第二高的工资,Will 的工资排第三。销售部门(Sales)只有两名员工,Henry 的工资最高,Sam 的工资排第二。
分析:
1)部门相同的情况下,表的自比较,比较b.Salary > a.Salary中不重复b.Salary的个数小于3的情况。(即前三名)
select b.Name Department, a.Name Employee, a.Salary Salary
from Employee a join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id
where 3>(
select count(distinct c.Salary) from Employee c
where c.Salary > a.Salary and a.DepartmentId = c.DepartmentId
) # 关键
2)引入局部变量的计算@
存在一个如下问题,薪水相同的序号不连续,会自动增加1
select tt.Department, tt.Employee, tt.Salary from (
select te.Department,te.Employee,
case
when @p = ID then @r := @r + 1
when @p := ID then @r:=1
end as rank1,
@rk := (case when @sa = te.Salary then @rk else @r end) rank ,
@sa := te.Salary Salary
from (select @p:=0,@r:=0,@rk:=0,@sa:=0) ss,(
select a.DepartmentId ID, b.Name Department ,a.Name Employee ,a.Salary Salary
from Employee a left join Department b
on a.DepartmentId = b.Id
order by a.DepartmentId , a.Salary desc
) te
) tt where tt.rank <=3;
实现如下(4 应为3):
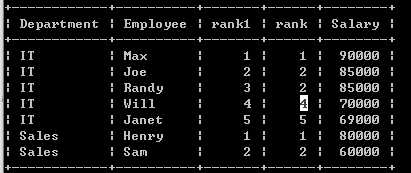
7、删除表中序号ID更大的重复项

思路:表的自连接。查询出email相等且id大的,在删除
delete a from Person a ,Person b where a.Email = b.Email and a.Id > b.Id
8、
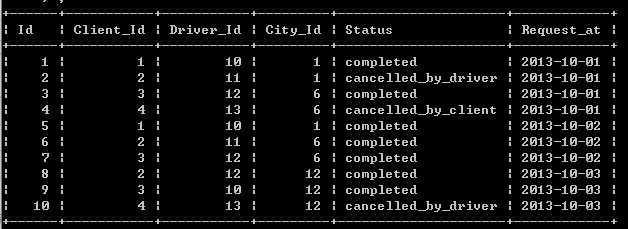
Trips 表中存所有出租车的行程信息。每段行程有唯一键 Id,Client_Id 和 Driver_Id 是 Users 表中 Users_Id 的外键。Status 是枚举类型,枚举成员为 (‘completed’, ‘cancelled_by_driver’, ‘cancelled_by_client’)。
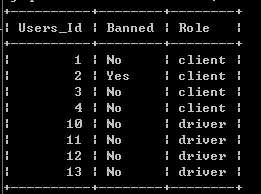
Users 表存所有用户。每个用户有唯一键 Users_Id。Banned 表示这个用户是否被禁止,Role 则是一个表示(‘client’, ‘driver’, ‘partner’)的枚举类型。
Trips表
Users表
写一段 SQL 语句查出 2013年10月1日 至 2013年10月3日 期间非禁止用户的取消率。基于上表,你的 SQL 语句应返回如下结果,取消率(Cancellation Rate)保留两位小数。
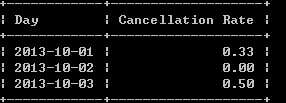
分析:1)、2)可以实现结果,但存在一定的问题,未考虑Driver_Id = Users_Id且被禁止的情况,因题目刚好Driver_Id均未被禁止,所以可以实现结果,1)2)还待需改进。1)改进可以在where后加and Driver_Id <>
1)case when
select t.Request_at Day ,
round(sum(case when t.Status <> ‘completed‘ then 1 else 0 end)/count(t.Request_at),2) as `Cancellation Rate` from
(
select * from Trips where Client_Id <> (
select Users_Id from Users where Banned = ‘Yes‘ and Role = ‘client‘
)
)t
where t.Request_at between "2013-10-01" and "2013-10-03"
group by t.Request_at
2) 左连接
select a.Request_at Day,
round(sum(case when a.Status <> ‘completed‘ then 1 else 0 end)/count(a.Request_at),2) as `Cancellation Rate` from
Trips a left join Users b
on a.Client_Id = b.Users_Id
where b.Banned ="No" and a.Request_at between "2013-10-01" and "2013-10-03"
group by a.Request_at
3) if
select a.Request_at Day,
round(sum( if(a.Status = ‘completed‘,0,1) ) / count(a.Status),2) as `Cancellation Rate`
from Trips a join Users b on
a.Client_Id = b.Users_Id and b.Banned = ‘No‘
join Users c on
a.Driver_Id = c.Users_Id and c.Banned = ‘No‘
where a.Request_at between "2013-10-01" and "2013-10-03"
group by a.Request_at
4) 方法2改进 左连接
select a.request_at as Day, round( sum( if (a.Status = ‘completed‘,0,1) ) / count(a.Status), 2 ) as `Cancellation Rate` from trips a left join ( select users_id from Users where banned = ‘Yes‘ ) b on (a.Client_Id = b.users_id) left join ( select users_id from Users where banned = ‘Yes‘ ) c on (a.Driver_Id = c.users_id) where b.users_id is null and c.users_id is null and a.Request_at between ‘2013-10-01‘ and ‘2013-10-03‘ group by a.Request_at;
8、座位表
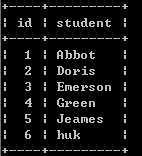
小美是一所中学的信息科技老师,她有一张 seat 座位表,平时用来储存学生名字和与他们相对应的座位 id。其中纵列的 id 是连续递增的,小美想改变相邻俩学生的座位。学生总数奇数,最后一位不换位置。偶数需要换。
seat表:
实现效果如下:
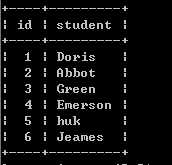
思路:操作id,偶数id-1,奇数id+1,奇数id最大时,id不变
1)case when
select (case when id % 2 = 0 then id - 1 when id = (select max(id) from seat) then id else id +1 end) id , student from seat order by id ;
2) if
select if (mod(id,2)=0,id-1,if(id =(select max(id) from seat),id,id+1)) id ,student from seat order by id ;
3) union 、自连接
( select s1.id ,s2.student from seat s1, seat s2 where s1.id = s2.id -1 and s1.id MOD 2 =1 ) union ( select s1.id, s2.student from seat s1, seat s2 where s1.id = s2.id + 1 and s1.id MOD 2 = 0 ) union ( select s1.id, s1.student from seat s1, seat s2 where s1.id mod 2 = 1 and s1.id = (select max(id) from seat ) ) order by id
标签:student and 操作 编号 分析 create group _id manage
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hqczsh/p/11465216.html