标签:red resultset etc exce toc begin res 服务 rest
(一)场景与方案
场景:java端从数据库读取100W数据进行后台业务处理。
常规实现1:分页读取出来。缺点:需要排序后分页读取,性能低下。
常规实现2:一次性读取出来。缺点:需要很大内存,一般计算机不行。
非常规实现:建立长连接,利用服务端游标,一条一条流式返回给java端。
非常规实现优化:jdbc中有个重要的参数fetchSize(它对业务实现无影响,即不会限制读取条数等),优化后可显著提升性能。
(二)代码与执行结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { getAll(1); getAll(10); getAll(100); getAll(1000); } public static void getAll(int fetchSize) { try { long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(MYSQL_URL); connection.setAutoCommit(false); //为了设置fetchSize,必须设置为false String sql = "select * from test"; PreparedStatement psst = connection.prepareStatement(sql,ResultSet.TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); psst.setFetchSize(fetchSize); ResultSet rs = psst.executeQuery(); int totalCount=0; while (rs.next()) { totalCount++; } rs.close(); psst.close(); connection.close(); long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("totalCount:"+totalCount+";fetchSize:"+fetchSize+";耗时:"+(endTime-beginTime)+"ms"); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
执行结果如下——
totalCount:3185194;fetchSize:1;耗时:23770ms totalCount:3185194;fetchSize:10;耗时:23253ms totalCount:3185194;fetchSize:100;耗时:21890ms totalCount:3185194;fetchSize:1000;耗时:20985ms
可以看到,当fetchSize为1000时,性能有提升。(看一些网友的数据,性能提升更多)
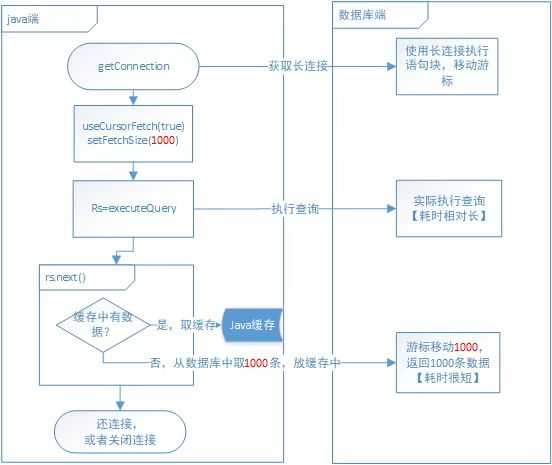
(三)原理分析
1、先在服务端执行查询后将数据缓存在服务端。(耗时相对较长)
2、java端获取数据时,利用服务端游标进行指针跳动,如果fetchSize为1000,则一次性跳动1000条,返回给java端缓存起来。(耗时较短,跳动次数为N/1000)
3、在调用next函数时,优先从缓存中取数,其次执行2过程。(内存读取,耗时可忽略)
题外话:spring的JdbcCursorItemReader是对fetchSize的良好应用。
标签:red resultset etc exce toc begin res 服务 rest
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/baimingqian/p/11761942.html