标签:worker LEDE one java pointer epo 工作流程 支持 稳定性
1.引言
合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处。第一:降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗。第二:提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要的等到线程创建就能立即执行。第三:提高线程的可管理性。线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。但是要做到合理的利用线程池,必须对其原理了如指掌。
2.线程池使用
Executors提供的四种线程 1.newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。 2.newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。 3.newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。 4.newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
1.newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。示例如下
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i=0;i<5;i++){ final int index = i; try { Thread.sleep(index * 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } executorService.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "," +index); } }); } //控制台信息 pool-1-thread-1,0 pool-1-thread-1,1 pool-1-thread-1,2 pool-1-thread-1,3 pool-1-thread-1,4
2.newFixedThreadPool创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。示例如下
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { final int index = i; fixedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + index); Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } //控制台信息 pool-1-thread-1,0 pool-1-thread-2,1 pool-1-thread-3,2 pool-1-thread-4,3 pool-1-thread-1,4
3.newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持周期和定时任务示例如下
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); System.out.println("before:" + System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); scheduledThreadPool.schedule(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("延迟3秒执行的哦 :" + System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); } }, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("after :" +System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); //控制台信息 before:1518012703 after :1518012703 延迟3秒执行的哦 :1518012706 System.out.println("before:" + System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); scheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("延迟1秒之后,3秒执行一次:" +System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); } }, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("after :" +System.currentTimeMillis()/1000);
控制台消息 before:1518013024 after :1518013024 延迟1秒之后,3秒执行一次:1518013025 延迟1秒之后,3秒执行一次:1518013028 延迟1秒之后,3秒执行一次:1518013031
4.newSingleThreadExecutor创建一个单线程化的线程池,只会用工作线程来执行任务,保证顺序,示例如下
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); for (int i=0;i<10;i++) { final int index = i; singleThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "," + index); Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); }
控制台信息 pool-1-thread-1,0 pool-1-thread-1,1 pool-1-thread-1,2 pool-1-thread-1,3 pool-1-thread-1,4
向线程池提交任务 ThreadPoolExecutor类中execute()和submit()区别 execute()方法实际上是Executor中声明的方法,在ThreadPoolExecutor进行了具体的实现,这个方法是ThreadPoolExecutor的核心方法,通过这个方法可以向线程池提交一个任务,交由线程池去执行。
submit()方法是在ExecutorService中声明的方法,在AbstractExecutorService就已经有了具体的实现,在ThreadPoolExecutor中并没有对其进行重写,这个方法也是用来向线程池提交任务的,但是它和execute()方法不同,它能够返回任务执行的结果,通过源码查看submit()方法的实现,会发现它实际上还是调用的execute()方法,只不过它利用了Future来获取任务执行结果。
/** * @throws RejectedExecutionException {@inheritDoc} * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} */ public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) { if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException(); RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null); execute(ftask); return ftask; }
线程池的关闭 我们可以通过调用线程池的shutdown或shutdownNow方法来关闭线程池,但是它们的实现原理不同,shutdown的原理是只是将线程池的状态设置成SHUTDOWN状态,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程。shutdownNow的原理是遍历线程池中的工作线程,然后逐个调用线程的interrupt方法来中断线程,所以无法响应中断的任务可能永远无法终止。shutdownNow会首先将线程池的状态设置成STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行或暂停任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表。
只要调用了这两个关闭方法的其中一个,isShutdown方法就会返回true。当所有的任务都已关闭后,才表示线程池关闭成功,这时调用isTerminaed方法会返回true。至于我们应该调用哪一种方法来关闭线程池,应该由提交到线程池的任务特性决定,通常调用shutdown来关闭线程池,如果任务不一定要执行完,则可以调用shutdownNow。
3. 线程池的分析
流程分析:线程池的主要工作流程如下图: Java线程池主要工作流程
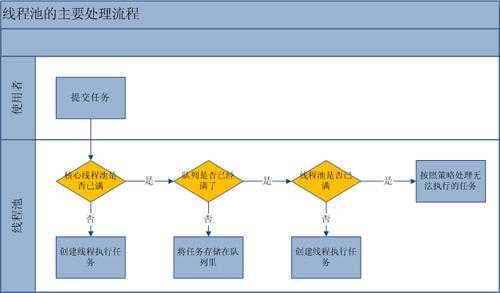
从上图我们可以看出,当提交一个新任务到线程池时,线程池的处理流程如下:
源码分析。上面的流程分析让我们很直观的了解的线程池的工作原理,让我们再通过源代码来看看是如何实现的。线程池执行任务的方法如下:
public void execute(Runnable command) { if (command == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int c = ctl.get(); if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { if (addWorker(command, true)) return; c = ctl.get(); } if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { int recheck = ctl.get(); if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) reject(command); else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0) addWorker(null, false); } else if (!addWorker(command, false)) reject(command); }
工作线程。线程池创建线程时,会将线程封装成工作线程Worker,Worker在执行完任务后,还会无限循环获取工作队列里的任务来执行。
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vkvYJnKfQyuUeD_BDQy_1g
获取面试经等学习资料,可以扫描下方二维码

标签:worker LEDE one java pointer epo 工作流程 支持 稳定性
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lemonrel/p/11699704.html