标签:get eth 添加 gen class bean maven依赖 request prototype
本篇知识点有:maven依赖,applicationContext.xml配置文件,Scope作用域,初始化和销毁,延时初始化lazy-init,工厂Factory,Aware接口,动态bean。内容可能过多,建议准备好瓜子可乐,不足之处,多多指正。
因为我们使用的是maven + spring-context学习的,所以在使用spring之前,我们要先把maven依赖导入进来,导入spring-context5.2.0.RELEASE版本。
导入代码如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.2.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
一般我们把这个配置文件命名为applicationContext_xxx.xml,xxx为功能
在IDEA中,创建这个配置文件步骤:选择resources文件夹,右键--->new----->XML configuration File---->Spring Config
这个配置里面一般是用来管理spring要管理的bean,注意:bean不能为接口或抽象类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> </beans>
spring2.0版本之前的版本作用域只有两种:prototype(原型)和singleton(单例)。
spring2..0版本1之后新增了三种作用域:request(请求),session(会话),global session(Http Session作用域)。
什么是作用域?
通俗来说就是指定spring中管理的bean在什么时候生效,在什么范围内作用生效。
下面一起来了解一下这些作用域的作用。
1、prototype原型(又名 non-singleton非单例)
每次getBean的时候都会重新new一个新的对象。
2、singleton单例
在spring容器创建的时候已经创建了bean对象,每次getBean的时候,会从容器中去获取bean对象,只会被创建一次,遵循单例模式。
3、request请求
在web环境下生效,被spring管理的bean,它的生存周期在一个完整的请求周期里面。
4、session会话
在web环境下生效,被spring管理的bean,它的生存周期在一个完整的session里面,session关闭或者程序结束的时候,它的生存周期也会结束,不同的人有不同的会话,互相不干扰。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--scope设置这个bean的作用域--> <bean id="getEmp" scope="prototype" class="com.dao.EmpDao"/> </beans>
spring提供了全局default-init-method,default-destroy-method和单个init-method,destroy-method
1、全局初始化和销毁
设置了全局初始化和销毁方法的bean,会在bean的创建和销毁时去bean中寻找init和destroy方法,并且调用此方法,如果没有,就不调用。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-init-method="init" default-destroy-method="destroy"> </bean>
2、单个初始化和销毁
设置了单个初始化或销毁方法的bean,将覆盖掉全局的初始化和销毁方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-init-method="init" default-destroy-method="destroy"> <bean id="getEmp" scope="singleton" class="com.dao.EmpDao" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> </bean> </bean>
延时初始化只对Scope为singleton的对象有效,因为单例对象在容器加载时候就会创建,如果bean过多,就会造成资源负载,性能低,spring提供了一个lazy-init,设置为true的时候,容器启动时不会立即实例化bean对象,等到getBean时才实例化。
1、全局延时加载
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-init-method="true"> </beans>
2、单个延时加载
和初始化销毁一样,设置了单个延时加载会将全局的覆盖掉。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-init-method="true"> <bean id="getEmp" scope="singleton" class="com.dao.EmpDao" lazy-init="true"> </bean> </beans>
三种工厂实现:静态,实例,接口
我们通过工厂AFactory类或者MyFactory将类A创建出来
A类
package com.dao; public class A { }
AFactory类
package com.dao; public class AFactory { private static A a = new A(); //静态 public static A createA(){ return a; } //实例 public A createA2(){ return a; } }
MyFactory类
package com.dao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean; public class MyFactory implements FactoryBean<A> { //得到对象 @Override public A getObject() throws Exception { return new A(); } //得到bean类型 @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return A.class; } //是否使用单例 @Override public boolean isSingleton() { return true; } }
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 静态,createA必须为静态方法--> <bean id="getA" class="com.dao.AFactory" factory-method="createA"> </bean> <!-- 实例--> <bean id="AFactory" class="com.dao.AFactory"></bean> <bean id="getA2" factory-bean="AFactory" factory-method="createA2"></bean> <!-- 接口--> <bean id="getA3" class="com.dao.MyFactory"></bean> </beans>
测试:
package com.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestFactory { @Test public void test_AFactory(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Object obj1 = context.getBean("getA"); Object obj2 = context.getBean("getA2"); Object obj3 = context.getBean("getA3"); System.out.println(obj1+"------getA"); System.out.println(obj2+"------getA2"); System.out.println(obj3+"------getA3"); } }
测试结果: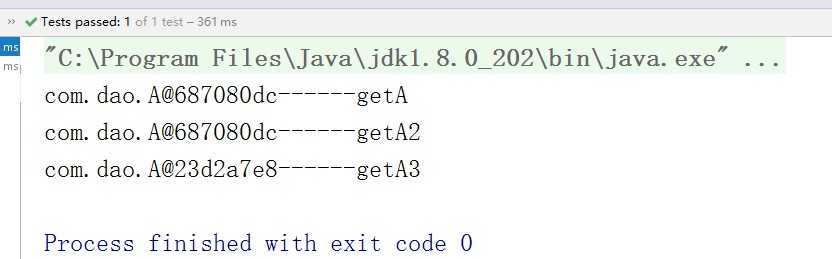
因为使用单例作用域,所有第一个和第二个的对象是一样的。
以上三种方法都能实现工厂模式创建出A类对象。
被spring管理的类实现Aware接口可以自动注入一些内容。
package aware; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class SomeBean implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware { private ApplicationContext context; private String name; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.context = applicationContext; } public ApplicationContext getContext(){ return this.context; } public String getName(){ return this.name; } @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id="someBean" class="aware.SomeBean"/> </beans>
测试:
package aware;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_aware.xml");
SomeBean bean = context.getBean("someBean", SomeBean.class);
ApplicationContext context2 = bean.getContext();
String name = bean.getName();
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(context == context2);
//因为自动注入了一些内容,所有我们可以获取得到
}
}
有些时候,我们不知道有什么bean是需要注册的,它是动态,不确定的,那么需要一个能够动态自动帮我们注册bean的方法
package dynamic; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; public class DynamicRegistrator implements BeanFactoryAware { private BeanFactory beanFactory ; @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { this.beanFactory = beanFactory; } public <T> T register(String name,Class<T> clz,Object... args){ // 通过传入一个bean类型来创建实体定义构造器对象,并且将实体类设置在里面的beanDefinition实体定义对象中的 //beanClass中 ---beanClass为Object类型 BeanDefinitionBuilder definitionBuilder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(clz); //遍历我们传的参数,因为是可变参数,所以通过for循环遍历 for (Object arg : args) { //使用实体定义构造器对象添加bean构造方法的参数,为什么构造参数能够完整无误的添加进来? //因为BeanDefinitionBuilder对象中有一个constructorArgIndex字段用来记录数,addConstructorArgValue方法 // 每次添加一个参数constructorArgIndex就加一。 definitionBuilder.addConstructorArgValue(args); } //通过getRawBeanDefinition获取原始实体定义方法获得一个beanDefinition实体定义类对象 BeanDefinition definition = definitionBuilder.getRawBeanDefinition(); //使用实体定义注册类.注册实体定义的方法,将准备注册的bean的自定义id名称,实体定义类对象实现注册 //将beanFactory强转成BeanDefinitionRegistry接口类型, //然后使用BeanDefinitionRegistry注册实体对象定义的方法 ((BeanDefinitionRegistry)beanFactory).registerBeanDefinition(name, definition); //注册完成,使用实体工厂的getBean返回一个实体对象 return beanFactory.getBean(name, clz); // 流程:1、先创建一个实体定义构造器(并且将beanDefinition的beanClass设置为传过去的实体对象) // 2、添加构造方法的参数 // 3、获取实体定义对象 // 4、将实体定义对象和的bean的id注册 // 5、返回需要的对象,因为已经注册过了,所以得到bean不会出错,实现了动态bean } }
xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id="registrator" class="dynamic.DynamicRegistrator" /> </beans>
使用:
package dynamic; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //得到容器对象 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_dynamic.xml"); //得到动态记录类 DynamicRegistrator registrator = context.getBean("registrator", DynamicRegistrator.class); //创建对象 B b = registrator.register("b", B.class); System.out.println("-----debug: b = " + b); B b2 = context.getBean("b", B.class); System.out.println("-----debug: b2 = " + b2); System.out.println(b==b2); } }
结束!
标签:get eth 添加 gen class bean maven依赖 request prototype
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liweixml/p/11695627.html