标签:use on() 定义 gets bst 练习 inner substr 测试程序
实验七 接口的定义与使用
第一部分:理论知识
一、接口、lambda和内部类; Comparator与comparable接口;
1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数;comparator接口的方法是compare,有两个参数。
comparator自定义比较器。comparable实现接口。
2.对象克隆
1 深拷贝与浅拷贝。如果对象是不可变的,那么默认的浅拷贝也没有问题;否则,就要使用深拷贝。
2)默认的克隆方法是浅拷贝,clone方法是Object的一个protected方法。
3) 要让一个对象可以克隆,则需要如下步骤:
a.实现cloneable接口
b.重定义clone方法,并指定public访问修饰符。
c.重定义的clone方法要逐一拷贝每一个域。
4.如果一个要clone的对象没有实现cloneable接口,那么编译器就会抛出一个CloneNotSupportedException异常。
形似cloneable这样的接口叫做标记接口,标记接口没有实现任何的方法,他的作用只是允许在类型查询中使用instanceOf。
即便默认浅拷贝能够满足要求,还是徐亚需要实现Cloneable接口,将clone重新定义为public,再调用super.clone().
5.lambda表达式
1) 传代码而非传值。
2) lambda的语法规则:(参数)->以及一个表达式
3)如果计算无法在一个表达式中完成,那么就使用{}。
4)即使lambda没有参数,任然要提供空括号,就算无参方法一样。
5)如果可以推导出一个lambda表达式的参数类型,则可以忽略其类型。
6)如果方法只要一个参数,而且这个 参数的类型可以推导得出,那么甚至可以省略小括号。
6)无需指定lambda表达式的返回类型。lambda表达式返回类型总可以由上下文推导出。
7)如果一个lambda表达式只在某些分支返回一个值,而在另一些分支不返回,这是不合法的。
8)只有一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口。
9)lambda表达式中捕获的变量必须是最终变量,这个变量初始化之后就不能再为他赋新值,不能做更改。
10)在lambda表达式中,声明一个与局部变量同名的参数或局部变量是不可合法的。
11)在一个lambda表达式中使用this关键字,是指创建这个lambda表达式的方法的this参数。
6.内部类
作用:内部类方法可以访问外围类的数据,包括私有的数据.
内部类可以对同一个包种的其他类隐藏起来.
使用anonymous内部类定义回调函数类.
第二部分:实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握接口定义方法;
(2) 掌握实现接口类的定义要求;
(3) 掌握实现了接口类的使用要求;
(4) 掌握程序回调设计模式;
(5) 掌握Comparator接口用法;
(6) 掌握对象浅层拷贝与深层拷贝方法;
(7) 掌握Lambda表达式语法;
(8) 了解内部类的用途及语法要求。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第6章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行阅读教材214页-215页程序6-1、6-2,理解程序并分析程序运行结果;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握接口的实现用法;
l 掌握内置接口Compareable的用法。
6-1代码:
package interfaces;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of the Comparable interface.
* @version 1.30 2004-02-27
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EmployeeSortTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//构建数组对象;
Employee[] staff = new Employee[3];
//用三个staff对象填充数组;
staff[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 35000);
staff[1] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000);
staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 38000);
Arrays.sort(staff);//按字母排序方法;
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary());
}
}
例题 6-2 代码:
package interfaces;
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>
{
//声明属性;
private String name;
private double salary;
//构造方法;
public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
//Name属性访问器;
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
//Salary属性访问器;
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
//计算工资方法;
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
/**
* Compares employees by salary
* @param other another Employee object
* @return a negative value if this employee has a lower salary than
* otherObject, 0 if the salaries are the same, a positive value otherwise
*/
public int compareTo(Employee other)//compareTo方法;
{
return Double.compare(salary, other.salary);//包装器,调用compare方法;
}
}
程序测试结果:
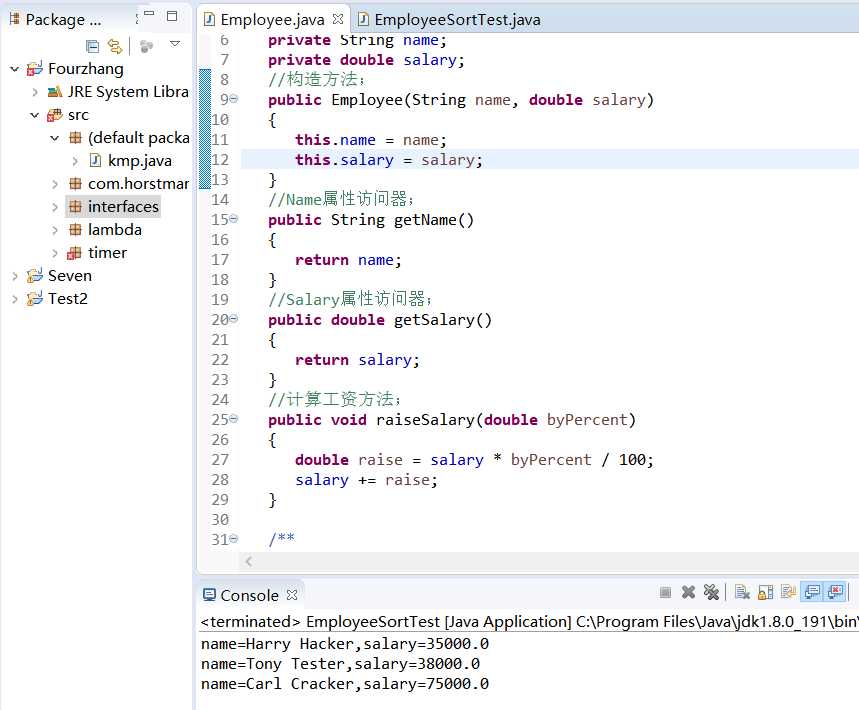
测试程序2:
l 编辑、编译、调试以下程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
1 interface A
2 {
3 double g=9.8;
4 void show( );
5 }
6 class C implements A
7 {
8 public void show( )
9 {System.out.println("g="+g);}
10 }
11
12 class InterfaceTest
13 {
14 public static void main(String[ ] args)
15 {
16 A a=new C( );
17 a.show( );
18 System.out.println("g="+C.g);
19 }
20 }
程序测试结果:
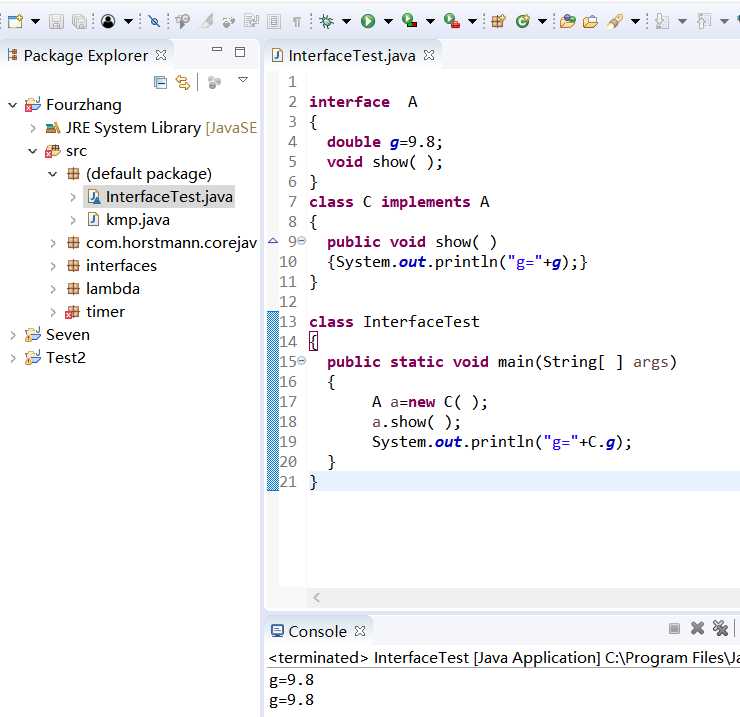
测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材223页6-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 26行、36行代码参阅224页,详细内容涉及教材12章。
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握回调程序设计模式;
6-3 代码:
package timer;
/**
@version 1.02 2017-12-14
@author Cay Horstmann
*/
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.time.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer;
//用JavaUTIL计时器解决与java.util.Timer的矛盾
public class TimerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ActionListener listener = new TimePrinter();
//构造一个调用侦听器的计时器;
//每十秒一次;
Timer t= new Timer(1000, listener);
t.start();
// keep program running until the user selects "OK"
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit(0);
}
}
class TimePrinter implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("At the tone, the time is "
+ Instant.ofEpochMilli(event.getWhen()));
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
}
}
程序6-3测试结果:
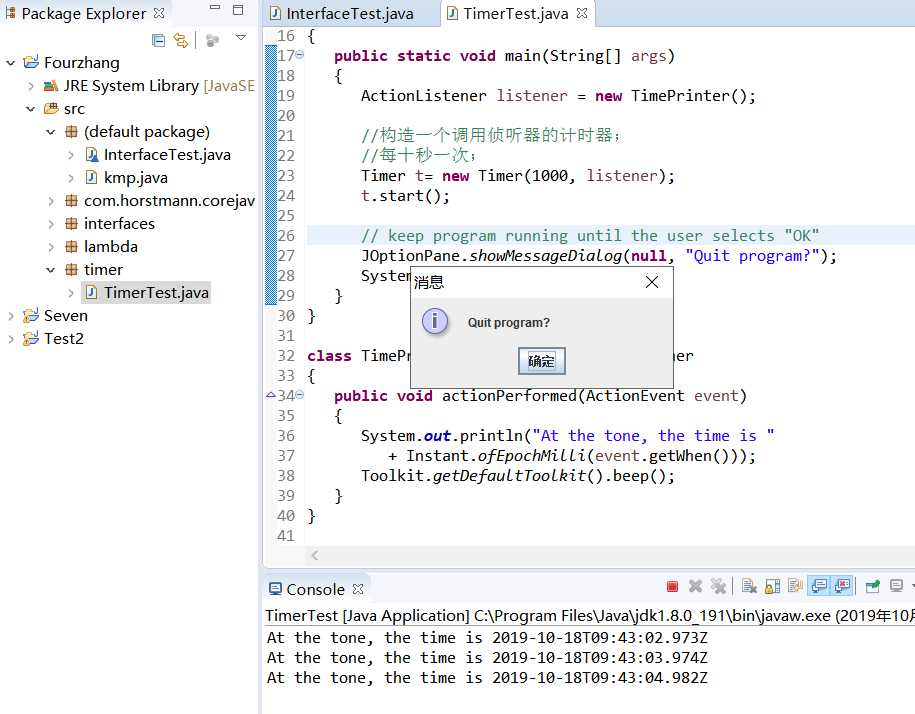
测试程序4:
l 调试运行教材229页-231页程序6-4、6-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握对象克隆实现技术;
l 掌握浅拷贝和深拷贝的差别。
6-4 代码:
package clone;
/**
* This program demonstrates cloning.
* @version 1.11 2018-03-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class CloneTest
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
Employee original = new Employee("John Q. Public", 50000);
original.setHireDay(2000, 1, 1);
Employee copy = original.clone();
copy.raiseSalary(10);
copy.setHireDay(2002, 12, 31);
System.out.println("original=" + original);
System.out.println("copy=" + copy);
}
}
6-5 代码:
package clone;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class Employee implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private Date hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = new Date();
}
public Employee clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
Employee cloned = (Employee) super.clone();//返回Object对象后强制类型转换;
// 克隆可变部分
cloned.hireDay = (Date) hireDay.clone();
return cloned;
}
/**
* Set the hire day to a given date.
* @param year the year of the hire day
* @param month the month of the hire day
* @param day the day of the hire day
*/
public void setHireDay(int year, int month, int day)
{
Date newHireDay = new GregorianCalendar(year, month - 1, day).getTime();
// 实例字段变异实例
hireDay.setTime(newHireDay.getTime());
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
public String toString()
{
return "Employee[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]";
}
}
程序测试结果:
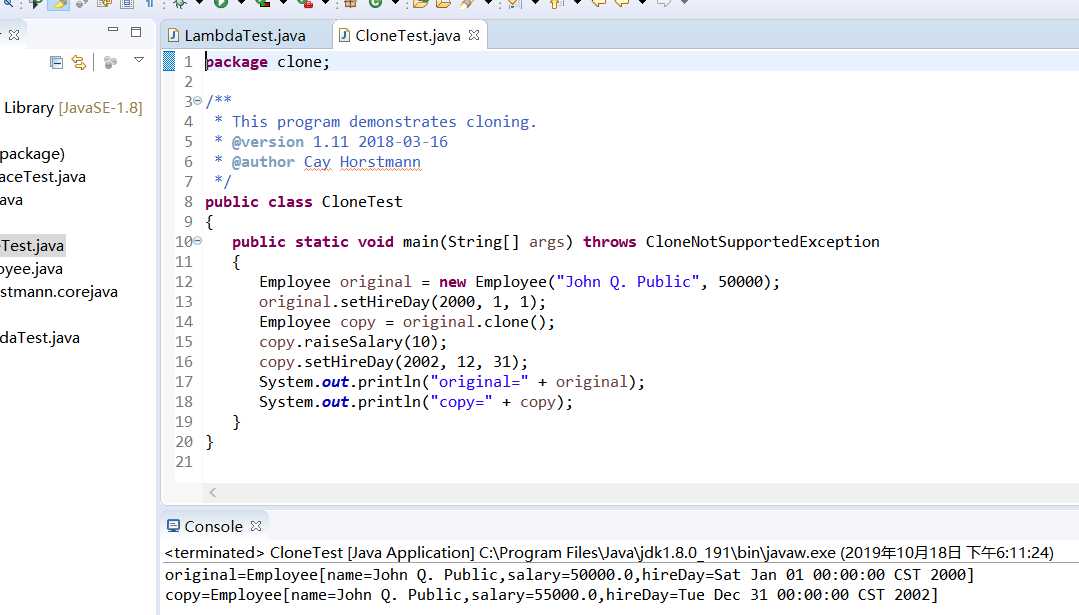
实验2: 导入第6章示例程序6-6,学习Lambda表达式用法。
l 调试运行教材233页-234页程序6-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
将27-29行代码与教材223页程序对比,将27-29行代码与此程序对比,体会Lambda表达式的优点。
6-6 代码:
6-6 代码:
package lambda;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of lambda expressions.
* @version 1.0 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
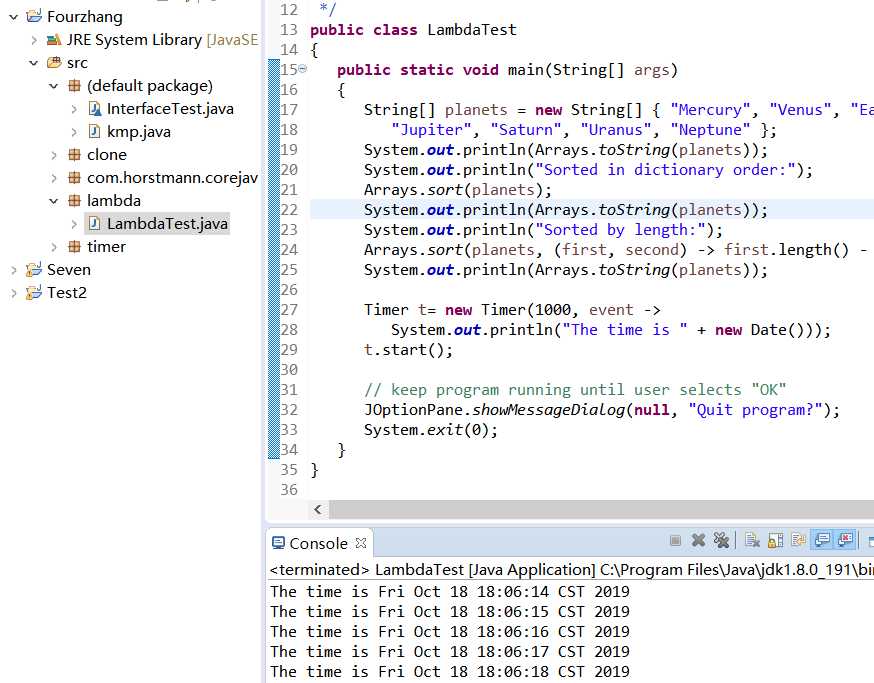
public class LambdaTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//定义并初始化string类数组;
String[] planets = new String[] { "Mercury", "Venus", "Earth", "Mars",
"Jupiter", "Saturn", "Uranus", "Neptune" };
//排序前输出;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted in dictionary order:");
Arrays.sort(planets);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted by length:");
//按单词长度排序后,使用lambda表达式;
Arrays.sort(planets, (first, second) -> first.length() - second.length());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
//方法引用;lambda表达式;
Timer t= new Timer(1000, event ->
System.out.println("The time is " + new Date()));
t.start();
// 继续运行程序,知道用户选择OK;
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit(0);
}
}
程序测试结果:
Lambda表达式在C#中的写法是“arg-list => expr-body”,“=>”符号左边为表达式的参数列表,右边则是表达式体(body)。参数列表可以包含0到多个参数,参数之间使用逗号分割。Lambda表达式的作用也是为了定义一个匿名方法。如果Lambda表达式的body是一个表达式(expression),而不是语句(statement)的话,那么它的body就可以省略大括号和return关键字。此外,如果Lambda表达式只包含一个参数的话,则参数列表的括号也可以省略。
当然,Lambda表达式也并不是可以完全替代delegate写法,例如带ref和out关键字的匿名方法,就必须使用.NET 2.0中的delegate才能构造出来了。
实验3: 编程练习
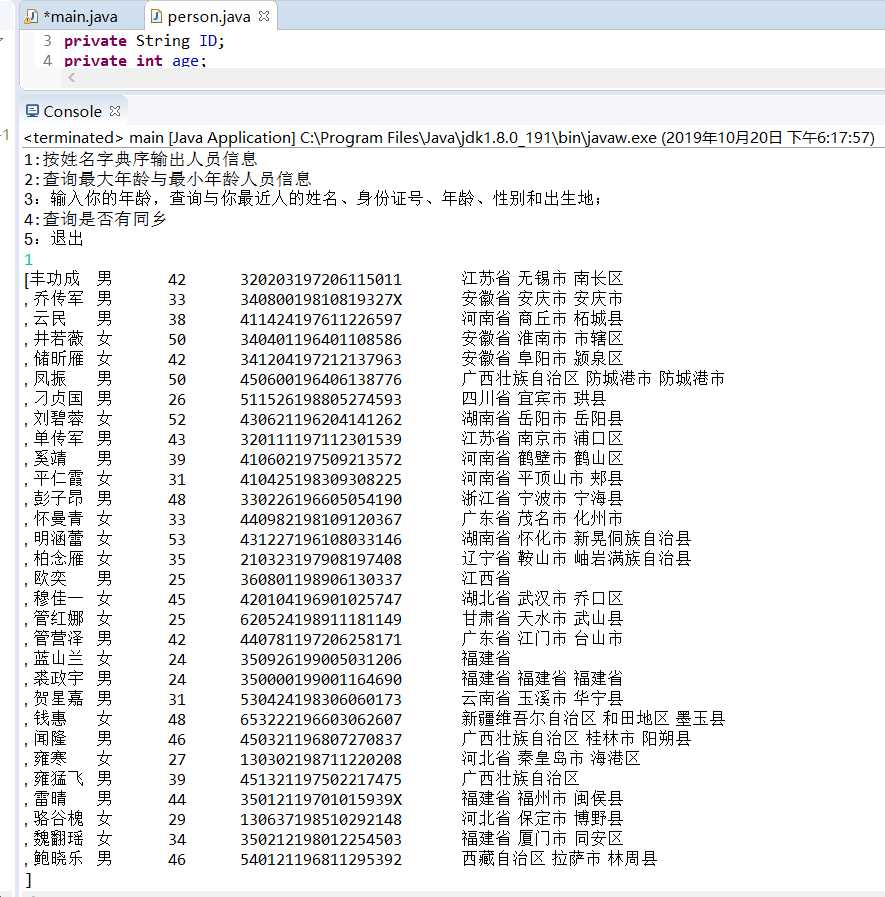
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
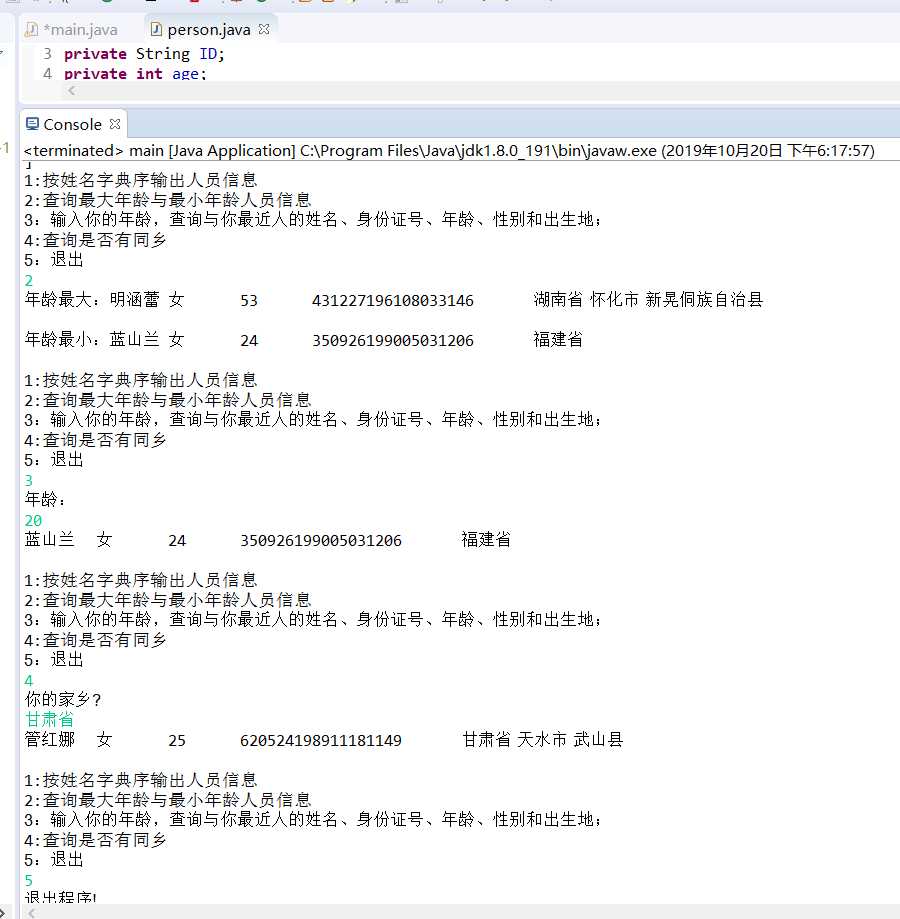
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class main{
private static ArrayList<person> Personlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Personlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("D:\\身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String ID = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String place =linescanner.nextLine();
person Person = new person();
Person.setname(name);
Person.setID(ID);
Person.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
Person.setage(a);
Person.setbirthplace(place);
Personlist.add(Person);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("查找不到信息");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息读取有误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息");
System.out.println("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息");
System.out.println("3:输入你的年龄,查询与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;");
System.out.println("4:查询是否有同乡");
System.out.println("5:退出");
int nextInt = scanner.nextInt();
switch (nextInt) {
case 1:
Collections.sort(Personlist);
System.out.println(Personlist.toString());
break;
case 2:
int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<Personlist.size();i++)
{
j=Personlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
}
}
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+Personlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+Personlist.get(k2));
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near=agenear(yourage);
int d=yourage-Personlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println(""+Personlist.get(near));
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("你的家乡?");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(0,3);
String place2=find.substring(0,3);
for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++)
{
if(Personlist.get(i).getbirthplace().substring(1,4).equals(place))
System.out.println(""+Personlist.get(i));
}
break;
case 5:
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("退出程序!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
}
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j=0,min=53,d=0,k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++)
{
d=Personlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(d<0) d=-d;
if (d<min)
{
min=d;
k=i;
}
} return k;
}
}
public class person implements Comparable<person> {
private String name;
private String ID;
private int age;
private String sex;
private String birthplace;
public String getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getID() {
return ID;
}
public void setID(String ID) {
this.ID= ID;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex;
}
public void setsex(String sex) {
this.sex= sex;
}
public String getbirthplace() {
return birthplace;
}
public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace= birthplace;
}
public int compareTo(person o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getname());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+ID+"\t"+birthplace+"\n";
}
}
程序测试结果:
实验4:内部类语法验证实验
实验程序1:
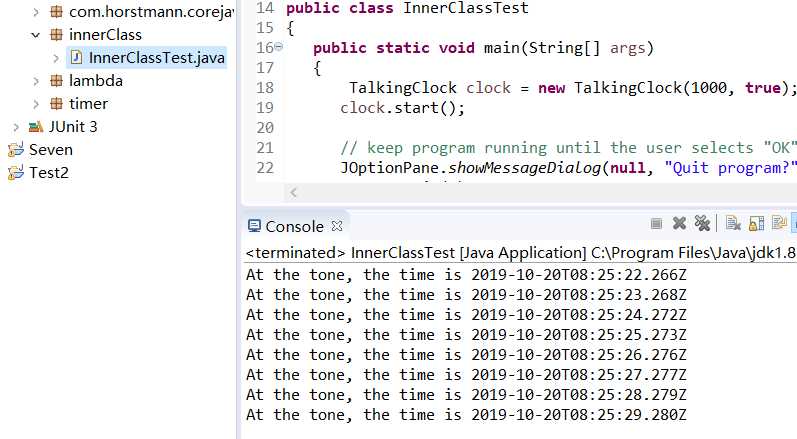
l 编辑、调试运行教材246页-247页程序6-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解内部类的基本用法。
6-7 代码:
package innerClass;
2
3 import java.awt.*;
4 import java.awt.event.*;
5 import java.util.*;
6 import javax.swing.*;
7 import javax.swing.Timer;
8
9 /**
10 * This program demonstrates the use of inner classes.
11 * @version 1.11 2015-05-12
12 * @author Cay Horstmann
13 */
14 public class InnerClassTest
15 {
16 public static void main(String[] args)
17 {
18 TalkingClock clock = new TalkingClock(1000, true);
19 clock.start();
20
21 // 保持程序运行知道用户选择OK;
22 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
23 System.exit(0);
24 }
25 }
26
27 /**
28 * A clock that prints the time in regular intervals.
29 */
30 class TalkingClock
31 {
32 private int interval;
33 private boolean beep;
34
35 /**
36 * Constructs a talking clock
37 * @param interval the interval between messages (in milliseconds)
38 * @param beep true if the clock should beep
39 */
40 public TalkingClock(int interval, boolean beep)
41 {
42 this.interval = interval;
43 this.beep = beep;
44 }
45
46 /**
47 * Starts the clock.
48 */
49 public void start()
50 {
51 ActionListener listener = new TimePrinter();
52 Timer t = new Timer(interval, listener);
53 t.start();
54 }
55
56 public class TimePrinter implements ActionListener
57 {
58 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
59 {
60 System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
61 if (beep) Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
62 }
63 }
64 }
程序测试结果:
实验程序2:
l 编辑、调试运行教材254页程序6-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握匿名内部类的用法。
6-8 代码:
import java.awt.*;
2 import java.awt.event.*;
3 import java.util.*;
4 import javax.swing.*;
5 import javax.swing.Timer;
6
7 /**
8 * This program demonstrates anonymous inner classes.
9 * @version 1.11 2015-05-12
10 * @author Cay Horstmann
11 */
12 public class AnonymousInnerClassTest
13 {
14 public static void main(String[] args)
15 {
16 TalkingClock clock = new TalkingClock();
17 clock.start(1000, true);
18
19 // 保持程序运行知道用户选择OK;
20 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
21 System.exit(0);
22 }
23 }
24
25 /**
26 * A clock that prints the time in regular intervals.
27 */
28 class TalkingClock
29 {
30 /**
31 * Starts the clock.
32 * @param interval the interval between messages (in milliseconds)
33 * @param beep true if the clock should beep
34 */
35 //匿名内部类;
36 public void start(int interval, boolean beep)
37 {
38 ActionListener listener = new ActionListener()
39 {
40 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
41 {
42 System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
43 if (beep) Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
44 }
45 };
46 Timer t = new Timer(interval, listener);
47 t.start();
48 }
49 }
程序测试结果:
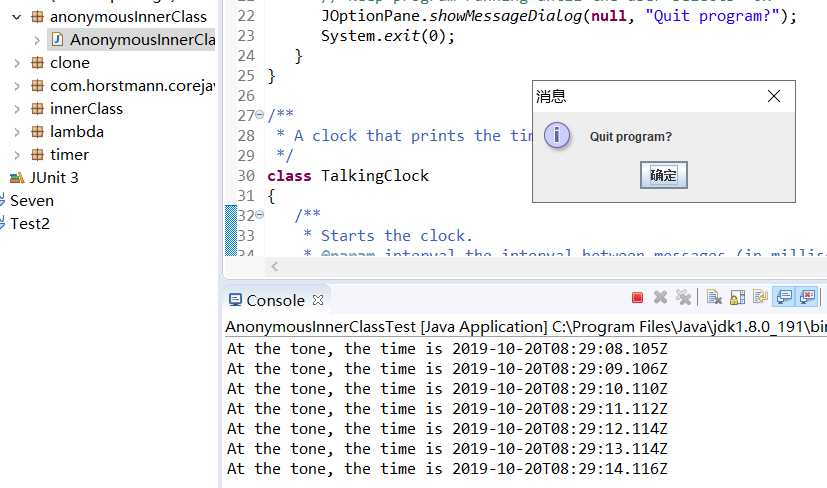
实验程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材257页-258页程序6-9,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解静态内部类的用法。
6-9 代码:
package staticInnerClass;
2
3 /**
4 * This program demonstrates the use of static inner classes.
5 * @version 1.02 2015-05-12
6 * @author Cay Horstmann
7 */
8 public class StaticInnerClassTest
9 {
10 public static void main(String[] args)
11 {
12 double[] d = new double[20];
13 for (int i = 0; i < d.length; i++)
14 d[i] = 100 * Math.random();
15 ArrayAlg.Pair p = ArrayAlg.minmax(d);
16 System.out.println("min = " + p.getFirst());
17 System.out.println("max = " + p.getSecond());
18 }
19 }
20
21 class ArrayAlg
22 {
23 /**
24 * A pair of floating-point numbers
25 */
26 public static class Pair
27 {
28 private double first;
29 private double second;
30
31 /**
32 * Constructs a pair from two floating-point numbers
33 * @param f the first number
34 * @param s the second number
35 */
36 public Pair(double f, double s)
37 {
38 first = f;
39 second = s;
40 }
41
42 /**
43 * Returns the first number of the pair
44 * @return the first number
45 */
46 public double getFirst()
47 {
48 return first;
49 }
50
51 /**
52 * Returns the second number of the pair
53 * @return the second number
54 */
55 public double getSecond()
56 {
57 return second;
58 }
59 }
60
61 /**
62 * Computes both the minimum and the maximum of an array
63 * @param values an array of floating-point numbers
64 * @return a pair whose first element is the minimum and whose second element
65 * is the maximum
66 */
67 public static Pair minmax(double[] values)
68 {
69 double min = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
70 double max = Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY;
71 for (double v : values)
72 {
73 if (min > v) min = v;
74 if (max < v) max = v;
75 }
76 return new Pair(min, max);
77 }
78 }
程序测试结果:
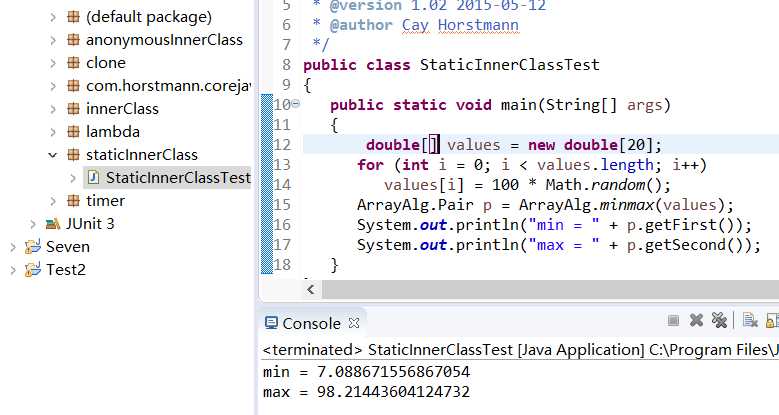
三、实验总结
本章主要学习了掌握接口定义方法;实现接口类的定义要求;实现了接口类的使用要求;程序回调设计模式;Comparator接口用法;对象浅层拷贝与深层拷贝方法;Lambda表达式语法;内部类的用途及语法要求。并知道了object类的clone方法,通过学长在群里的讲解明白了接口和继承之间的区别。在今后会更加努力。
陈来弟-201871010101《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第八周学习总结
标签:use on() 定义 gets bst 练习 inner substr 测试程序
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wing2438/p/11699930.html