1.1.copy函数
通过copy函数可以把一个切片内容复制到另一个切片中
(1)把长切片拷贝到短切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度
copy(s1,s2)
fmt.Println(s1) //[3 4]
fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]
}
(2)把短切片拷贝到长切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度
copy(s2,s1)
fmt.Println(s1) //[1 2]
fmt.Println(s2) //[1 2 5 6]
}
(3)把切片片段拷贝到切片中
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
s1 := []int {1,2}
s2 := []int{3,4,5,6}
//copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度
copy(s1,s2[1:3])
fmt.Println(s1) //[[4 5]
fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]
}
1.2.sort排序
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sort"
)
func main() {
num := []int{1,7,3,5,2}
//升序排序
sort.Ints(num)
fmt.Println(num) //[1 2 3 5 7]
//降序排序
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(num)))
fmt.Println(num) //[7 5 3 2 1]
}
1.3.双向链表
(1)双向链表的结构
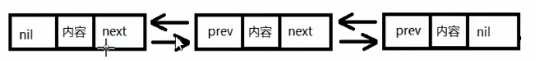
双向链表结构中元素在内存中不是紧邻空间,而是每个元素中存放上一个元素和后一个元素的地址
- 第一个元素称为(头)元素,前连接(前置指针域)为nil
- 最后一个元素称为 尾(foot)元素,后连接(后置指针域)尾nil
双向链表的优点
- 在执行新增元素或删除元素时效率高,获取任意一个元素,可以方便的在这个元素前后插入元素
- 充分利用内存空间,实现内存灵活管理
- 可实现正序和逆序遍历
- 头元素和尾元素新增或删除时效率较高
双向链表的缺点
- 链表增加了元素的指针域,空间开销比较大
- 遍历时跳跃性查找内容,大量数据遍历性能低
(2)双向链表容器List
在Go语言标准库的container/list包提供了双向链表List
List结构体定义如下
- root表示根元素
- len表示链表中有多少元素
// List represents a doubly linked list.
// The zero value for List is an empty list ready to use.
type List struct {
root Element // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used
len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element
}
其中Element结构体定义如下
- next表示下一个元素,使用Next()可以获取到
- prev表示上一个元素,使用Prev()可以获取到
- list表示元素属于哪个链表
- Value表示元素的值,interface()在Go语言中表示任意类型
// Element is an element of a linked list.
type Element struct {
// Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements.
// To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented
// as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last
// list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list
// element (l.Front()).
next, prev *Element
// The list to which this element belongs.
list *List
// The value stored with this element.
Value interface{}
}
1.4.操作List
(1)直接使用container/list包下的New()新建一个空的List
添加,遍历,取首尾,取中间元素
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//实例化
mylist := list.New()
fmt.Println(mylist)
//添加
mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"]
mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"]
mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"]
//在最后一个元素的前面添加
mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"]
mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"]
//遍历
for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){
fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //a e b d c
}
fmt.Println("")
//取首尾
fmt.Println(mylist.Front().Value) //a
fmt.Println(mylist.Back().Value) //c
//取中间的元素,通过不断的Next()
n := 3
var curr *list.Element
if n > 0 && n <= mylist.Len(){
if n == 1 {
curr = mylist.Front()
}else if n == mylist.Len(){
curr = mylist.Back()
}else {
curr = mylist.Front()
for i := 1; i < n; i++{
curr = curr.Next()
}
}
}else {
fmt.Println("n的数值不对")
}
fmt.Println(curr.Value) //b
}
(2)移动元素
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//实例化
mylist := list.New()
fmt.Println(mylist)
//添加
mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"]
mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"]
mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"]
//在最后一个元素的前面添加
mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"]
mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"]
//移动,把第一个元素一道最后一个元素的前面
mylist.MoveBefore(mylist.Front(),mylist.Back())
//mylist.MoveAfter(mylist.Back(),mylist.Front())
//把最后一个元素移动到最前面
//mylist.MoveToFront(mylist.Back())
//把第一个元素移动到最后面
//mylist.MoveToBack(mylist.Front())
for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){
fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //e b d a c
}
}
(3)删除
mylist.Remove(mylist.Front())
1.5.双向循环列表
(1)循环链表特点是没有节点的指针域为nil,通过任何一个元素都可以找到其它元素
环形链表结构如下
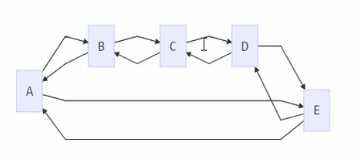
双向循环链表和双向链表区别
- 双向循环链表没有严格意义上的头元素和尾元素
- 没有元素的前连接和后连接为nil
- 一个长度为n的双向循环链表,通过某个元素向某个方向移动,在查找最多n-1次,一定会找到另一个元素
(2)在container/ring包下结构体Ring源码如下
- 官方明确说明了Ring是循环链表的元素,又是环形链表
- 实际使用时Ring遍历就是环形链表第一个元素
// A Ring is an element of a circular list, or ring.
// Rings do not have a beginning or end; a pointer to any ring element
// serves as reference to the entire ring. Empty rings are represented
// as nil Ring pointers. The zero value for a Ring is a one-element
// ring with a nil Value.
//
type Ring struct {
next, prev *Ring
Value interface{} // for use by client; untouched by this library
}
(3)创建和查看
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//查看元素内容
//循环链表有几个元素,func就执行几次,i当前执行元素的内容
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 2 3 4
})
fmt.Println("")
//取中间元素,用移动
fmt.Println(r.Move(3).Value) //3
}
(4)增加
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//增加
r1 := ring.New(2)
r1.Value = 5
r1.Next().Value = 6
r.Link(r1)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 5 6 1 2 3 4
})
}
(5)删除
package main
import (
"container/ring"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
//r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素
r := ring.New(5)
r.Value = 0
r.Next().Value = 1
r.Next().Next().Value = 2
//r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3
//r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4
r.Prev().Value = 4
r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3
//删除
r.Unlink(1)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4
})
}
删除后面两个
//删除
r.Unlink(2)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 3 4
})
r.Next()删除
//删除
r.Next().Unlink(2)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 4
})qu
超出范围,取5的余数
//删除
r.Unlink(6)
r.Do(func(i interface{}) {
fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4
})
1.Go-copy函数、sort排序、双向链表、list操作和双向循环链表
标签:push library color rcu clu interface The nal touch
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gaidy/p/11757358.html
