标签:style blog http io color os ar for sp
题意: 给一个数的序列,询问一些区间,问区间内与区间其他所有的数都互质的数有多少个。
解法: 直接搞有点难, 所谓正难则反,我们求区间内与其他随便某个数不互质的数有多少个,然后区间长度减去它就是答案了。
那么怎么求区间内与区间其他某个数不互质的数的个数(记为cnt)呢? 我们用L[i],R[i]表示在整个序列中左边与 i 最近的与 i 不互质的数的位置,R[i]表示右边的,L[i],R[i]我们可以正反扫一遍顺便分解因子,用个pos[]记录很方便地求出。那么区间内的cnt为L[i]或R[i]在区间内的 i 的个数。
令事件 A:i 的 L[i]在区间内 B:i 的 R[i]在区间内, 则答案为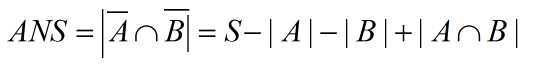
即 cnt = |A|+|B|-|A∩B|
那么
事件A 记为 [L[i],i] 在区间内
事件B 记为 [i,R[i] 在区间内
事件|A∩B| 记为 [L[i],R[i]]在区间内
用三个vector分别存下三种区间。
解决区间内有多少个区间可以用离线树状数组做。
注意: sort 结构体vector时务必在结构体中内嵌比较函数,手写cmp函数再 sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp) 会超时。我也不知道为啥。
代码:

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std; #define N 200007 struct node{ int l,r,ind; node(int _l,int _r,int _ind):l(_l),r(_r),ind(_ind){} node(){} bool operator<(const node &B)const{ return r<B.r; } }Q[N]; vector<node> AB[3]; int ans[3][N],T[N]; int a[N],pos[N],maxi,L[N],R[N],n,m,c[N]; int cmp(node ka,node kb) { return ka.r < kb.r; } int lowbit(int x) { return x&-x; } void modify(int x) { if(x <= 0) return; while(x <= n) { c[x]++; x += lowbit(x); } } int getsum(int x) { int res = 0; while(x > 0) { res += c[x]; x -= lowbit(x); } return res; } void init() { int i,j; for(i=0;i<=maxi;i++) pos[i] = 0; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { int tmp = a[i]; for(j=2;j*j<=tmp;j++) { if(tmp%j == 0) { L[i] = max(L[i],pos[j]); pos[j] = i; while(tmp%j == 0) tmp/=j; } } if(tmp != 1) { L[i]=max(L[i],pos[tmp]); pos[tmp]=i; } } for(i=0;i<=maxi;i++) pos[i] = n+1; for(i=n;i>=1;i--) { int tmp = a[i]; for(j=2;j*j<=tmp;j++) { if(tmp%j == 0) { R[i] = min(R[i],pos[j]); pos[j] = i; while(tmp%j == 0) tmp/=j; } } if(tmp != 1) { R[i]=min(R[i],pos[tmp]); pos[tmp]=i; } } } void GET(int k) { memset(c,0,sizeof(c)); int i,j = 0; for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { int L = Q[i].l; int R = Q[i].r; int ind = Q[i].ind; while(j < n && AB[k][j].r <= R) modify(AB[k][j].l), j++; ans[k][ind] = getsum(R)-getsum(L-1); } } int main() { int i,j; while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF && n+m) { maxi = 0; memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans)); for(i=0;i<3;i++) AB[i].clear(); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]), maxi = max(maxi,a[i]); L[i] = 0, R[i] = n+1; } init(); for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&Q[i].l,&Q[i].r); Q[i].ind = i; T[i] = Q[i].r-Q[i].l+1; } sort(Q+1,Q+m+1); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { AB[0].push_back(node(L[i],i,0)); //A : L[i]在区间内的数的个数 AB[1].push_back(node(i,R[i],0)); //B : R[i]在区间内的数的个数 AB[2].push_back(node(L[i],R[i],0)); //A交B } for(i=0;i<3;i++) { sort(AB[i].begin(),AB[i].end()); GET(i); } for(i=1;i<=m;i++) printf("%d\n",T[i]-ans[0][i]-ans[1][i]+ans[2][i]); //容斥原理 } return 0; }
HDU 4777 Rabbit Kingdom --容斥原理+树状数组
标签:style blog http io color os ar for sp
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/p/4054935.html