标签:ola 结果 UNC 压缩 span if else new 简单 aci
1、lambda是什么?
看个例子:
g = lambda x:x+1
看一下执行的结果:
g(1)
>>>2
g(2)
>>>3
当然,你也可以这样使用:
lambda x:x+1(1)
>>>2
可以这样认为,lambda作为一个表达式,定义了一个匿名函数,上例的代码x为入口参数,x+1为函数体,用函数来表示为:
1 def g(x):
2 return x+1
非常容易理解,在这里lambda简化了函数定义的书写形式。是代码更为简洁,但是使用函数的定义方式更为直观,易理解。
Python中,也有几个定义好的全局函数方便使用的,filter, map, reduce 

>>> foo = [2, 18, 9, 22, 17, 24, 8, 12, 27]
>>>
>>> print filter(lambda x: x % 3 == 0, foo)
[18, 9, 24, 12, 27]
>>>
>>> print map(lambda x: x * 2 + 10, foo)
[14, 46, 28, 54, 44, 58, 26, 34, 64]
>>>
>>> print reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, foo)
139
上面例子中的map的作用,非常简单清晰。但是,Python是否非要使用lambda才能做到这样的简洁程度呢?在对象遍历处理方面,其实Python的for..in..if语法已经很强大,并且在易读上胜过了lambda。
比如上面map的例子,可以写成:
print [x * 2 + 10 for x in foo]
非常的简洁,易懂。
filter的例子可以写成:
print [x for x in foo if x % 3 == 0]
同样也是比lambda的方式更容易理解。
上面简要介绍了什么是lambda,下面介绍为什么使用lambda,看一个例子(来自apihelper.py):
processFunc = collapse and (lambda s: " ".join(s.split())) or (lambda s: s)
在Visual Basic,你很有可能要创建一个函数,接受一个字符串参数和一个 collapse 参数,并使用 if 语句确定是否压缩空白,然后再返回相应的值。这种方式是低效的,因为函数可能需要处理每一种可能的情况。每次你调用它,它将不得不在给出你所想要的东西之前,判断是否要压缩空白。在 Python 中,你可以将决策逻辑拿到函数外面,而定义一个裁减过的 lambda 函数提供确切的 (唯一的) 你想要的。这种方式更为高效、更为优雅,而且很少引起那些令人讨厌 (哦,想到那些参数就头昏) 的错误。
通过此例子,我们发现,lambda的使用大量简化了代码,使代码简练清晰。但是值得注意的是,这会在一定程度上降低代码的可读性。
习条件运算时,对于简单的 if else 语句,可以使用三元运算来表示,即:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
# 普通条件语句if 1 == 1: name = ‘wupeiqi‘else: name = ‘alex‘ # 三元运算name = ‘wupeiqi‘ if 1 == 1 else ‘alex‘ |
对于简单的函数,也存在一种简便的表示方式,即:lambda表达式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# ###################### 普通函数 ####################### 定义函数(普通方式)def func(arg): return arg + 1 # 执行函数result = func(123) # ###################### lambda ###################### # 定义函数(lambda表达式)my_lambda = lambda arg : arg + 1 # 执行函数result = my_lambda(123) |
lambda存在意义就是对简单函数的简洁表示
一、map
遍历序列,对序列中每个元素进行操作,最终获取新的序列。
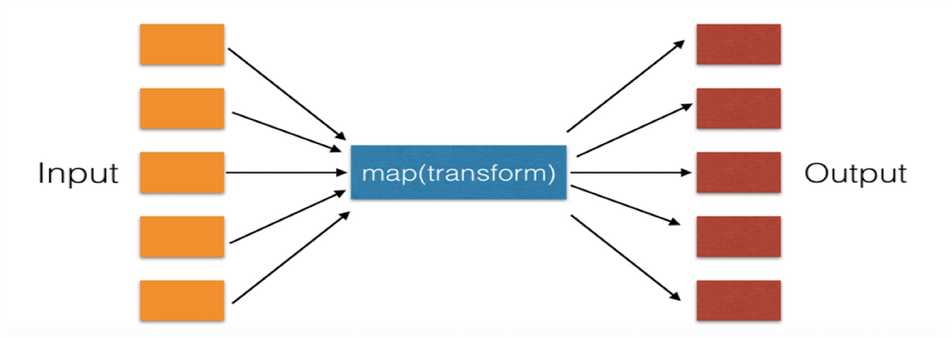
li = [11, 22, 33] new_list = map(lambda a: a + 100, li)
如果要想打印出new_list,必须用list函数转换
print(new_list)
<map object at 0x0000020226F3BE10>
print(list(new_list))
[12, 23, 34]
li = [11, 22, 33] sl = [1, 2, 3] new_list = map(lambda a, b: a + b, li, sl)
二、filter
对于序列中的元素进行筛选,最终获取符合条件的序列
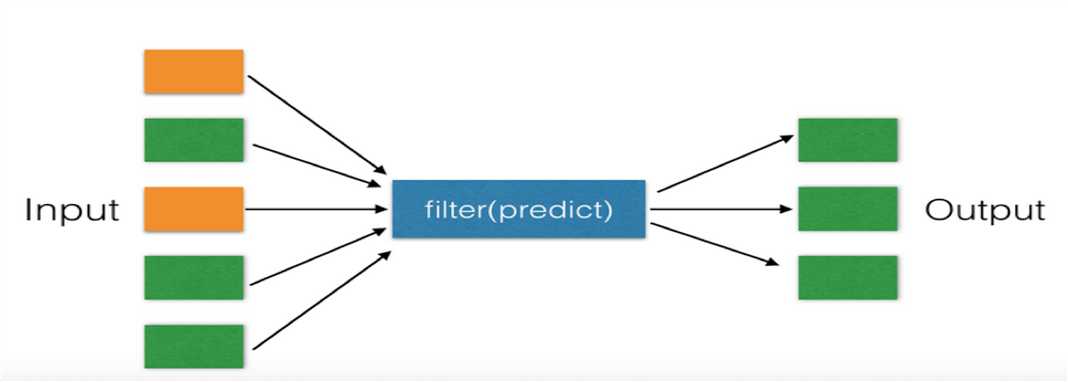
li = [11, 22, 33] new_list = filter(lambda arg: arg > 22, li) #filter第一个参数为空,将获取原来序列
三、reduce
对于序列内所有元素进行累计操作
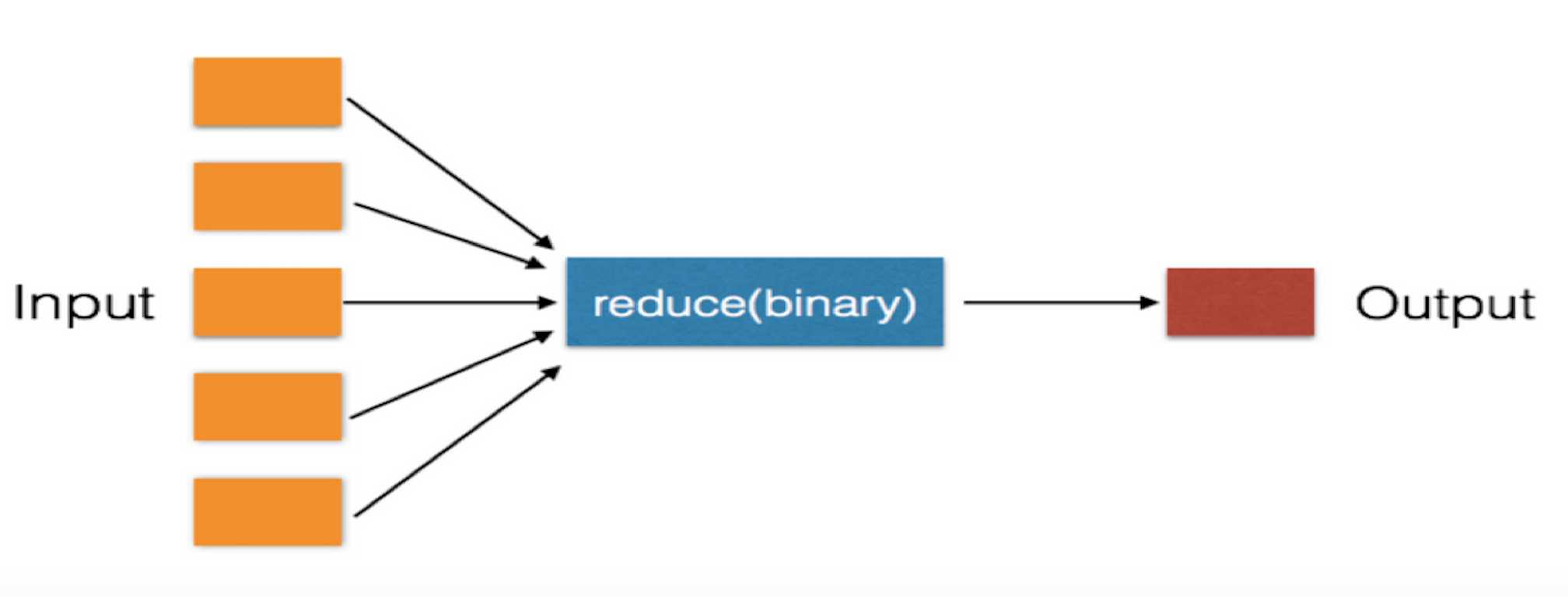
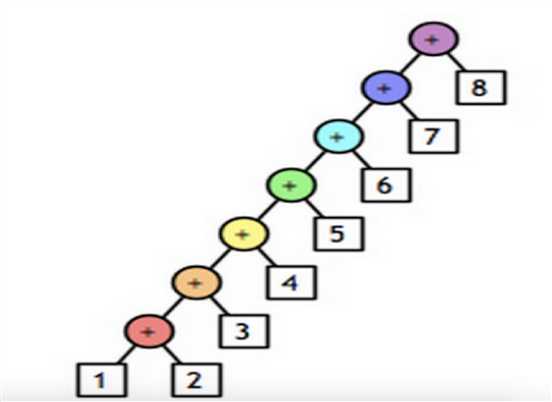
li = [11, 22, 33] result = reduce(lambda arg1, arg2: arg1 + arg2, li) # reduce的第一个参数,函数必须要有两个参数 # reduce的第二个参数,要循环的序列 # reduce的第三个参数,初始值
转自
python lambda表达式用法 - 蔡钊 - 博客园
https://www.cnblogs.com/caizhao/p/7905094.html
标签:ola 结果 UNC 压缩 span if else new 简单 aci
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/paul8339/p/12001236.html