标签:include names 效率 类的成员 namespace 面向 一个 return 指定
所谓继承就是从先辈处得到属性和行为特征。类的继承,是新的类从已有类那里得到已有的特性。从另一个角度来看这个问题,从已有类产生新类的过程就是类的派生。类的继承与派生机制允许程序员在保持原有类特性的基础上,进行更具体、更详细的修改和扩充。由原有的类产生新类时,新类便包含了原有类特征,同时也可以加入自己所特有的新特性。原有的类称为基类或父类,产生的新类称为派生类或子类。
面向对象程序设计中最重要的一个概念是继承。继承允许我们依据另一个类来定义一个类,这使得创建和维护一个应用程序变得更容易。这样做,也达到了重用代码功能和提高执行效率的效果。
当创建一个类时,不需要重新编写新的数据成员和成员函数,只需指定新建的类继承了一个已有的类的成员即可。
单继承
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名
{
派生类新定义成员
};多继承
class 派生类名:继承方式1 基类1,继承方式2 基类2
{
派生类成员声明;
};当一个类派生自基类,该基类可以被继承为 public、protected 或 private 几种类型。继承的方式规定了如何访问从基类继承的成员。当使用不同类型的继承时,遵循以下几个规则:
公有继承
| 基类成员访问属性 | 派生类成员访问属性 |
|---|---|
| public | public |
| protected | protected |
| private | 无法访问 |
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX() { return x; }
float GetY() { return y; }
private:
float x, y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx, float yy)
{
x = xx;
y = yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff, float yOff)
{
x = xOff;
y = yOff;
}
class Rectangle : public Point
{
public:
void initR(float x, float y, float w, float h)
{
initP(x, y);
W = w;
H = h;
}
float GetW() { return W; }
float GetH() { return H; }
private:
float W, H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r;
r.initR(1,2,3,4);
r.Move(5,7);
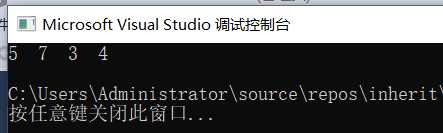
cout << r.GetX() <<" "<< r.GetY() <<" "<< r.GetW() <<" "<< r.GetH() << endl;
}运行截图
私有继承
| 基类成员访问属性 | 派生类成员访问属性 |
|---|---|
| public | private |
| protected | private |
| private | 无法访问 |
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX() { return x; }
float GetY() { return y; }
private:
float x, y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx, float yy)
{
x = xx;
y = yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff, float yOff)
{
x = xOff;
y = yOff;
}
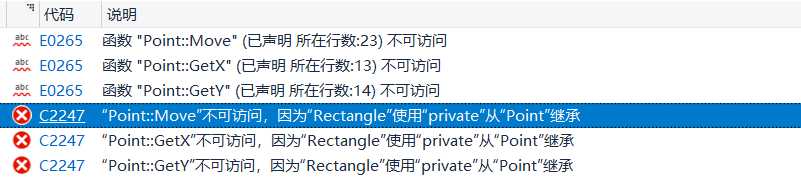
class Rectangle : private Point // 将上一段代码里的public改成了private
{
public:
void initR(float x, float y, float w, float h)
{
initP(x, y);
W = w;
H = h;
}
float GetW() { return W; }
float GetH() { return H; }
private:
float W, H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r;
r.initR(1,2,3,4);
r.Move(5,7);
cout << r.GetX() <<" "<< r.GetY() <<" "<< r.GetW() <<" "<< r.GetH() << endl;
}运行截图
保护继承
| 基类成员访问属性 | 派生类成员访问属性 |
|---|---|
| public | protected |
| protected | protected |
| private | 无法访问 |
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
void initP(float xx,float yy);
void Move(float xOff,float yOff);
float GetX() { return x; }
float GetY() { return y; }
private:
float x, y;
};
void Point::initP(float xx, float yy)
{
x = xx;
y = yy;
}
void Point::Move(float xOff, float yOff)
{
x = xOff;
y = yOff;
}
class Rectangle : protected Point //将第一段代码里的public改成protected
{
public:
void initR(float x, float y, float w, float h)
{
initP(x, y);
W = w;
H = h;
}
float GetW() { return W; }
float GetH() { return H; }
private:
float W, H;
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r;
r.initR(1,2,3,4);
r.Move(5,7);
cout << r.GetX() <<" "<< r.GetY() <<" "<< r.GetW() <<" "<< r.GetH() << endl;
}
运行截图

通过比较私有继承和保护继承可以看出,实际上在直接派生类中,所有成员的访问属性都是完全相同的。但是,如果派生类作为新的基类继续派生时,二者就会产生差别
标签:include names 效率 类的成员 namespace 面向 一个 return 指定
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/li1377665196/p/11662638.html