标签:入门 降级 amp 最简 高效 ado 数据源 重启 期望

Photo by Janke Laskowski on Unsplash
参考书籍:《Flume构建高可用、可扩展的海量日志采集系统》 ——Hari Shreedharan 著
以下简称“参考书籍”,文中部分资料和图片会标注引用自书中。官方文档简称“官文”。
文章为个人从零开始学习记录,如有错误,还请不吝赐教。

Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统,可以高效地收集、聚合和移动大量的日志数据。它具有基于流数据流的简单灵活的体系结构。它具有鲁棒性(Robust)和容错性,具有可调的可靠性机制和多种故障转移和恢复机制。它使用了一个简单的、可扩展的数据模型,允许在线分析应用程序。
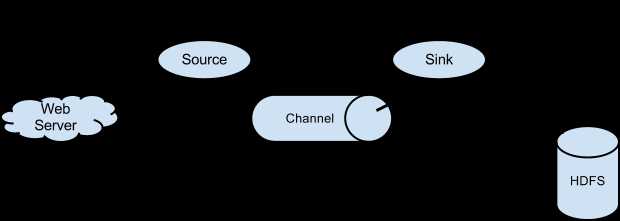
基本工作原理:
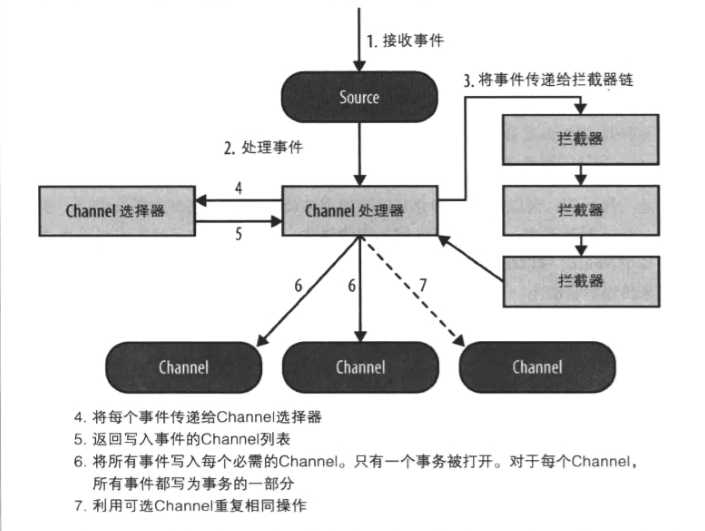
图片取自参考书籍
Flume Agent配置存储在本地配置文件中。这是一个遵循Java Properties文件格式的文本文件。可以在同一个配置文件中指定一个或多个Agent的配置。配置文件包括Agent中每个Source、Sink和Channel的属性以及它们如何连接在一起形成数据流。
source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件,它可以从其他系统中接收数据,像 Java消息服务(JMS)或者其他处理的输出结果,或其他Flume Agent的Sink通过RPC发送的数据。数据源从外部系统或者其他Agent(或者自身生产)接收数 据,并将数据写人到一个或多个Channel中,这些Channel是提前为Source配置过的。这也是Source最基本的职责。
Flume的配置系统验证每个Source的配置和屏蔽错误配置的Source,可以确保:
Flume最重要的特性之一就是Flume部署水平扩展的简单性。可以很容易完成扩展的原因是,很容易为Flume调度添加新的Agent,也很容易配置新的这些Agent发送数据给其他FlumeAgent.类似地,一旦添加了新的Agent,仅仅通过更新配置文件,就能很简单地配置已经运行的Agent来写入这个新的Agent。下面简单的概括官文中提到的几种Flume Source,详细的介绍可参考其他资料,文章后半部分也有一些练习例子。
Channel是位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel允许source和Sink运作在不同的速率上。Channel是Flume保证数据不丢失的关键,当然这是在正确配置的情况下。Source写入数据到一个或多个Channel中,再由一个或多个Sink读取。Sink 只能从一个Channel读取数据,而多个Sink可以从相同的Channel读取以获得更好的性能。
Channel允许source 在同一Channel上操作,以拥有自己的线程模型而不必担心Sink从Channel读取数据,反之亦然。位于Source和Sink之间的缓冲区也允许它们工作在不同的速率,因为写操作发生在缓冲区的尾部,读取发生在缓冲区的头部。这也使得Flume Agent能处理 source “高峰小时”的负载,即使Sink无法立即读取Channel.
Channel允许多个Source和Sink在它们上面进行操作。Channel本质上是事务性的。每次从Channel中写人和读取数据,都在事务的上下文中发生。只有当写事务被提交,事务中的event才可以被任意Sink读取。同样,如果一个Sink已经成功读取了一个event,该event对于其他Sink是不可用的,除非该Sink回滚事务。
Flume官文中的几种Channel:
从Flume Agent移除数据并写人到另一个Agent或数据存储或一些其他系统的组件被称为Sink。Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量移除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启动一个事务。批量event一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent, Sink就利用Channel 提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除event。
Sink使用标准的Flume配置系统进行配置。每个Agent可以没有Sink或若干Sink.每个Sink只能从一个Channel中读取event。如果Sink没有配置Channel,那么Sink就会从Agent中被移除。配置系统保证:
Flume可以聚合线程到Sink组,每个Sink 组可以包含一个或多个Sink.如果一个Sink没有定义Sink组,那么该Sink可以被认为是在一个组内,且该Sink是组内的唯一成员。简单概括:
另外,还有一些没有提到的Sink,比如Kafka Sink、ElasticSearch Sink等之后视情况补充。
Flume Interceptors(拦截器)是设置在Source和Channel之间的插件式组件。Source将Event写入到Channel之前可以使用Interceptors对数据进行过滤和一些处理。每个Interceptors实例只处理同一个Source接收到的Event。在一个 Flume处理流程中可以添加任意数量的Interceptors来链式处理数据,由拦截器链的最后一个拦截器写入数据到Channel。
Channel选择器决定了Source接收的事件写入哪些Channel。如果Flume写入一个Channel时发生故障而发生在其他Channel的事件无法被回滚就会抛出ChannelException导致事务失败。
Flume内置了两种Channel选择器:
Flume为每个Sink组实例化一个Sink Processors来执行Sink组内的任务,Sink组可以包含任意个Sink,一般这用于RPC Sink,在层之间以负载均衡或故障转移的方式传输数据。每个Sink组在活跃列表中被声明为一个组件,就像Source、Sink和Channel一样,使用sinkgroups关键字。每个Sink组是一个需要命名的组件,因为每个Agent可以有多个Sink组。需要注意的是Sink组中所有Sink是不会在同时被激活,任何时候只有它们中的一个用来发送数据。因此,Sink组不应该用来更快地清除Channel,在这种情况下,多个Sink应该只是设置为自己操作自己,而没有Sink组,且它们应该配置从相同的Channel进行读取。
vim HelloFlume.conf //创建Agent配置文件
# example.conf: A single-node Flume configuration
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
# 这个例子监听了本机的44444端口netcat服务
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
#### 配置内容到此结束 ####
bin/flume-ng agent --name a1 --conf conf/ --conf-file learn/part1/HelloFlume.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
# 注意几个参数
# --name 表示启动的agent name ,因为上面配置文件里写了a1,所以这里写a1,key可以简写为-n
# --conf 表示flume的conf目录 ,key可以简写为-c
# --conf-file 表示启动当前agent使用的配置文件,指向上面创建的配置文件,key可以简写为 -f
# 启动成功会发现当前终端被阻塞,启动另一个终端
nc localhost 44444
hello flume
回到阻塞的终端看最新的日志
2019-9-18 09:52:55,583 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor)
[INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)]
Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 66 6C 75 6D 65 hello flume }
直接贴出配置内容
# file-flume.conf 从本地文件系统监控变化并通过avro sink将数据传输给另外两个flume #
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = k1 k2
#configure the source
# 使用TailDir的方式监视文件变化,这种方式可以以较高效率实现断点续传
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /root/public/result/t2.txt
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part2/position.json
#将选择器设置为复制,其实不写也可以,因为这是默认值,熟悉一下
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
# 两个sink分别绑定不同端口
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k2.port = 12346
#bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
# flume-hdfs.conf 从avro source接收数据并上传到hdfs sink #
#name
a2.sources = r1
a2.channels = c1
a2.sinks = k1
#source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = master
a2.sources.r1.port = 12345
#channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
#上传到hdfs的路径
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://master:9000/flume/part2/events/%y-%m-%d/%H%M/%S
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = events
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次,这里因为是学习测试,所以设置的值比较小方便查看
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30
#设置每个文件的滚动大小,这里最好设置成比HDFS块大小小一点
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217000
#文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
# file-local.conf 从avro source接收数据并存储到本地 #
#name
a3.sources = r1
a3.channels = c1
a3.sinks = k1
#source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = master
a3.sources.r1.port = 12346
#channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
#注意这里写出的本地文件路径要提前创建好文件夹,否则flume不会帮你创建导致异常错误
a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part2/localResult/
#bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1配置完成即可开启flume,注意启动的参数要和选择的配置文件中的Agent Name相同
bin/flume-ng agent --name a1 --conf conf/ --conf-file learn/part2/file-flume.conf
bin/flume-ng agent --name a2 --conf conf/ --conf-file learn/part2/flume-hdfs.conf
bin/flume-ng agent --name a3 --conf conf/ --conf-file learn/part2/flume-local.conf由于监控的是本地的某个文件,所以以任意方式向该文件添加信息即可,结果:
[root@master localResult]# hadoop fs -ls -R /flume
drwxr-xr-x - root supergroup 0 2019-9-18 14:33 /flume/part2
drwxr-xr-x - root supergroup 0 2019-9-18 14:33 /flume/part2/events
drwxr-xr-x - root supergroup 0 2019-9-18 14:33 /flume/part2/events/19-9-18
drwxr-xr-x - root supergroup 0 2019-9-18 14:33 /flume/part2/events/19-9-18/1400
drwxr-xr-x - root supergroup 0 2019-9-18 14:35 /flume/part2/events/19-9-18/1400/00
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 3648 2019-9-18 14:34 /flume/part2/events/19-9-18/1400/00/events.1569911635854
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 2231 2019-9-18 14:35 /flume/part2/events/19-9-18/1400/00/events.1569911670803
[root@master localResult]# ls -lh /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part2/localResult/
总用量 8.0K
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2.5K 9月 18 14:34 1569911627438-1
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3.4K 9月 18 14:34 1569911627438-2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 9月 18 14:34 1569911627438-3
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 9月 18 14:35 1569911627438-4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 9月 18 14:35 1569911627438-5故障转移
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
#configure the source,以命令的方式监控本地文件变动
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /root/public/result/t2.txt
#channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k2.port = 12346
#bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1 另外两个Flume启动的配置只有port和name参数不一样,所以只贴出一份
#name
a2.sources = r1
a2.channels = c1
a2.sinks = k1
#source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = master
a2.sources.r1.port = 12345
#channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
#bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f learn/part3/file-flume.conf
bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f learn/part3/flume-sink1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f learn/part3/flume-sink2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console由于配置了Sink k2的优先级比k1高,所以一开始日志信息会全部发送到k2,使用Ctrl+c结束掉k2后信息被转移到k1
至于负载均衡配置,只需要修改几个参数即可
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random因为每个Avro Sink对Avro Source保持持续开放的连接,拥有写人到相同Agent的多个Sink会增加更多的socket连接,且在第二层Agent上占据更多的资源。对相同Agent增加大量Sink之前必须要谨慎考虑。
现在计划让Node1和Node2节点生产数据,采集的日志信息一起聚合到Master机器上,直接上配置
# flume-node1.conf #
#name
a2.sources = r1
a2.channels = c1 c2
a2.sinks = k1 k2
#source
a2.sources.r1.type = exec
a2.sources.r1.command = tail -F /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part4/input/t1.txt
a2.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = avro
a2.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a2.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a2.sinks.k2.type = logger
#bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 # flume-node2.conf #
#name
a3.sources = r1
a3.channels = c1 c2
a3.sinks = k1 k2
#source
a3.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a3.sources.r1.positionFile = /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part4/taildir_position.json
a3.sources.r1.filegroups = f1
a3.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part4/input/t1.txt
a3.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = avro
a3.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a3.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a3.sinks.k2.type = logger
#bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a3.sinks.k2.channel = c2 #name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = k1 k2
#configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = master
a1.sources.r1.port = 12345
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a1.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part4/result/
a1.sinks.k2.type = logger
#bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2配置如上,其实既然跨机器那么Agent name 是否相同都无所谓了,每个配置文件中的两个channel和sink是为了将信息打印到控制台,假如出现了错误方便观察。来一段简单的脚本慢慢的生成数据。
#!/bin/bash
hs=`hostname`
for i in $(seq 1 20)
do
echo "来自${hs}的第${i}条日志" >> /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part4/input/t1.txt
sleep 1
done MASTER:FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f learn/part4/flume-master.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
NODE1:FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f learn/part4/flume-node1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
NODE2:FLUME_HOME/bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f learn/part4/flume-node2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
NODE1:FLUME_HOME/learn/part4/input/generate.sh
NODE2:FLUME_HOME/learn/part4/input/generate.sh
### 数据生成和传输完成后 ###
MASTER:FLUME_HOME/learn/part4/result ls -l
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 368 9月 18 20:38 1569933489286-1
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 774 9月 18 20:38 1569933489286-2### · 拦截器 + 自定义拦截器 ###
通过一些小例子结合着不同的拦截器进行理解消化,现在有如下结构
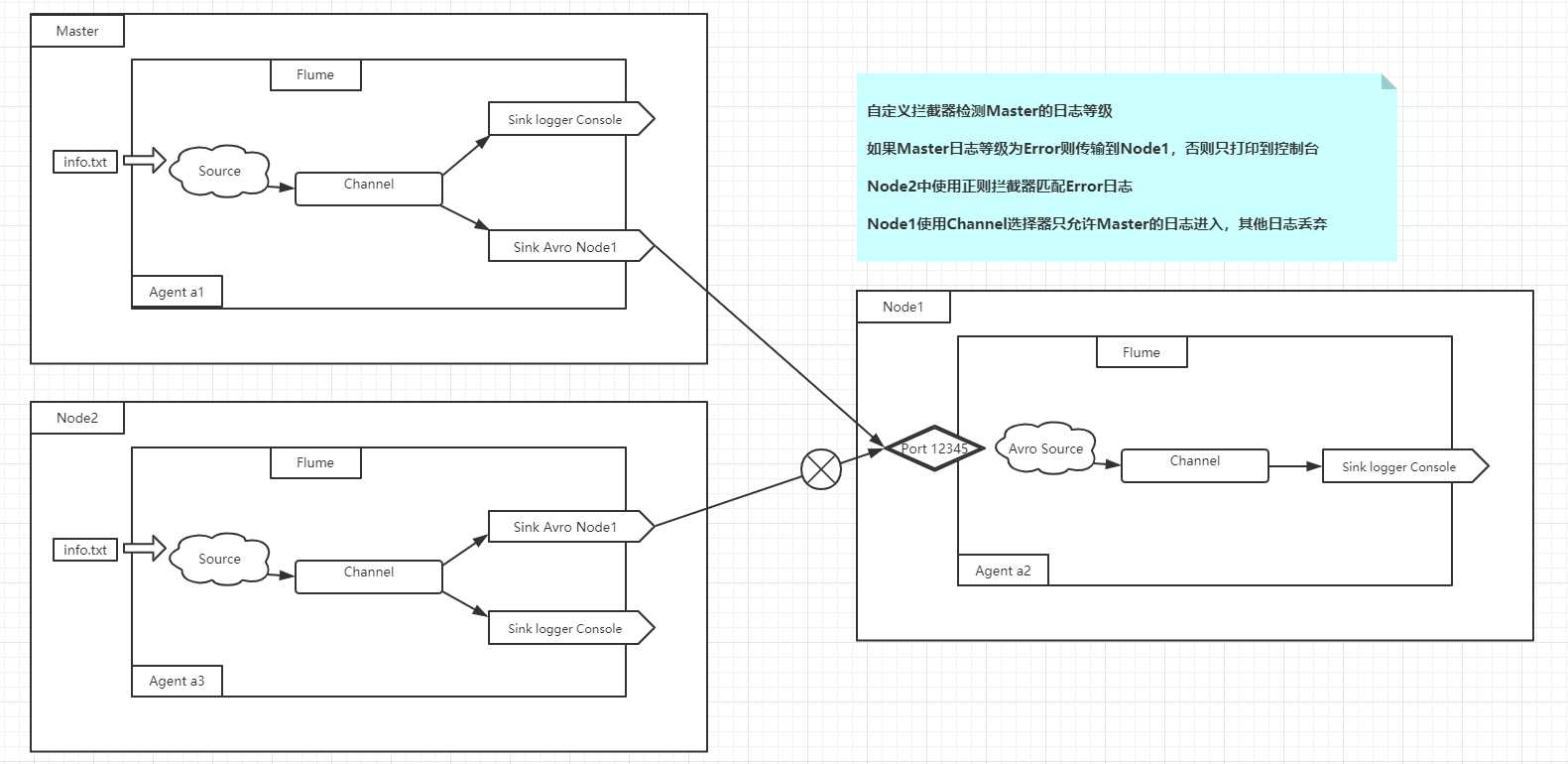
则有如下配置
#flume-master.conf
#name
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels =c1 c2
a1.sinks =k1 k2
#configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part6/input/info.txt
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 i2 i3
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = static
#使用静态拦截器为每个事件添加键值对
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.key = des
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.value = UsingStaticInterceptor
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type = host
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.useIP = false
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.type = priv.landscape.interceptorDemo.LevelInterceptor$Builder
#自定义拦截器
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = level
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.error = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.other = c2
#channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = node1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a1.sinks.k2.type = logger
#bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2 #其中自定义拦截器的关键Java代码 :
public class LevelInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private List<Event> eventList;
@Override
public void initialize() {
eventList = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
String body = new String(event.getBody());
if (body.contains("ERROR")) {
headers.put("level", "error");
} else {
headers.put("level", "other");
}
return event;
}
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) {
eventList.clear();
for (Event event : events) {
eventList.add(intercept(event));
}
return eventList;
}
....... ## flume-node1.conf
#name
a2.sources = r1
a2.channels = c1 c2
a2.sinks = k1 k2
#source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = node1
a2.sources.r1.port = 12345
a2.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a2.sources.r1.selector.header = host
a2.sources.r1.selector.mapping.Master = c1
a2.sources.r1.selector.mapping.Node2 = c2
a2.sources.r1.selector.mapping.default = c2
#channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
a2.sinks.k2.type = null
#bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 #flume-node2.conf
#name
a3.sources = r1
a3.channels = c1 c2
a3.sinks = k1 k2
#source
a3.sources.r1.type = exec
a3.sources.r1.command = tail -F /usr/local/soft/flume-1.9.0/learn/part6/input/info.txt
a3.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 i2
a3.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = regex_filter
a3.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.regex = \[ERROR\]
a3.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type = host
a3.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.useIP = false
#channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
#sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = avro
a3.sinks.k1.hostname = node1
a3.sinks.k1.port = 12345
a3.sinks.k2.type = logger
#bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a3.sinks.k2.channel = c2Event是flume中数据的基本形式,在IDE中添加Flume SDK的Maven依赖,查看Event接口
public interface Event {
public Map<String, String> getHeaders();
public void setHeaders(Map<String, String> headers);
public byte[] getBody();
public void setBody(byte[] body);
}Event接口的默认实现有 SimpleEvent 和 JSONEvent,内部结构不尽相同,可以通过EventBuilder类中的静态方法来快速构建一个Event。
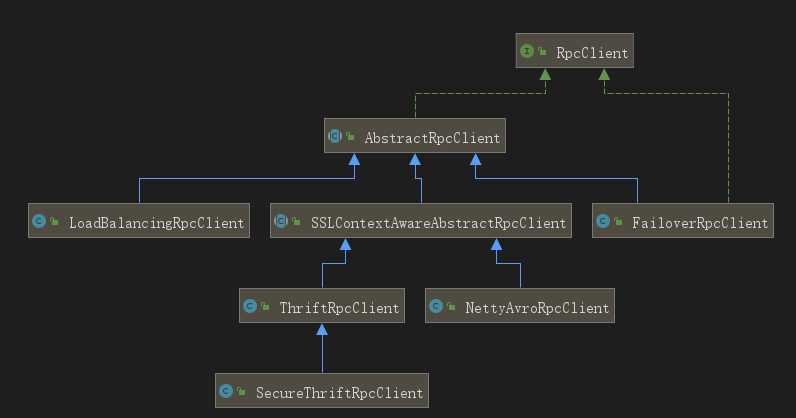
再看RpcClient接口,其中通过append方法来发送一个flume event,也可以通过继承AbstractRpcClient来实现一个RpcClient。
public interface RpcClient {
public int getBatchSize();
public void append(Event event) throws EventDeliveryException;
public void appendBatch(List<Event> events) throws EventDeliveryException;
public boolean isActive();
public void close() throws FlumeException;
}其实现结构如图:
那么尝试使用最简单的代码向Agent发送一次event
public class FlumeClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws EventDeliveryException {
RpcClient client = RpcClientFactory.getDefaultInstance("master", 12345);
client.append(EventBuilder.withBody("hello , 这里是RPC Client".getBytes()));
client.close();
}
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Flume Agent:
2019-9-20 19:37:21,576 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor)
[INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)]
Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F 20 2C 20 E8 BF 99 E9 87 8C E6 98 hello , ........ }看书ing.....
标签:入门 降级 amp 最简 高效 ado 数据源 重启 期望
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/novwind/p/11620626.html