标签:编程 turn ace tom 映射关系 exception 关系 form 生成
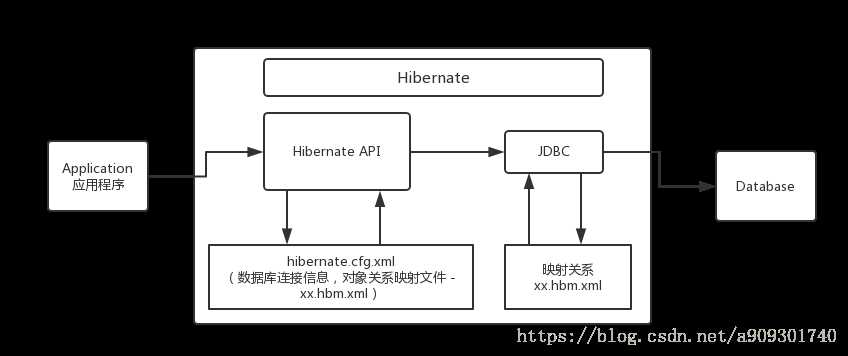
Hibernate是一个开放源代码的对象关系映射框架,它对JDBC进行了非常轻量级的对象封装,它将POJO与数据库表建立映射关系,是一个全自动的orm框架,hibernate可以自动生成SQL语句,自动执行,使得Java程序员可以随心所欲的使用对象编程思维来操纵数据库。 Hibernate可以应用在任何使用JDBC的场合,既可以在Java的客户端程序使用,也可以在Servlet/JSP的Web应用中使用,最具革命意义的是,Hibernate可以在应用EJB的JaveEE架构中取代CMP,完成数据持久化的重任。
ORM:Object Relational Mapping(对象关系映射)。指的是将一个Java中的对象与关系型数据库中的表建立一种映射关系,从而操作对象就可以操作数据库中的表。
1、对象化。
hibernate可以让开发人员以面相对象的思想来操作数据库。jdbc只能通过SQL语句将元数据传送给数据库,进行数据操作。而hibernate可以在底层对元数据和对象进行转化,使得开发者只用面向对象的方式来存取数据即可。
2、更好的移植性。
hibernate使用xml或JPA的配置以及数据库方言等等的机制,使得hibernate具有更好的移植性,对于不同的数据库,开发者只需要使用相同的数据操作即可,无需关心数据库之间的差异。而直接使用JDBC就不得不考虑数据库差异的问题。
3、开发效率高。
hibernate提供了大量的封装(这也是它最大的缺点),很多数据操作以及关联关系等都被封装的很好,开发者不需写大量的sql语句,这就极大的提高了开发者的开发效率。
4、缓存机制的使用。
hibernate提供了缓存机制(session缓存,二级缓存,查询缓存),对于那些改动不大且经常使用的数据,可以将它们放到缓存中,不必在每次使用时都去查询数据库,缓存机制对提升性能大有裨益。

documentation :Hibernate开发的文档
lib :Hibernate开发包
required :Hibernate开发的必须的依赖包
optional :Hibernate开发的可选的jar包
project :Hibernate提供的项目
CREATE TABLE `cst_customer` ( `cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘客户编号(主键)‘, `cust_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘客户名称(公司名称)‘, `cust_source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户信息来源‘, `cust_industry` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户所属行业‘, `cust_level` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户级别‘, `cust_phone` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘固定电话‘, `cust_mobile` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘移动电话‘, PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
package com.turtle.dao; import java.io.Serializable; public class Customer implements Serializable { // 客户编号(主键) private Long cust_id; // 客户名称(公司名称) private String cust_name; // 客户信息来源 private String cust_source; // 客户所属行业 private String cust_industry; // 客户级别 private String cust_level; // 固定电话 private String cust_phone; // 移动电话 private String cust_mobile; public Long getCust_id() { return cust_id; } public void setCust_id(Long cust_id) { this.cust_id = cust_id; } public String getCust_name() { return cust_name; } public void setCust_name(String cust_name) { this.cust_name = cust_name; } public String getCust_source() { return cust_source; } public void setCust_source(String cust_source) { this.cust_source = cust_source; } public String getCust_industry() { return cust_industry; } public void setCust_industry(String cust_industry) { this.cust_industry = cust_industry; } public String getCust_level() { return cust_level; } public void setCust_level(String cust_level) { this.cust_level = cust_level; } public String getCust_phone() { return cust_phone; } public void setCust_phone(String cust_phone) { this.cust_phone = cust_phone; } public String getCust_mobile() { return cust_mobile; } public void setCust_mobile(String cust_mobile) { this.cust_mobile = cust_mobile; } }
映射需要通过XML的配置文件来完成,这个配置文件可以任意命名。尽量统一命名规范(类名.hbm.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- 建立类与表的映射 --> <class name="com.turtle.dao.Customer" table="cst_customer"> <!-- 建立类中的属性与表中的主键对应 --> <id name="cust_id" column="cust_id" > <generator class="native"/> </id> <!-- 建立类中的普通的属性和表的字段的对应 --> <property name="cust_name" column="cust_name" length="32" /> <property name="cust_source" column="cust_source" length="32"/> <property name="cust_industry" column="cust_industry"/> <property name="cust_level" column="cust_level"/> <property name="cust_phone" column="cust_phone"/> <property name="cust_mobile" column="cust_mobile"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
【class标签的配置】
标签用来建立类与表的映射关系
属性:
name :类的全路径
table :表名(类名与表名一致,table可以省略)
catalog :数据库名
【id标签的配置】
标签用来建立类中的属性与表中的主键的对应关系
属性:
name :类中的属性名
column :表中的字段名(类中的属性名和表中的字段名如果一致,column可以省略)
length :长度
type :类型
【property标签的配置】
标签用来建立类中的普通属性与表的字段的对应关系
属性:
name :类中的属性名
column :表中的字段名
length :长度
type :类型
not-null :设置非空
unique :设置唯一
Hibernate的核心配置文件的名称:hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!-- 连接数据库的基本参数 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate_demo</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property> <!-- 配置Hibernate的方言 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <!-- 可选配置================ --> <!-- 打印SQL --> <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化SQL --> <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property> <!-- 自动创建表 --> <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 配置C3P0连接池 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.provider_class">org.hibernate.c3p0.internal.C3P0ConnectionProvider</property> <!--在连接池中可用的数据库连接的最少数目 --> <property name="c3p0.min_size">5</property> <!--在连接池中所有数据库连接的最大数目 --> <property name="c3p0.max_size">20</property> <!--设定数据库连接的过期时间,以秒为单位, 如果连接池中的某个数据库连接处于空闲状态的时间超过了timeout时间,就会从连接池中清除 --> <property name="c3p0.timeout">120</property> <!--每3000秒检查所有连接池中的空闲连接 以秒为单位--> <property name="c3p0.idle_test_period">3000</property> <mapping resource="com/turtle/dao/Customer.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
必须的配置
连接数据库的基本的参数
驱动类
url路径
用户名
密码
方言
可选的配置
显示SQL :hibernate.show_sql
格式化SQL :hibernate.format_sql
自动建表 :hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto
none :不使用hibernate的自动建表
create :如果数据库中已经有表,删除原有表,重新创建,如果没有表,新建表。(测试)
create-drop :如果数据库中已经有表,删除原有表,执行操作,删除这个表。如果没有表,新建一个,使用完了删除该表。(测试)
update :如果数据库中有表,使用原有表,如果没有表,创建新表(更新表结构)
validate :如果没有表,不会创建表。只会使用数据库中原有的表。(校验映射和表结构)。
映射文件的引入
引入映射文件的位置
<mapping resource="com/turtle/dao/Customer.hbm.xml"/>
package com.turtle.test; import com.turtle.dao.Customer; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class TestCustomer { public static void main(String [] args){ // 1、加载配置文件 Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); // 2、创建一个SessionFactory对象 SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(); // 3、创建Session对象 Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); // 4、开启事务 Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); try{ Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCust_name("测试用户1"); // 调用Hibernate自带的API来进行保存操作 session.save(customer); // 提交事务 transaction.commit(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); // 回滚事务 transaction.rollback(); }finally { // 关闭连接 session.close(); } } }

hibernate.properties
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
hibernate.cfg.xml
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure();
加载映射文件
// 手动加载映射
configuration.addResource("com/itheima/hibernate/demo1/Customer.hbm.xml");
SessionFactory内部维护了Hibernate的连接池和Hibernate的二级缓存(不讲)。是线程安全的对象。一个项目创建一个对象即可。
Session代表的是Hibernate与数据库的链接对象。不是线程安全的。与数据库交互桥梁。
Session中的API
保存方法:
Serializable save(Object obj);
查询方法:
T get(Class c,Serializable id);
T load(Class c,Serializable id);
修改方法
void update(Object obj);
删除方法
void delete(Object obj);s
保存或更新
void saveOrUpdate(Object obj)
Hibernate中管理事务的对象。
commit();
rollback();
标签:编程 turn ace tom 映射关系 exception 关系 form 生成
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhh19981104/p/11829150.html