标签:except cep 下标 用户 val als 变量 return runtime
队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的结构来存储队列的数据,则队列数组的声明如下图。其中,maxSize 是该队列的最大容量。
因为队列的输出、输入是分别从前后端来处理,因此需要两个变量 front 及 rear 分别记录队列前后端的下标, front 会随着数据输出而改变,而 rear 则是随着数据输入而改变。如图所示:
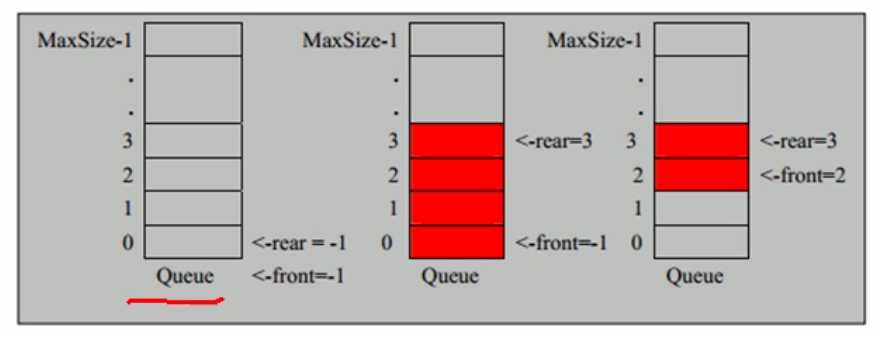
当将数据存入队列时称为 “addQueue”,addQueue 的处理需要有两个步骤:思路分析:
(1)将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当 front == rear 【空】
(2)若尾指针 rear 小于 队列的最大小标 maxSize-1,则将数据存入 rear 所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。rear == maxSize-1【队列满】
代码实现:

1 public class ArrayQueueDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 测试 5 // 创建一个队列 6 ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3); 7 char key = ‘ ‘; // 接收用户输入 8 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 9 boolean loop = true; 10 11 // 输出一个菜单 12 while(loop) { 13 System.out.println("s(show):显示队列"); 14 System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序"); 15 System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列"); 16 System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据"); 17 System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头数据"); 18 19 key = scanner.next().charAt(0); // 接收一个字符 20 switch (key) { 21 case ‘s‘: 22 queue.showQueue(); 23 break; 24 case ‘a‘: 25 System.out.println("输入一个数"); 26 int value = scanner.nextInt(); 27 queue.addQueue(value); 28 break; 29 case ‘g‘: 30 try { 31 int res = queue.getQueue(); 32 System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res); 33 } catch (Exception e) { 34 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 35 } 36 break; 37 case ‘h‘: 38 try { 39 int res = queue.headQueue(); 40 System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n",res); 41 } catch (Exception e) { 42 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); 43 } 44 case ‘e‘: 45 scanner.close(); 46 loop = false; 47 break; 48 default: 49 break; 50 } 51 } 52 System.out.println("程序结束"); 53 } 54 55 } 56 57 // 使用数组模拟队列-编写一个ArrayQueue 类 58 class ArrayQueue { 59 private int maxSize; // 表示数组的最大容量 60 private int front; // 指向队列头 61 private int rear; // 指向队列尾 62 private int[] arr; // 该数据用来存放数据,模拟队列 63 64 // 创建队列的构造方法 65 public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) { 66 maxSize = arrMaxSize; 67 arr = new int[maxSize]; 68 front = -1; // 指向队列头部,分析出 front 是指向队列头的前一个位置 69 rear = -1; // 指向队列尾,指向队列尾的数据(即就是队列最后一个数据) 70 } 71 72 // 判断队列是否满 73 public boolean isFull() { 74 return rear == maxSize - 1; 75 } 76 77 // 判断队列是否为空 78 public boolean isEmpty() { 79 return rear == front; 80 } 81 82 // 添加数据到队列 83 public void addQueue(int n) { 84 // 判断队列是否满 85 if (isFull()) { 86 System.out.println("队列已满,不能加入数据"); 87 return; 88 } 89 rear++; // 让 rear 后移 90 arr[rear] = n; 91 } 92 93 // 获取队列的数据,出队列 94 public int getQueue() { 95 // 判断队列是否空 96 if (isEmpty()) { 97 // 通过抛出异常 98 throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据"); 99 } 100 front++; 101 return arr[front]; 102 } 103 104 // 显示队列的所有数据 105 public void showQueue() { 106 // 遍历数组 107 if (isEmpty()) { 108 System.out.println("队列为空,没有数据"); 109 return; 110 } 111 112 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 113 System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]); 114 } 115 } 116 117 // 显示队列的头数据,不是取出数据 118 public int headQueue() { 119 if (isEmpty()) { 120 throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有数据"); 121 } 122 return arr[front + 1]; 123 } 124 125 }
问题分析并优化:
(1)目前数组使用一次就不能使用,没有达到复用的效果。
(2)将这个数组使用算法,改进成一个环形的数组。
标签:except cep 下标 用户 val als 变量 return runtime
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/niujifei/p/11550025.html