标签:== main info finally getter 算法 start 数据 tor
1.编写递归算法程序:一列数的规则如下: 0、1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34...... 求数列的第40位数是多少。
public class TestRecursion { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 调用fibo方法并输出结果 */ int n = 40; TestRecursion tr = new TestRecursion(); System.out.println(tr.fibo(n)); } /** * 定义递归方法 */ private long fibo(int n) { /** * 递归结束条件1:数列的第一个数0 */ if (n == 0){ return 0; } /** * 递归结束条件2:数列的第二个数是1 */ if (n == 1){ return 1; } /** * 运用递归求第n个数 */ return fibo(n - 1)+fibo(n - 2); } }
运行结果:
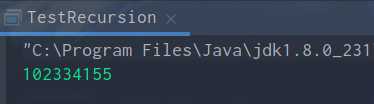
2.编写多线程程序,模拟多个人通过一个山洞的模拟。这个山洞每次只能通过一个人,每个人通过山洞的时间为5秒,有10个人同时准备过此山洞,显示每次通过山洞人的姓名和顺序。
/** * 山洞类实现了Runnable接口 */ public class Cave implements Runnable { /** * 初始人数为设为0 */ private int crossedNum = 0; @Override public void run() { cross(); } private synchronized void cross() { try { /** * 每个人通过山洞的时间为5秒 */ Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } /** * 人数计数 */ crossedNum++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"通过了山洞,这是第"+crossedNum+"个通过的人"); } }
/** * 2.编写多线程程序,模拟多个人通过一个山洞的模拟。 * 这个山洞每次只能通过一个人,每个人通过山洞的时间为5秒,有10个人同时准备过此山洞,显示每次通过山洞人的姓名和顺序。 */ public class TestMultiThreading { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 创建一个山洞 */ Cave ca = new Cave(); /** * 创建十个过山洞的线程 */ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread t = new Thread(ca,"t"+i); t.start(); } } }
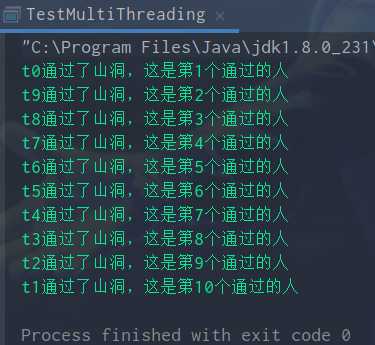
运行结果:
间隔5秒输出一次结果,最终图如下
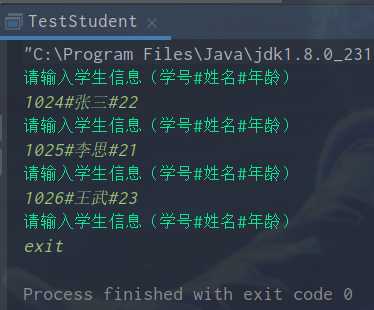
3.由控制台按照固定格式输入学生信息,包括学号,姓名,年龄信息,当输入的内容为exit退出;将输入的学生信息分别封装到一个Student对象中,再将每个Student对象加入到一个集合中,要求集合中的元素按照年龄大小正序排序;最后遍历集合,将集合中学生信息写入到记事本,每个学生数据占单独一行。
/** * 创建学生类,实现Comparable接口 */ public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { /** * 私有属性:学号,姓名,年龄 */ private Integer stuId; private String name; private Integer age; /** *构造方法 */ public Student() { } public Student(Integer stuId, String name, Integer age) { this.stuId = stuId; this.name = name; this.age = age; } /** * getter和setter方法 */ public Integer getStuId() { return stuId; } public void setStuId(Integer stuId) { this.stuId = stuId; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public int compareTo(Student stu) { return this.age - stu.age; } public String toString(){ return "Student [age = " + age + ",name = " + name +",stuId = " + stuId + "]"; } }
public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { Set<Student> stuSet = saveStudentInfo(); outputInfo(stuSet); } private static Set<Student> saveStudentInfo() { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); /** * 创建TreeSet保存学生信息 */ Set<Student> stuSet = new TreeSet<Student>(); while (true){ /** * 输入提示 */ System.out.println("请输入学生信息(学号#姓名#年龄)"); String inputData = input.nextLine(); /** * 判断是否退出 inputData.equals("exit") */ if ("exit".equals(inputData)){ break; } /** * 把用户输入的学生信息分割为String[] */ String [] info = inputData.split("#"); /** * 将输入信息封装到Student对象中 */ Student stu = new Student(Integer.parseInt(info[0]),info[1], Integer.parseInt(info[2])); /** * 将学生对象加入集合 */ stuSet.add(stu); } return stuSet; } private static void outputInfo(Set<Student> stuSet){ File file = new File("e:/student.txt"); /** * 创建文件输出流对象 */ FileWriter fw = null; try { fw = new FileWriter(file); Iterator<Student> it = stuSet.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ String info = it.next().toString(); /** * 将字符串写入记事本 */ fw.write(info); /** * 完成换行 */ fw.write("\r\n"); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
运行结果:

标签:== main info finally getter 算法 start 数据 tor
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sinoaccer/p/11960643.html