标签:方法 string mil fileread end arrays ros else ase
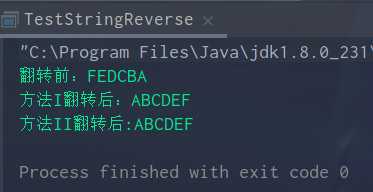
1.不使用函数实现字符串的翻转
/** * 1.不使用函数实现字符串的翻转 */ public class TestStringReverse { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "FEDCBA"; System.out.println("翻转前:"+s1); /** * 此处需注意用s1接收方法的返回值,不然输出的还是没翻转之前的s1 */ s1 = reverseI(s1); System.out.println("方法I翻转后:"+s1); s1 = reverseII(reverseII(s1)); System.out.println("方法II翻转后:"+s1); } /** * 方法I */ public static String reverseI(String str){ /** * 实现思路:将字符串存入一个字符数组中,首尾交换,每交换一次起始位置+1,结束位置-1 * 调用toCharArray()方法,返回一个字符数组,方便通过下标取放字符,最终实现字符串的翻转 */ char[] ch = str.toCharArray(); /** * 定义起始和结束位置下标索引号 */ int start = 0; int end = ch.length - 1; char temp; while (start < end){ temp = ch[start]; ch[start] = ch[end]; ch[end] = temp; start++; end--; } /** * public String(char value[]) 此方法实现传入一个字符数组,返回一个字符串 */ String str0 = new String(ch); return str0; } /** * 方法II */ public static String reverseII(String str){ /** * 调用toCharArray()方法,返回一个字符数组,方便通过下标取放字符,最终实现字符串的翻转 */ char[] ch = str.toCharArray(); /** * 定义一个空字符串 */ String str0 = ""; for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) { /** * 此法 str0 = temp + str0 中temp和str0的顺序是不能调换的,这是关键 */ char temp = ch[i]; str0 = temp + str0; } return str0; } }
运行结果:
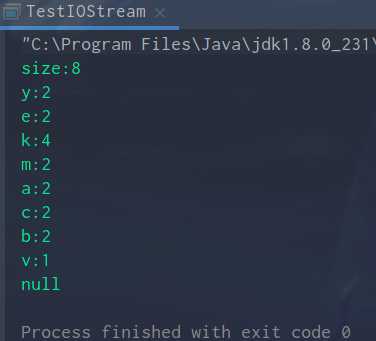
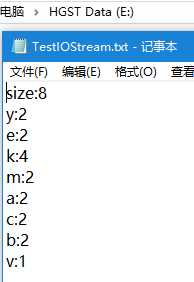
2.给定一个字符串,如"yekmaakkccekymbvb",求字符串中有多少种字符以及每个字符的个数;把结果写入E盘名为TestIOStream.txt的文本文件中;读出刚才写入TestIOStream.txt文本文件的内容。
public class TestIOStream { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "yekmaakkccekymbvb"; Map<String,Integer> map = count(str); write(map); read(); } /** * 求字符串中有多少种字符及每个字符的个数 */ public static Map<String,Integer> count(String s){ Map<String,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<String,Integer>(); for (int i = 0;i < s.length();i++){ /** * public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) 截取字符串中的子串 * (前闭后开) * substring(i,i + 1)每次截取一个字符 * 定义一个key接收返回的子串 */ String key = s.substring(i,i + 1); /** * 定一个整型value接收map.get(key)返回的值 */ Integer value = map.get(key); /** * 判断value若为空,即 */ if (value == null){ map.put(key,1); }else { map.put(key,value+1); } } return map; } /** * 把结果写入E盘名为TestIOStream.txt的文件夹中 */ public static void write(Map<String,Integer> map){ PrintWriter pw = null; try { pw = new PrintWriter("e:/TestIOStream.txt"); pw.println("size:"+map.size()); Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry entry : entrySet){ pw.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { pw.close(); } } /** * 读出刚才写入的文本文件的内容 */ public static void read(){ BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("e:/TestIOStream.txt")); String str = null; do { str = br.readLine(); System.out.println(str); }while (str != null); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
运行结果:
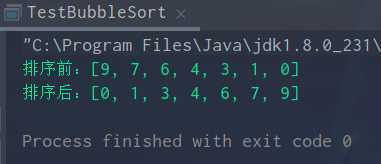
3.使用冒泡排序对一个int数组进行排序。
public class TestBubbleSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int [] arr = {9,7,6,4,3,1,0}; //int [] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}; System.out.println("排序前:"+Arrays.toString(arr)); bubbleSort(arr); System.out.println("排序后:"+Arrays.toString(arr)); } public static void bubbleSort(int [] arr){ for (int i = 0;i < arr.length - 1;i++){ boolean flag = false; for (int j = 0;j < arr.length - 1 - i;j++){ if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){ int temp = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; flag = true; } } if (!flag){ break; } } } }
运行结果:
标签:方法 string mil fileread end arrays ros else ase
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sinoaccer/p/11964306.html