标签:use 调用 指定 log pos name generate headers 元素
https://www.cnblogs.com/clamp7724/p/11693572.html
在这个例子的基础上修改
1.前台向后台传参
1.1:超链接传递参数
在index.jsp页面添加超链接
<a href="hello/helloparams?name=‘yzha‘&password=‘123456‘">Hello params</a>
<!--据说有的浏览器hello/helloparams不行,谷歌是可以的,别的不知道...-->
修改controller --- HelloWorldController
package hello_word; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; @Controller //注解表示这是一个controller //@RequestMapping(path = "/hello") 这里也可以加RequestMapping注解,如果加在类上则表示一级路径,那样跳转路径就变成了hello/helloworld,
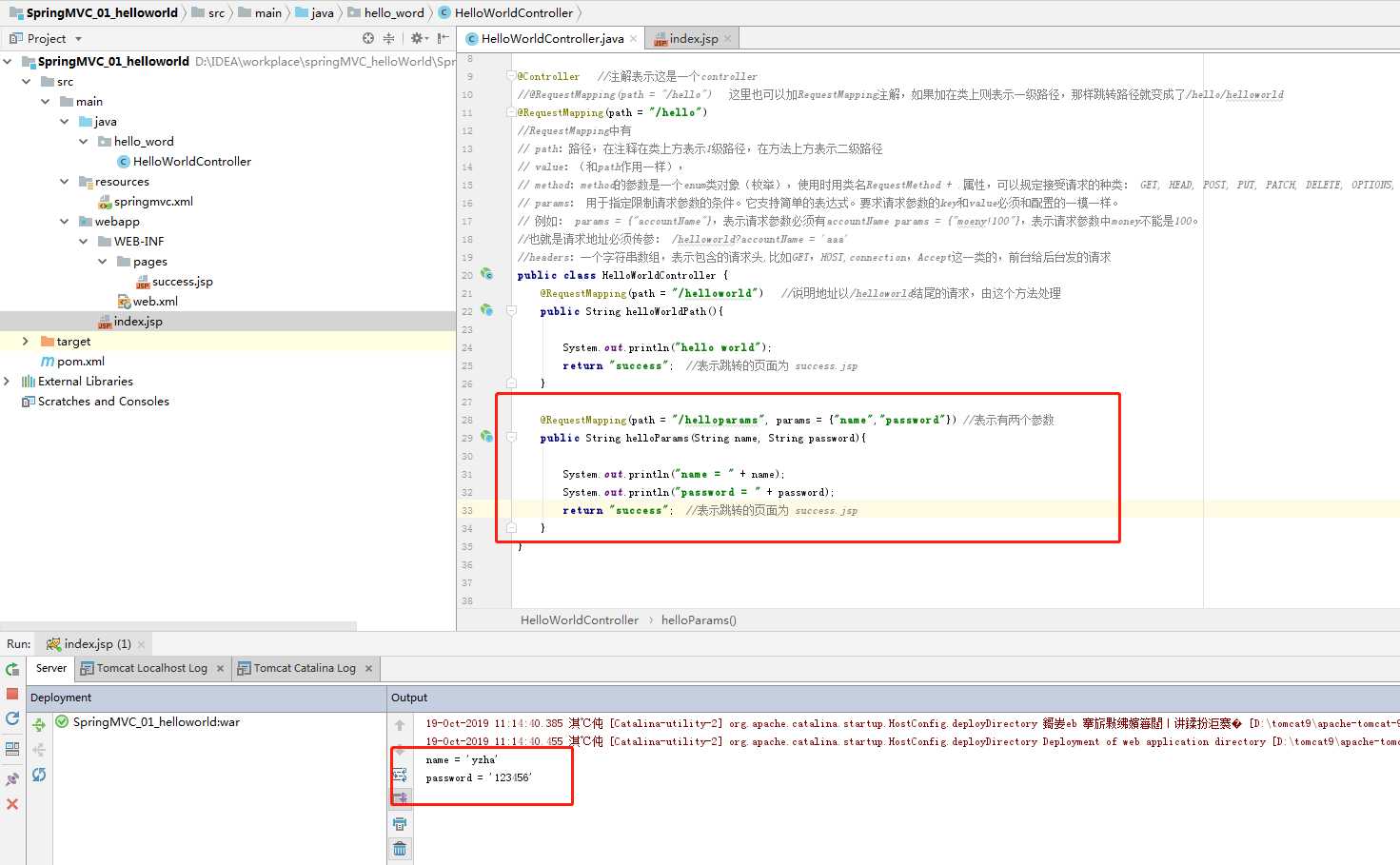
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello") //RequestMapping中有 // path:路径,在注释在类上方表示1级路径,在方法上方表示二级路径 // value:(和path作用一样), // method:method的参数是一个enum类对象(枚举),使用时用类名RequestMethod + .属性,可以规定接受请求的种类: GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE; // params: 用于指定限制请求参数的条件。它支持简单的表达式。要求请求参数的key和value必须和配置的一模一样。 // 例如: params = {"accountName"},表示请求参数必须有accountName params = {"moeny!100"},表示请求参数中money不能是100。 //也就是请求地址必须传参: /helloworld?accountName = ‘aaa‘ //headers:一个字符串数组,表示包含的请求头,比如GET,HOST,connection,Accept这一类的,前台给后台发的请求 public class HelloWorldController { @RequestMapping(path = "/helloworld") //说明地址以/helloworld结尾的请求,由这个方法处理 public String helloWorldPath(){ System.out.println("hello world"); return "success"; //表示跳转的页面为 success.jsp } @RequestMapping(path = "/helloparams", params = {"name","password"}) //表示有两个参数 public String helloParams(String name, String password){ System.out.println("name = " + name); System.out.println("password = " + password); return "success"; //表示跳转的页面为 success.jsp } }
其实主要就是添加了新的controller方法来处理index.jsp新加的的请求
@RequestMapping(path = "/helloparams", params = {"name","password"}) //表示有两个参数
public String helloParams(String name, String password){//springmvc 中使用方法参数的方式接收参数,可以接受基本类型,string,甚至是对象(javaBean)
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("password = " + password);
return "success"; //表示跳转的页面为 success.jsp
}
点下面的链接,后台输出了前台传递过来的信息(为了清楚可以在启动服务后先clean一下后台的output)
2. form表单传递对象参数 (工作中一般是用这个)
为了正式点先修改一下左边的列表,在hello_world文件夹下建2个package,一个叫controller存放各种controller,一个叫domain,用来存放存放数据的class类
把之前的HelloWorldController放到Controller package中,在domain package里创建新的class,起名Account,用来接收前台传递过来的对象(两个属性name,password要和前台表单中name一致,添加对应的get,set方法)
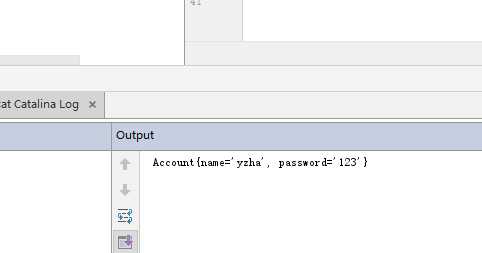
这里我重写了toString方法,用来显示结果。 toString是java中object类自带的方法,System.out.print(object对象)的时候,默认调用的就是这个方法。
创建get,set,toString 如果是idea,可以在代码空白处 右键 - Generate,里面有方法根据属性自动生成
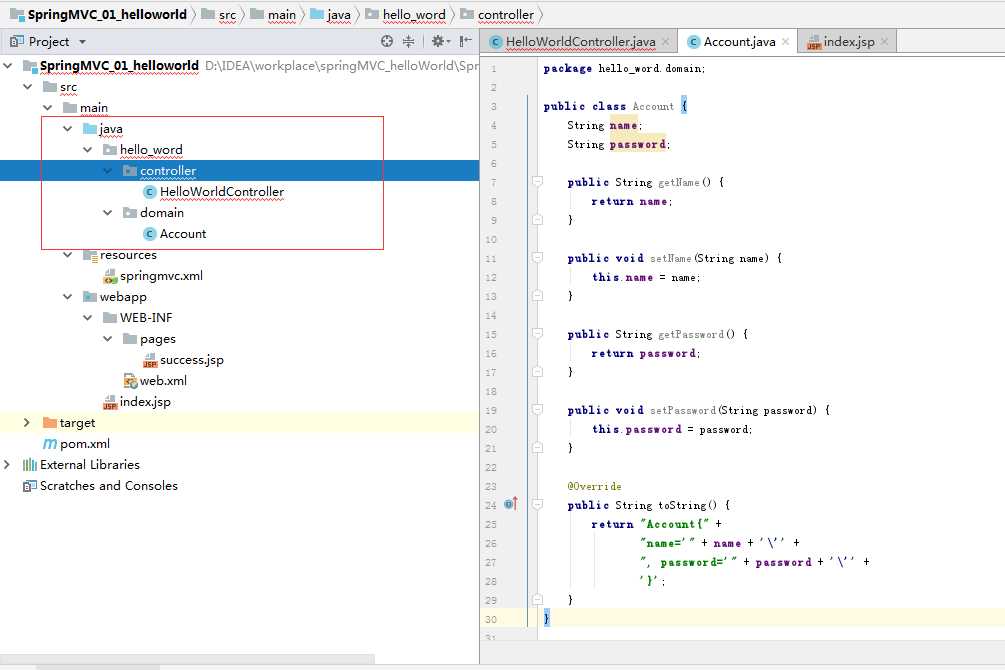
Account类的代码:
package hello_word.domain; public class Account { String name; String password; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", password=‘" + password + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
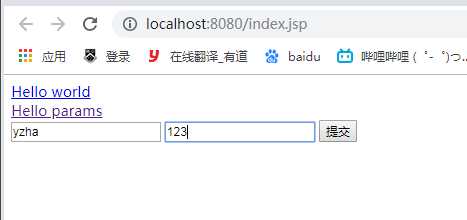
修改index.jsp,添加form表单
<form action="/hello/helloobject" method = post>
<!--action是提交路径,method是提交方式,form里面的元素的name属性要和controller中接收的对象类里的属性名一致,这样spring低层的反射才可以找到对应的set方法-->
<input type="text" name = ‘name‘>
<input type="text" name = ‘password‘>
<input type ="submit" value = "提交">
</form>
修改controller --- HelloWorldController
添加一个新的方法处理这个form请求。
@RequestMapping(path = "/helloobject") public String helloParams(Account account){//表示有一个Account对象作为参数,因为两个类不在同一个package里需要import这个class System.out.println(account);//因为重写了Account的toString方法,这里可以直接用print显示内容 return "success"; //表示跳转的页面为 success.jsp }
1.3. 传递的引用类型中有引用类型属性(Account中有其他class类的属性,比如 user 信息)
创建user类,用来存用户的信息,创建方式和account一样,这里age是int属性,spring底层(大部分情况下)可以将传回的String字符串自动转化成对应属性类型。如果情况很特殊可能需要自己写set方法处理。
package hello_word.domain; public class User { String name; int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", age=" + age + ‘}‘; } }
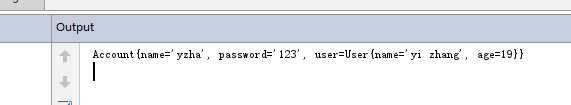
修改account类,加入user属性,重新生成get,set,toString方法
package hello_word.domain; public class Account { String name; String password; User user; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", password=‘" + password + ‘\‘‘ + ", user=" + user + ‘}‘; } }
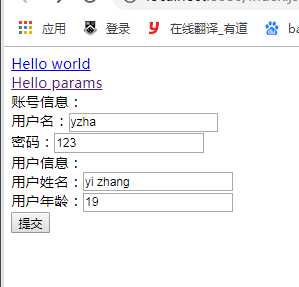
修改index中的表单: 类中类的情况,可以用 属性.属性的属性 来传递参数。 Account中user属性的name属性,就用了user.name
<form action="/hello/helloobject" method = post> <!--action是提交路径,method是提交方式,form里面的元素的name属性要和controller中接收的对象类里的属性名一致--> 账号信息:<br/> 用户名:<input type="text" name = ‘name‘><br/> 密码:<input type="text" name = ‘password‘><br/> 用户信息:<br/> 用户姓名:<input type="text" name = ‘user.name‘><br/> 用户年龄:<input type="text" name = ‘user.age‘><br/> <input type ="submit" value = "提交"> </form>
标签:use 调用 指定 log pos name generate headers 元素
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/clamp7724/p/11703406.html