标签:开头 stat 绿色 导致 value ide tis 编程 print
在本号之前写过的文章中,曾经给大家介绍过 Java Stream管道流是用于简化集合类元素处理的java API。在使用的过程中分为三个阶段。在开始本文之前,我觉得仍然需要给一些新朋友介绍一下这三个阶段,如图:
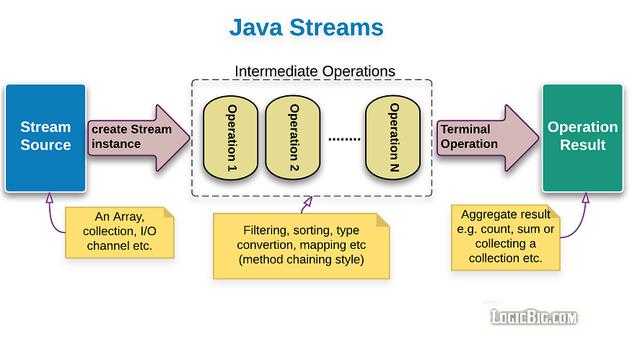
在开始学习之前,仍然有必要回顾一下我们之前给大家讲过的一个例子:
List<String> nameStrs = Arrays.asList("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe","Lemur");
List<String> list = nameStrs.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("L"))
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.sorted()
.collect(toList());
System.out.println(list);[LEMUR, LION]如果你不使用java Stream管道流的话,想一想你需要多少行代码完成上面的功能呢?回到正题,这篇文章就是要给大家介绍第三阶段:对管道流处理结果都可以做哪些操作呢?下面开始吧!
如果我们只是希望将Stream管道流的处理结果打印出来,而不是进行类型转换,我们就可以使用forEach()方法或forEachOrdered()方法。
Stream.of("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion")
.parallel()
.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.of("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion")
.parallel()
.forEachOrdered(System.out::println);Monkey
Lion
Giraffe
Lemur
Lionjava Stream 最常见的用法就是:一将集合类转换成管道流,二对管道流数据处理,三将管道流处理结果在转换成集合类。那么collect()方法就为我们提供了这样的功能:将管道流处理结果在转换成集合类。
通过Collectors.toSet()方法收集Stream的处理结果,将所有元素收集到Set集合中。
Set<String> collectToSet = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
//最终collectToSet 中的元素是:[Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur],注意Set会去重。同样,可以将元素收集到List使用toList()收集器中。
List<String> collectToList = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 最终collectToList中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]上面为大家介绍的元素收集方式,都是专用的。比如使用Collectors.toSet()收集为Set类型集合;使用Collectors.toList()收集为List类型集合。那么,有没有一种比较通用的数据元素收集方式,将数据收集为任意的Collection接口子类型。
所以,这里就像大家介绍一种通用的元素收集方式,你可以将数据元素收集到任意的Collection类型:即向所需Collection类型提供构造函数的方式。
LinkedList<String> collectToCollection = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));
//最终collectToCollection中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]注意:代码中使用了LinkedList::new,实际是调用LinkedList的构造函数,将元素收集到Linked List。当然你还可以使用诸如LinkedHashSet::new和PriorityQueue::new将数据元素收集为其他的集合类型,这样就比较通用了。
通过toArray(String[]::new)方法收集Stream的处理结果,将所有元素收集到字符串数组中。
String[] toArray = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
) .toArray(String[]::new);
//最终toArray字符串数组中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]使用Collectors.toMap()方法将数据元素收集到Map里面,但是出现一个问题:那就是管道中的元素是作为key,还是作为value。我们用到了一个Function.identity()方法,该方法很简单就是返回一个“ t -> t ”(输入就是输出的lambda表达式)。另外使用管道流处理函数distinct()来确保Map键值的唯一性。
Map<String, Integer> toMap = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity(), //元素输入就是输出,作为key
s -> (int) s.chars().distinct().count()// 输入元素的不同的字母个数,作为value
));
// 最终toMap的结果是: {Monkey=6, Lion=4, Lemur=5, Giraffe=6} Collectors.groupingBy用来实现元素的分组收集,下面的代码演示如何根据首字母将不同的数据元素收集到不同的List,并封装为Map。
Map<Character, List<String>> groupingByList = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
s -> s.charAt(0) , //根据元素首字母分组,相同的在一组
// counting() // 加上这一行代码可以实现分组统计
));
// 最终groupingByList内的元素: {G=[Giraffe], L=[Lion, Lemur, Lion], M=[Monkey]}
//如果加上counting() ,结果是: {G=1, L=3, M=1}
boolean containsTwo = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).anyMatch(i -> i == 2);
// 判断管道中是否包含2,结果是: true
long nrOfAnimals = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur"
).count();
// 管道中元素数据总计结果nrOfAnimals: 4
int sum = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).sum();
// 管道中元素数据累加结果sum: 6
OptionalDouble average = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).average();
//管道中元素数据平均值average: OptionalDouble[2.0]
int max = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).max().orElse(0);
//管道中元素数据最大值max: 3
IntSummaryStatistics statistics = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).summaryStatistics();
// 全面的统计结果statistics: IntSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=6, min=1, average=2.000000, max=3}
标签:开头 stat 绿色 导致 value ide tis 编程 print
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zimug/p/11839517.html