标签:bsp algo size 分析 std ack pow algorithm func
在 redis 源码中 dictScan 算法中用到了用到了非常经典的二进制反转算法,该算法对二进制的反转高效而实用,同时对于理解位运算也有非常大的帮助。先呈现源码:
/* Function to reverse bits. Algorithm from: * http://graphics.stanford.edu/~seander/bithacks.html#ReverseParallel */ static unsigned long rev(unsigned long v) { unsigned long s = 8 * sizeof(v); // bit size; must be power of 2, 此处为32 unsigned long mask = ~0; //11111111111111111111111111111111 while ((s >>= 1) > 0) { //循环5次 mask ^= (mask << s); // 取得想要局部对换的掩码 // 左移s位并保留低位,右移s位并保留高位,然后两部分或运算 // 这里是实现移位的精华所在,结合下面打印信息有助于理解 v = ((v >> s) & mask) | ((v << s) & ~mask); } return v; }
源码的总体思路是:用迭代的思想将32位的二进制数先将前16位和后16位对换,然后将前16位二进制数的前8位和后8位对换,后16位类似,再讲前8位的二进制数的前4位和后4位对换。。。最终实现整个二进制的反转。当然这里的实现过程非常巧妙,这也是位运算神秘而神奇的特点,理解这个过程,对于理解计算机的原理都有很大的帮助。
但上面的描述得还是比较抽象,还不足以帮助理解上面的算法实现,下面来对算法的实现过程加一些打印,以便更好的理解算法的实现原理。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 打印二进制 void printBits(const unsigned long v) { unsigned long mask = 1 << 31; while ((mask) > 0) { int bit = (v & mask) ? 1 : 0; cout << bit; mask >>= 1; } cout << endl; } static unsigned long rev_test(unsigned long v) { unsigned long s = 8 * sizeof(v); // bit size; must be power of 2 unsigned long mask = ~0; cout << "s : "; printBits(s); cout << "mask : "; printBits(mask); while ((s >>= 1) > 0) { cout << endl; cout << "s : "; printBits(s); cout << "mask : "; printBits(mask); cout << "mask<<s: "; printBits(mask << s); mask ^= (mask << s); cout << "mask^= : "; printBits(mask); v = ((v >> s) & mask) | ((v << s) & ~mask); cout << "v : "; printBits(v); } return v; } int main() { unsigned long v = 8; cout << "v : "; printBits(v); cout << endl; v = rev_test(v); cout << endl; cout << "v : "; printBits(v); cout << endl << endl << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
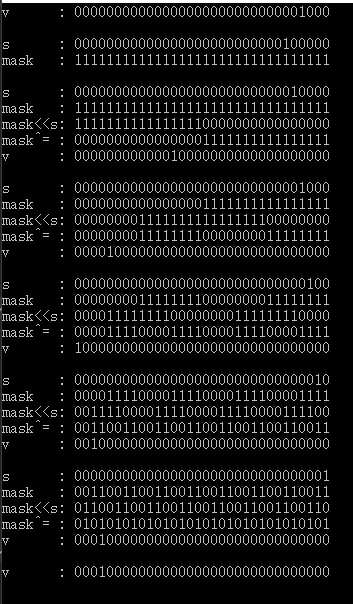
运行上述程序结果如下:
标签:bsp algo size 分析 std ack pow algorithm func
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/evenleee/p/11832693.html