标签:print src 第一个 输出 upper vector ++i 支持 catch

//fig15_04.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator> //ostream_iterator istream_iterator
using namespace std;
//输入两个数 输出两个数的和
int main()
{
istream_iterator<int> inputInt(cin);//与cin关联上
int num1 = *inputInt;//接受一个整数
++inputInt;//移动到下一个输入值
int num2 = *inputInt;//接受下一个输入
ostream_iterator<int> outputInt(cout);//与cout关联上
cout << "the sum is ";
*outputInt = num1 + num2;//接受一个输出
cout << endl;
return 0;
}迭代器还可以这么用 ,卧槽!
//fig15_10.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void printVector(const vector<T>& integers)
{
for (auto constIterator = integers.cbegin();
constIterator != integers.cend(); ++constIterator)
{
cout << *constIterator << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
template <typename T>
void printReverseVector(const vector<T>& integers)
{
for (auto constReverseIterator = integers.crbegin();
constReverseIterator != integers.crend(); ++constReverseIterator)
{
cout << *constReverseIterator << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
const size_t SIZE = 6;
int value[SIZE] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
vector<int> integers;
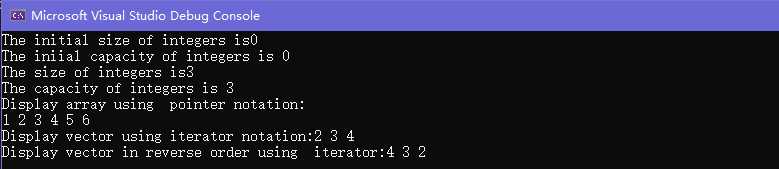
cout << "The initial size of integers is" << integers.size()
<< "\nThe iniial capacity of integers is " << integers.capacity() << endl;
integers.push_back(2);
integers.push_back(3);
integers.push_back(4);
cout << "The size of integers is" << integers.size()
<< "\nThe capacity of integers is " << integers.capacity() << endl;
cout << "Display array using pointer notation:" << endl;
for (const int* ptr = begin(value); ptr != end(value); ++ptr)
{
cout << *ptr << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Display vector using iterator notation:";
printVector(integers);
cout << "Display vector in reverse order using iterator:";
printReverseVector(integers);
return 0;
}
//fig15_11.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const size_t SIZE = 6;
array<int, SIZE> values = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
vector<int> integers(values.cbegin(),values.cend());//使用array来初始化vector
ostream_iterator<int>output(cout, " ");//通过迭代cout来输出元素,以空格来分隔
//输出
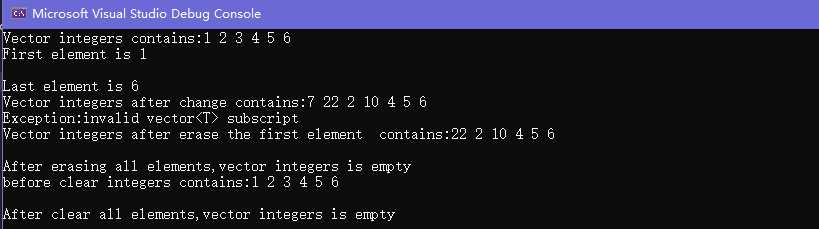
cout << "Vector integers contains:";
copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);
//首尾元素
//front和back返回的是元素的引用,而begin和end返回的是随机访问迭代器
if (!integers.empty())//检查vector是否为空,不检查的话 如果integers是空,则运行时报错
{
cout << "\nFirst element is " << integers.front() << endl;
cout << "\nLast element is " << integers.back() << endl;
}
//随机访问
integers[0] = 7;
integers.at(2) = 10;
//输出
cout << "Now Vector integers contains:";
copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);
cout << endl;//7 2 10 4 5 6
//在第一个元素后面插入22
integers.insert(integers.cbegin() + 1, 22);
//输出
cout << "Vector integers after change contains:";
copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);
cout << endl;//7 22 2 10 4 5 6
try
{
integers.at(200) = 1;//at提供越界检查
}
catch (out_of_range&outOfRange)
{
cout<<"Exception:"<<outOfRange.what()<<endl;
}
//移除首元素
integers.erase(integers.cbegin());
//输出
cout << "Vector integers after erase the first element contains:";
copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);
cout << endl;
//使用迭代器清空
integers.erase(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend());
cout << "\nAfter erasing all elements,vector integers " << (integers.empty() ? "is" : "is not") << " empty" << endl;
//使用array来插入元素
integers.insert(integers.cbegin(), values.cbegin(), values.cend());
cout << "before clear integers contains:";
copy(integers.cbegin(), integers.cend(), output);
cout << endl;
//清空
integers.clear();
cout << "\nAfter clear all elements,vector integers " << (integers.empty() ? "is" : "is not") << " empty" << endl;
return 0;
}
//fig15_13.cpp
//List
#include <list>
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void printList(const list<T>& listRef)
{
if (listRef.empty())
{
cout << "list is empty!" << endl;
}
else
{
ostream_iterator<T> output(cout, " ");
copy(listRef.cbegin(), listRef.cend(), output);
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
const size_t SIZE = 4;
array<int, SIZE>ints = { 1,2,3,4 };
list<int> values;
list<int> otherValues;
values.push_front(1);
values.push_front(2);
values.push_back(4);
values.push_back(3);
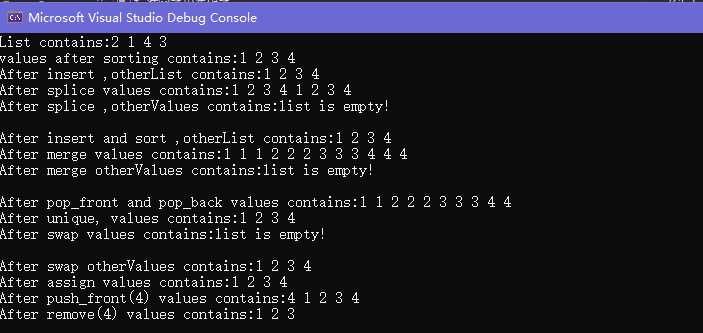
cout << "List contains:";
printList(values);
//排序
values.sort();
cout << "values after sorting contains:";
printList(values);
//使用array来插入otherValues
otherValues.insert(otherValues.cbegin(), ints.cbegin(), ints.cend());
cout << "After insert ,otherList contains:";
printList(otherValues);
//splice做了两步:第一步将othevalues里的值插入到values.cend(),第二步将otherValues里的值清空
values.splice(values.cend(), otherValues);
cout << "After splice values contains:";
printList(values);
cout << "After splice ,otherValues contains:";
printList(otherValues);
otherValues.insert(otherValues.cbegin(), ints.cbegin(), ints.cend());
cout << "After insert and sort ,otherList contains:";
otherValues.sort();
printList(otherValues);
values.sort();
//使用merge前,两个容器必须先排序
//merge也是做了两步,第一步将两个容器归并(类似于归并排序),第二步将otherValues清空
values.merge(otherValues);
cout << "After merge values contains:";
printList(values);
cout << "After merge otherValues contains:";
printList(otherValues);
values.pop_front();
values.pop_back();
cout << "After pop_front and pop_back values contains:";
printList(values);
//去重
values.unique();
cout << "After unique, values contains:";
printList(values);
//交换
values.swap(otherValues);
cout << "After swap values contains:";
printList(values);
cout << "After swap otherValues contains:";
printList(otherValues);
//赋值
values.assign(otherValues.cbegin(), otherValues.cend());
cout << "After assign values contains:";
printList(values);
values.push_front(4);
cout << "After push_front(4) values contains:";
printList(values);
//移除所有的4
values.remove(4);
cout << "After remove(4) values contains:";
printList(values);
return 0;
}
//fig15_14.cpp
//deque 双端队列
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
deque<double>values;
ostream_iterator<double> output(cout, " ");
//双端
values.push_front(2.2);
values.push_front(3.5);
values.push_back(1.1);
//随机访问
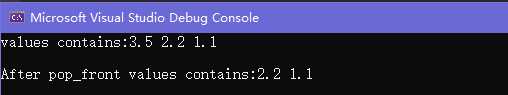
cout << "values contains:";
for (size_t i = 0; i < values.size(); ++i)
{
cout << values[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
values.pop_front();
cout << "\nAfter pop_front values contains:";
copy(values.cbegin(), values.cend(), output);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
//fig15_15.cpp
//multi_set
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const size_t SIZE = 6;
array<int, SIZE> a = { 11,21,13,21,54,66 };
//按照从小到大顺序排序 less<int>
multiset<int, less<int>> intMultiset;
ostream_iterator<int> output(cout, " ");
//count 是说该元素在multiset中含有几个
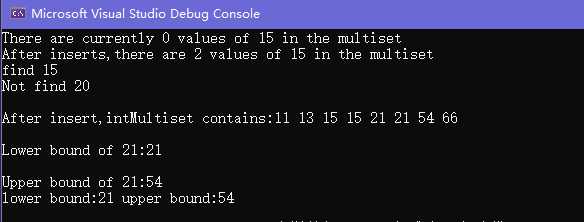
cout << "There are currently " << intMultiset.count(15)
<< " values of 15 in the multiset" << endl;//0
intMultiset.insert(15);
intMultiset.insert(15);
cout << "After inserts,there are " << intMultiset.count(15)
<< " values of 15 in the multiset" << endl;//2
//查找
auto result = intMultiset.find(15);
if (result!=intMultiset.end())
{
cout << "find 15" << endl;
}
result = intMultiset.find(20);
if (result == intMultiset.end())
{
cout << "Not find 20" << endl;
}
intMultiset.insert(a.cbegin(), a.cend());
cout << "\nAfter insert,intMultiset contains:";
copy(intMultiset.cbegin(), intMultiset.cend(), output);
cout << endl;
//确定某个值的边界
cout << "\nLower bound of 21:" << *(intMultiset.lower_bound(21)) << endl;//下边界
cout << "\nUpper bound of 21:" << *(intMultiset.upper_bound(21)) << endl;//上边界
//返回的是pair对象,包含下边界和上边界
auto p = intMultiset.equal_range(21);
cout << "lower bound:" <<*p.first << " upper bound:" << *p.second << endl;
return 0;
}
//fig15_16.cpp
//multimap
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
multimap<int, double, less<int>> mymap;
//count 是说该元素在multiset中含有几个
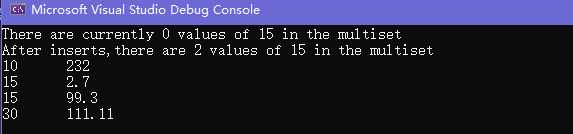
cout << "There are currently " << mymap.count(15)
<< " values of 15 in the multiset" << endl;//0
mymap.insert(make_pair(15, 2.7));
mymap.insert(make_pair(15, 99.3));
cout << "After inserts,there are " << mymap.count(15)
<< " values of 15 in the multiset" << endl;//2
mymap.insert(make_pair(30,111.11));
mymap.insert(make_pair(10,232));
//遍历
for (auto it : mymap)
{
cout << it.first << "\t" << it.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
//fig15_18.cpp
//map
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
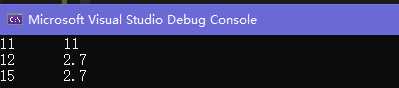
map<int, double, less<int>>mymap;
mymap.insert(make_pair(15, 2.7));
mymap.insert(make_pair(11, 2.7));
mymap.insert(make_pair(12, 2.7));
mymap.insert(make_pair(15, 2.6));//ignored
mymap.insert(make_pair(15, 2.1));//ignored
mymap[11] = 11;
for (auto it : mymap)
{
cout << it.first << "\t" << it.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
标签:print src 第一个 输出 upper vector ++i 支持 catch
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/tailiang/p/11659838.html