标签:equal ide stack wap 递归 cat bsp put moved
前言:不仅仅要实现,更要提升性能,精益求精,用尽量少的时间复杂度和空间复杂度解决问题。
【程序68】
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(){ } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
/** * 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。 */ public class Subject68 { public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode listNode0 = new ListNode(1); ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(2); ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(3); ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(3); listNode0.next = listNode1; listNode1.next = listNode2; listNode2.next = listNode3; listNode3.next = listNode4; ListNode listNode01 = new ListNode(5); ListNode listNode11 = new ListNode(7); listNode01.next = listNode11; ListNode tmp = mergeTwoLists(listNode3,listNode01); StringBuilder stringBuilder = null; while(tmp !=null){ //指向位置是否为空 if(stringBuilder == null){ stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append(tmp.val); }else{ stringBuilder.append(" -> "+ tmp.val); } tmp = tmp.next; // 指向下一个节点 } System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString()); } /** * 递归实现链表插入 * @param l1 * @param l2 * @return */ public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null) { return l2; } else if (l2 == null) { return l1; } else if (l1.val < l2.val) { l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } }
时间复杂度:O(n+m)
运行结果:

【程序69】
给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。 */ public class Subject69 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(generateParenthesis(4)); } /** * 递归解题 * @param n * @return */ public static List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) { if(n == 1){ List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("()"); return list; }else{ List<String> list = generateParenthesis(n-1); int sizes = list.size(); List<String> newList = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < sizes; i++) { String tmp = list.get(i); char[] arr = tmp.toCharArray(); for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) { String tmp0 = tmp.substring(0,j); String tmp1 = tmp.substring(j,tmp.length()); String tmp2 = tmp0 + "()" +tmp1; if(!newList.contains(tmp2)){ newList.add(tmp2); } } } return newList; } } }
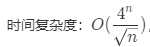
运行结果:

【程序70】
合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。
public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(){ } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
/** * 合并 k 个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。 */ public class Subject70 { public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode listNode0 = new ListNode(-10); ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(-3); ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(-1); ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(-1); ListNode listNode6 = new ListNode(0); listNode1.next = listNode0; listNode2.next = listNode1; listNode3.next = listNode2; listNode4.next = listNode3; listNode5.next = listNode4; listNode6.next = listNode5; ListNode listNode01 = new ListNode(-5); ListNode listNode02 = new ListNode(4); ListNode listNode03 = new ListNode(-8); ListNode listNode11 = null; ListNode listNode20 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode21 = new ListNode(-6); ListNode listNode22 = new ListNode(-5); ListNode listNode23 = new ListNode(-4); ListNode listNode24 = new ListNode(-2); ListNode listNode25 = new ListNode(2); ListNode listNode26 = new ListNode(3); listNode21.next = listNode20; listNode22.next = listNode21; listNode23.next = listNode22; listNode24.next = listNode23; listNode25.next = listNode24; listNode26.next = listNode25; ListNode listNode30 = new ListNode(-3); ListNode listNode31 = new ListNode(-3); ListNode listNode32 = new ListNode(-2); ListNode listNode33 = new ListNode(-1); ListNode listNode34 = new ListNode(0); listNode31.next = listNode30; listNode32.next = listNode31; listNode33.next = listNode32; listNode34.next = listNode33; ListNode[] arr = new ListNode[]{listNode6,listNode01,listNode02,listNode03,listNode11,listNode26,listNode34}; ListNode tmp= mergeKLists(arr); StringBuilder stringBuilder = null; while(tmp !=null){ //指向位置是否为空 if(stringBuilder == null){ stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append(tmp.val); }else{ stringBuilder.append(" -> "+ tmp.val); } tmp = tmp.next; // 指向下一个节点 } System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString()); } /** * 合并链表 * @param lists * @return */ public static ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) { if(lists.length == 0){ return null; } ListNode[] arr = mergeKLists0(lists); return arr[0]; } /** * 使用合并算法,组合链表 * @param lists * @return */ public static ListNode[] mergeKLists0(ListNode[] lists) { int length = lists.length; if(length == 1){ return lists; } ListNode[] listTmp = new ListNode[(int)Math.ceil(length/2.0)]; ListNode[] listTmp0 = null; for (int i = 0 ,j = 0; i < length; i = i+2 , j++) { ListNode tmp0 = null; if(i+1 <= length-1){ tmp0 = mergeTwoLists(lists[i],lists[i+1]); }else{ tmp0 = mergeTwoLists(lists[i],null); } listTmp[j] = tmp0; } listTmp0 = mergeKLists0(listTmp); return listTmp0; } /** * 递归实现链表插入 * @param l1 * @param l2 * @return */ public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null) { return l2; } else if (l2 == null) { return l1; } else if (l1.val < l2.val) { l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2); return l1; } else { l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next); return l2; } } }
时间复杂度:O(Nlogk)
运行结果:

【程序71】
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(){ } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
/** * 给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。 */ public class Subject71 { public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode listNode0 = new ListNode(1); ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(2); ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(3); ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(3); listNode0.next = listNode1; listNode1.next = listNode2; listNode2.next = listNode3; listNode3.next = listNode4; ListNode tmp = swapPairs(listNode0); StringBuilder stringBuilder = null; while(tmp !=null){ //指向位置是否为空 if(stringBuilder == null){ stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append(tmp.val); }else{ stringBuilder.append(" -> "+ tmp.val); } tmp = tmp.next; // 指向下一个节点 } System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString()); } /** * 交换链表数据位置 * @param head * @return */ public static ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) { ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode resultHead = newHead; while(head != null){ ListNode tmp0 = new ListNode(head.val); ListNode tmp1 = null; if(head.next != null){ tmp1 = new ListNode(head.next.val); newHead.next = tmp1; tmp1.next = tmp0; head = head.next.next; }else{ newHead.next = tmp0; head = null; } newHead = tmp0; } return resultHead.next; } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

【程序72】
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
给你一个链表,每k个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是k的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
示例 :
给定这个链表:1->2->3->4->5
当k= 2 时,应当返回: 2->1->4->3->5
当k= 3 时,应当返回: 3->2->1->4->5
说明 :
你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(){ } ListNode(int x) { val = x; } }
/** * 给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。 * 给你一个链表,每k个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。 * k是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。 * 如果节点总数不是k的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。 */ public class Subject72 { public ListNode head5 = new ListNode(0); public ListNode head4 = head5; public static void main(String[] args) { ListNode listNode0 = new ListNode(1); ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(2); ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(3); ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(-9); ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(3); listNode0.next = listNode1; listNode1.next = listNode2; listNode2.next = listNode3; listNode3.next = listNode4; ListNode listNode5 = new Subject72().reverseKGroup(listNode0,2); StringBuilder stringBuilder = null; while(listNode5 !=null){ //指向位置是否为空 if(stringBuilder == null){ stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append(listNode5.val); }else{ stringBuilder.append(" -> "+ listNode5.val); } listNode5 = listNode5.next; // 指向下一个节点 } System.out.println(stringBuilder.toString()); } /** * 逆序K链表 * @param head * @param k * @return */ public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k){ ListNode head0 = head; ListNode head1 = head; ListNode head2 = null; for (int i = 0; i < k-1; i++) { if(head0 != null){ head0 = head0.next; }else{ break; } } if(head0 != null){ head2 = head0.next; head0.next = null; }else{ head5.next = head; return head4.next; } ListNode head3 = reverseGroup(head); head5.next = head3; head5 = head3; while(head5.next != null){ head5 = head5.next; } reverseKGroup(head2,k); return head4.next; } /** * 链表反转 * @param head0 * @return */ public static ListNode reverseGroup(ListNode head0) { if(head0==null||head0.next==null){ return head0; } ListNode nowHead = reverseGroup(head0.next); head0.next.next=head0; head0.next=null; return nowHead; } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

【程序73】
给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
/** * 给定一个排序数组,你需要在原地删除重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回移除后数组的新长度。 * 不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。 */ public class Subject73 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,5,6,6,7}; System.out.println(new Subject73().removeDuplicates(nums)); } /** * 删除重复元素 * @param nums * @return */ public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) { int lengths = nums.length; if(lengths <=0 ){ return 0; } int side = 0; //空位置 int tmp = nums[0]; boolean flag = true; for (int i = 1; i < lengths; i++) { if(tmp == nums[i]){ if(flag){ side = i; flag = false; } }else{ tmp = nums[i]; if(side > 0){ nums[side] = nums[i]; side++; } } } if(side == 0){ return lengths; } return side; } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

【程序74】
给定一个数组 nums和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于val的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度。
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
/** * 给定一个数组 nums和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于val的元素,返回移除后数组的新长度。 * 不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在原地修改输入数组并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。 * 元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。 */ public class Subject74 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = new int[]{3,2,2,3}; System.out.println(new Subject74().removeElement(nums,3)); } /** * 删除元素 * @param nums * @param val * @return */ public static int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) { int lengths = nums.length; if(lengths <=0 ){ return 0; } int side = 0; for (int i = 0; i < lengths; i++) { if(val != nums[i]){ nums[side] = nums[i]; side++; } } return side; } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

【程序75】
实现strStr()函数。
给定一个haystack 字符串和一个 needle 字符串,在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置 (从0开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1。
/** * 实现strStr()函数。 * 给定一个haystack 字符串和一个 needle 字符串,在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串出现的第一个位置 (从0开始)。如果不存在,则返回 -1。 */ public class Subject75 { public static void main(String[] args) { String haystack = "ssss"; String needle = "a"; System.out.println(new Subject75().strStr(haystack,needle)); } /** * 实现strStr()函数 */ public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { if("".equals(needle) || needle == null){ return 0; }else{ if("".equals(haystack) || haystack == null ){ return -1; } } char[] arr0= haystack.toCharArray(); char[] arr1= needle.toCharArray(); return strStr0(arr0,arr1,0,arr0.length,-1); } /** * 递归处理 * @param arr0 * @param arr1 * @param side * @param lengths0 * @param result * @return */ public int strStr0(char[] arr0, char[] arr1,int side,int lengths0,int result) { if(result == 0){ return side-1; } boolean flag = false; for (int i = side; i < lengths0; i++) { if(arr0[i] == arr1[0]){ side = i; flag = true; break; } } int tmp = lengths0 - side; int lengths1 = arr1.length; if(tmp < lengths1 || !flag){ return -1; }else{ int identification = 0; for (int i = 1, j = side+1; i < lengths1; i++,j++) { if(arr0[j] != arr1[i]){ identification = -1; break; } } side = side+1; return strStr0(arr0,arr1,side, lengths0,identification); } } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

【程序76】
给定两个整数,被除数dividend和除数divisor。将两数相除,要求不使用乘法、除法和 mod 运算符。
返回被除数dividend除以除数divisor得到的商。
/** * 给定两个整数,被除数dividend和除数divisor。将两数相除,要求不使用乘法、除法和 mod 运算符。 * 返回被除数dividend除以除数divisor得到的商。 */ public class Subject76 { public static void main(String[] args) { int dividend = -2147483648; int divisor = -1; System.out.println(-2147483648/2); System.out.println(new Subject76().divide(dividend,divisor)); } /** * 实现除法,通过竖式的方式 * @param dividend * @param divisor * @return */ public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) { //排除一些特殊结果 if(dividend == 0){ return 0; } if(divisor == Integer.MIN_VALUE){ if(dividend > Integer.MIN_VALUE){ return 0; }else{ return 1; } } if(divisor == 1){ return dividend; } if(divisor == -1){ if(dividend == Integer.MIN_VALUE) { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; }else{ return -dividend; } } int result = 0; String s0 = String.valueOf(dividend); String s1 = String.valueOf(divisor); boolean flag = false; if(s0.charAt(0) == ‘-‘){ flag = true; }else{ s0 = "-"+s0; } if(s1.charAt(0) == ‘-‘){ if(flag){ flag = false; }else{ flag = true; } }else{ s1 = "-"+s1; divisor = -divisor; } int side = s1.length()-1; if(side > s0.length()-1){ return 0; } int dividend0 = Integer.parseInt(s0.substring(0,side+1)); //临时除数 while(true){ side++; int num = dividend0 - divisor; int i = 0; while(num <= 0){ i++; num = num - divisor; } result = Integer.parseInt(result+"0") + i; if(side >= s0.length()){ break; }else{ dividend0 = Integer.parseInt((num+divisor)+ "" +s0.charAt(side)); if(dividend0 > 0){ dividend0 = -dividend0; } } } if(flag){ return -result; }else{ return result; } } }
时间复杂度:O(1)
运行结果:

【程序77】
给定一个字符串s和一些长度相同的单词words。找出 s 中恰好可以由words 中所有单词串联形成的子串的起始位置。
注意子串要与words 中的单词完全匹配,中间不能有其他字符,但不需要考虑words中单词串联的顺序。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; /** * 给定一个字符串s和一些长度相同的单词words。找出 s 中恰好可以由words 中所有单词串联形成的子串的起始位置。 * 注意子串要与words 中的单词完全匹配,中间不能有其他字符,但不需要考虑words中单词串联的顺序。 */ public class Subject77 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "ababaabababababababababababababababababababababababbababababab"; String[] words = new String[]{"ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba","ab","ba"}; System.out.println(words.length); List<Integer> list = new Subject77().findSubstring(s,words); System.out.println(list); } public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int wordNum = words.length; if (wordNum == 0) { return res; } int wordLen = words[0].length(); HashMap<String, Integer> allWords = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); for (String w : words) { int value = allWords.getOrDefault(w, 0); allWords.put(w, value + 1); } //将所有移动分成 wordLen 类情况 for (int j = 0; j < wordLen; j++) { HashMap<String, Integer> hasWords = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); int num = 0; //记录当前 HashMap2(这里的 hasWords 变量)中有多少个单词 //每次移动一个单词长度 for (int i = j; i < s.length() - wordNum * wordLen + 1; i = i + wordLen) { boolean hasRemoved = false; //防止情况三移除后,情况一继续移除 while (num < wordNum) { String word = s.substring(i + num * wordLen, i + (num + 1) * wordLen); if (allWords.containsKey(word)) { int value = hasWords.getOrDefault(word, 0); hasWords.put(word, value + 1); //出现情况三,遇到了符合的单词,但是次数超了 if (hasWords.get(word) > allWords.get(word)) { // hasWords.put(word, value); hasRemoved = true; int removeNum = 0; //一直移除单词,直到次数符合了 while (hasWords.get(word) > allWords.get(word)) { String firstWord = s.substring(i + removeNum * wordLen, i + (removeNum + 1) * wordLen); int v = hasWords.get(firstWord); hasWords.put(firstWord, v - 1); removeNum++; } num = num - removeNum + 1; //加 1 是因为我们把当前单词加入到了 HashMap 2 中 i = i + (removeNum - 1) * wordLen; //这里依旧是考虑到了最外层的 for 循环,看情况二的解释 break; } //出现情况二,遇到了不匹配的单词,直接将 i 移动到该单词的后边(但其实这里 //只是移动到了出现问题单词的地方,因为最外层有 for 循环, i 还会移动一个单词 //然后刚好就移动到了单词后边) } else { hasWords.clear(); i = i + num * wordLen; num = 0; break; } num++; } if (num == wordNum) { res.add(i); } //出现情况一,子串完全匹配,我们将上一个子串的第一个单词从 HashMap2 中移除 if (num > 0 && !hasRemoved) { String firstWord = s.substring(i, i + wordLen); int v = hasWords.get(firstWord); hasWords.put(firstWord, v - 1); num = num - 1; } } } return res; } }
时间复杂度:O(n)
运行结果:

以上题目均来自:https://leetcode-cn.com/ ,如果你热爱编码,热爱算法,该网站一定适合你。
标签:equal ide stack wap 递归 cat bsp put moved
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jssj/p/12001809.html