标签:同步 RoCE inf cli html syn 特点 交换 new
AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是 “异步的 Javascript 和 XML”。即使用 Javascript 语言与服务器进行异步交互,传输的数据为 XML(当然,传输的数据不只是 XML)。
AJAX 不是新的编程语言,而是一种使用现有标准的新方法。
AJAX 最大的优点是在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,可以与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页内容。(这一特点给用户的感受是在不知不觉中完成请求和响应过程)
AJAX 不需要任何浏览器插件,但需要用户允许JavaScript在浏览器上执行。
搜索引擎根据用户输入的关键字,自动提示检索关键字。
还有一个很重要的应用场景就是注册时候的用户名的查重。
其实这里就使用了 AJAX 技术!当文件框发生了输入变化时,使用 AJAX 技术向服务器发送一个请求,然后服务器会把查询到的结果响应给浏览器,最后再把后端返回的结果展示出来。
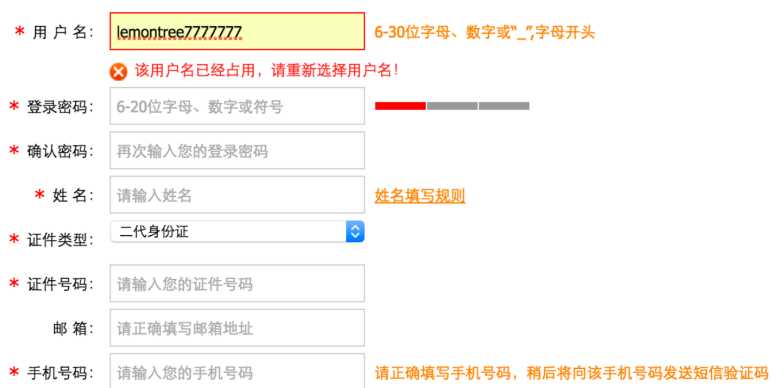
当输入用户名后,把光标移动到其他表单项上时,浏览器会使用 AJAX 技术向服务器发出请求,服务器会查询名为 lemontree7777777 的用户是否存在,最终服务器返回 true 表示名为 lemontree7777777 的用户已经存在了,浏览器在得到结果后显示 “用户名已被注册!”。
页面输入两个整数,通过AJAX传输到后端计算出结果并返回。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<title>Ajax局部刷新示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" id="num1">+
<input type="text" id="num2">=
<input type="text" id="sum">
<button id="submit">计算</button>
<script>
$("#submit").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/test_ajax/',
type: 'post',
data: {
n1: $("#num1").val(),
n2: $("#num2").val()
},
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
$("#sum").val(data)
},
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>def test_ajax(requests):
n1=int(requests.POST.get('n1'))
n2=int(requests.POST.get('n2'))
return HttpResponse(n1+n2)def login(request):
dic = {
'status': 100,
'msg': None
}
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'login.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
# ajax的data里面的name和pwd
username = request.POST.get('name')
password = request.POST.get('pwd')
if username == 'xi' and password == '123':
dic['msg'] = '登录成功'
# 让前端跳转
dic['url'] = 'http://www.baidu.com/'
else:
# return HttpResponse('用户名或密码错误')
# 返回json格式
dic['status'] = 101
dic['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
return JsonResponse(dic)<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>用户名:<input type="text" id="username"></p>
<p>密码:<input type="password" id="password"></p>
<input type="button" value="登录" id="login">
<span id="error"></span>
</body>
<script>
$('#login').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/login/',
type: 'post',
data: {
// 这里的name和pwd是后台需要取的数据
name: $('#username').val(),
pwd: $('#password').val(),
},
success: function (data) {
// 后台用JsonResponse返回数据
// data就会被自动转成对象(python字典对应的json格式)
// 这里的默认编码方式为urlencoded, 会自动转码成 name=xi&pwd=123
console.log(data);
// 后台用HttpResponse, 拿到的data就是json格式的字符串, 需要手动转成json格式对象
var data1 = JSON.parse(data)
console.log(typeof data1)
if (data1.status == 100) {
// 成功, 跳转到指定页面(location.href等于一个地址, 前端就会跳转到指定的url)
location.href = data1.url
} else {
$("#error").text(data1.msg)
}
}
})
})
</script>
</html>from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
import json
# Create your views here.
def login(request):
dic = {
'status': 100,
'msg': None
}
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'login.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
# ajax的data里面的name和pwd
username = request.POST.get('name')
password = request.POST.get('pwd')
if username == 'xi' and password == '123':
dic['msg'] = '登录成功'
# 让前端跳转
dic['url'] = 'http://www.baidu.com/'
else:
# return HttpResponse('用户名或密码错误')
# 返回json格式
dic['status'] = 101
dic['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
return JsonResponse(dic)
def login_json(request):
dic = {
'status': 100,
'msg': None
}
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.POST)
print(request.GET)
print(request.body)
ret = json.loads(str(request.body, encoding='utf-8'))
username = ret.get('name')
password = ret.get('pwd')
print(username, password)
return HttpResponse('OK')<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>用户名:<input type="text" id="username"></p>
<p>密码:<input type="password" id="password"></p>
<input type="button" value="登录" id="login">
<input type="button" value="提交json格式数据" id="sub">
<span id="error"></span>
</body>
<script>
$('#login').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/login/',
type: 'post',
data: {
// 这里的name和pwd是后台需要取的数据
name: $('#username').val(),
pwd: $('#password').val(),
},
success: function (data) {
// 后台用JsonResponse返回数据
// data就会被自动转成对象(python字典对应的json格式)
// 这里的默认编码方式为urlencoded, 会自动转码成 name=xi&pwd=123
console.log(data);
// 后台用HttpResponse, 拿到的data就是json格式的字符串, 需要手动转成json格式对象
var data1 = JSON.parse(data)
console.log(typeof data1)
if (data1.status == 100) {
// 成功, 跳转到指定页面(location.href等于一个地址, 前端就会跳转到指定的url)
location.href = data1.url
} else {
$("#error").text(data1.msg)
}
}
})
})
$('#sub').click(function () {
post_data = {
name: $('#username').val(),
pwd: $('#password').val(),
},
$.ajax({
url: '/login_json/',
type: 'post',
// 指定提交的编码格式是json格式, 就不会自动转码, 就会原封不动的传到后台
contentType: 'application/json',
// 传json格式字符串, 同时还需要手动指定编码方式
data: JSON.stringify(post_data),
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
}
})
})
</script>
</html>写一个装饰器,既能处理 urlencoded 格式,又能处理 json 格式
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
import json
# Create your views here.
def outer(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
# 为了防止错误,主要是处理urlencoded这种编码,让它不处理
try:
request.POST = json.loads(request.body)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
return ret
return inner
@outer
def login(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'login.html')
if request.is_ajax():
print(request.body)
print(request.POST)
# request.body是二进制,loads可以直接传
# request_dic = json.loads(request.body)
# request.POST = request_dic
name = request.POST.get('name')
pwd = request.POST.get('pwd')
print(name, pwd)
return HttpResponse('OK')
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>用户名:<input type="text" id="name"></p>
<p>密码:<input type="password" id="pwd"></p>
<button id="btn">提交</button>
</body>
<script>
$("#btn").click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '/login/',
type: 'post',
contentType: 'application/json',
// 把json对象转成字符串
data: JSON.stringify({
name: $("#name").val(),
pwd: $("#pwd").val(),
}),
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
},
})
})
</script>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>基于form表单上传</h2>
<form action="/file_upload/" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<p>名字:<input type="text" name="name"></p>
<p>文件:<input type="file" name="myfile"></p>
<p><input type="submit" value="上传"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
def file_upload(request):
print(request.POST.get('name'))
# 文件对象
myfile = request.FILES.get('myfile')
with open(myfile.name, 'wb') as f:
for line in myfile:
f.write(line)
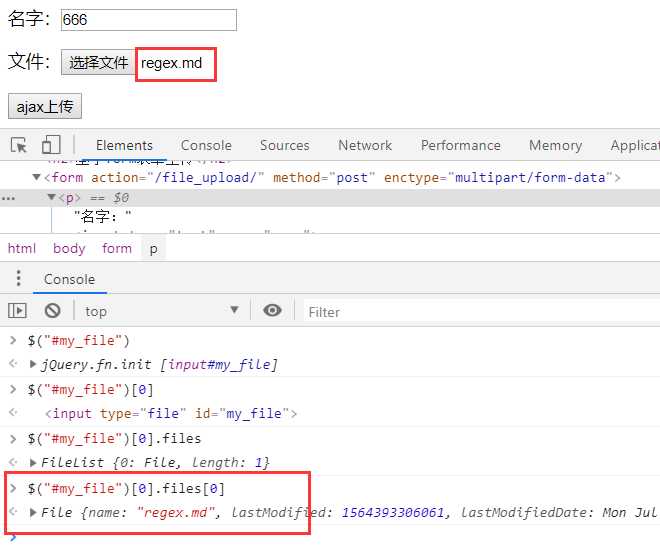
return HttpResponse('上传成功')基于ajax上传,要先取到文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="/static/jquery-3.3.1.js"></script>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>基于AJAX上传</h2>
<p>名字:<input type="text" id="id_name"></p>
<p>文件:<input type="file" id="id_myfile"></p>
<button id="btn_file">ajax上传</button>
</body>
<script>
$("#btn_file").click(function () {
// 取到文件
var myfile = $("#id_myfile")[0].files[0];
var formdata = new FormData();
// 放值
formdata.append('name', $("#id_name").val());
// 放文件
formdata.append('myfile', myfile);
$.ajax({
url: '/file_upload/',
type: 'post',
processData: false, // 不预处理数据,FormData已处理好
contentType: false, // 不指定编码,FormData已指定好
data: formdata,
success: function (data) {
console.log(data)
},
})
})
</script>
</html>from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
def file_upload(request):
print(request.POST.get('name'))
# 文件对象
myfile = request.FILES.get('myfile')
with open(myfile.name, 'wb') as f:
for line in myfile:
f.write(line)
return HttpResponse('上传成功')把对象序列化成 json 字符串
from django.core import serializers
def test(request):
book_list = models.Book.objects.all()[0:10]
ret = serializers.serialize("json", book_list)
return HttpResponse(ret)标签:同步 RoCE inf cli html syn 特点 交换 new
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuxirufeng/p/11614697.html