标签:code mui cte enc 检测 gray 处理 EDA 特征提取
从虹软开放了2.0版本SDK以来,由于具有免费、离线使用的特点,我们公司在人脸识别门禁应用中使用了虹软SDK,识别效果还不错,因此比较关注虹软SDK的官方动态。近期上线了ArcFace 3.0 SDK版本,确实做了比较大的更新。上一篇主要介绍了关于Android平台算法的改进,本篇将介绍一下关于Windows平台算法的更新。特征比对支持比对模型选择,有生活照比对模型和人证比对模型
识别率、防***效果显著提升
特征值更新,升级后人脸库需重新注册
在V3.0版本接入过程中,发现使用新的图像数据结构还是具有一定难度的,本文将从以下几点对该图像数据结构及使用方式进行介绍
SDK接口变动
图像数据结构
步长的作用
在接入ArcFace 3.0 SDK时,发现新增了ASFDetectFacesEx、ASFFaceFeatureExtractEx、ASFProcessEx、ASFProcessEx_IR一组接口,该组接口使用LPASF_ImageData结构体指针的方式传入图像数据,以人脸检测接口为例,具体接口比对如下:
原始接口:
MRESULT ASFDetectFaces(
MHandle hEngine, // [in] 引擎handle
MInt32 width, // [in] 图片宽度
MInt32 height, // [in] 图片高度
MInt32 format, // [in] 颜色空间格式
MUInt8* imgData, // [in] 图片数据
LPASF_MultiFaceInfo detectedFaces, // [out]检测到的人脸信息
ASF_DetectModel detectModel = ASF_DETECT_MODEL_RGB // [in] 预留字段,当前版本使用默认参数即可
);
新增接口:
MRESULT ASFDetectFacesEx(
MHandle hEngine, // [in] 引擎handle
LPASF_ImageData imgData, // [in] 图片数据
LPASF_MultiFaceInfo detectedFaces, // [out] 检测到的人脸信息
ASF_DetectModel detectModel = ASF_DETECT_MODEL_RGB // [in] 预留字段,当前版本使用默认参数即可
);
相对于原始接口,新增接口通过传入LPASF_ImageData图像数据结构指针替代原始接口传入图像数据的方式。
新增的图像数据结构引入了步长pi32Pitch的概念。
步长定义:图像对齐后一行的字节数。
图像结构定义:
typedef LPASVLOFFSCREEN LPASF_ImageData;
typedef struct __tag_ASVL_OFFSCREEN
{
MUInt32 u32PixelArrayFormat;
MInt32 i32Width;
MInt32 i32Height;
MUInt8* ppu8Plane[4];
MInt32 pi32Pitch[4];
}ASVLOFFSCREEN, *LPASVLOFFSCREEN;
虹软官方文档中对该图像数据结构的介绍:
| 类型 | 变量名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| MUInt32 | u32PixelArrayFormat | 颜色格式 |
| MInt32 | i32Width | 图像宽度 |
| MInt32 | i32Height | 图像高度 |
| MUInt8* | ppu8Plane | 图像数据 |
| MInt32 | pi32Pitch | 图像步长 |
OpenCV提供了IplImage和Mat两种比较常用的图像数据结构。
IplImage 图像数据结构
typedef struct _IplImage
{
int width; /* Image width in pixels. */
int height; /* Image height in pixels. */
char *imageData; /* Pointer to aligned image data. */
int widthStep; /* Size of aligned image row in bytes. */
... //其他字段这里不做展示,感兴趣的小伙伴可以查看下opencv中的头文件
}
IplImage;
Mat 图像数据结构
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| cols | 矩阵的列数(图像宽度) |
| rows | 矩阵的行数(图像高度) |
| data | uchar型的指针。Mat类分为了两个部分:矩阵头和指向矩阵数据部分的指针,data就是指向矩阵数据的指针。 |
| step | 图像对齐之后一行的字节数 |
通过以上描述我们看到OpenCV和虹软算法库针对图像数据结构都引入了图像步长的概念,这里我们了解一下图像步长。
OpenCV 读图会做图像对齐
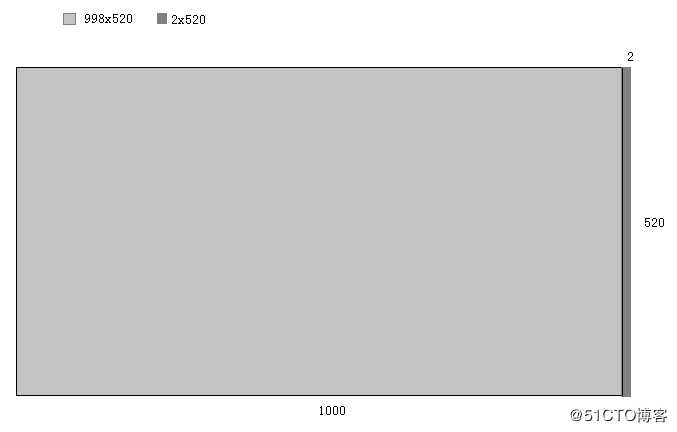
如下图,一张尺寸为998x520的图像,使用OpenCV读取图像数据后,图像尺寸仍为998x520,颜色格式为BGR24,但是图像步长并不是998 * 3,而是1000 * 3,右边填充了2个像素,OpenCV对图像做了四字节对齐,虹软SDK内部算法再通过传入的图像宽度去计算步长则会出现偏差,图像数据错乱,基本不可能检测到人脸。
以下是对一张大小为1000x554的图片,以不同步长进行解析的结果:
| 以1000为步长解析 | 以996为步长解析 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
可以看到,对于一张图像,如果使用了错误的步长去解析,我们可能就无法看到正确的图像内容。
结论:通过引入图像步长能够有效的避免高字节对齐的问题。
当前C/C++开发者对图像进行编解码处理一般都会用到OpenCV库,这里我们介绍一下如何将OpenCV转换为虹软的图像数据结构。虹软官方文档中说明支持七种颜色格式,我们就列出七种颜色格式的转换方法。
OpenCV 读取过来的图像一般为BGR24格式,可使用下述方法进行图像数据结构转换。
ASVL_PAF_GRAY格式(官网文档中也有示例),再使用下述方法进行转换。IplImage 转 ASVLOFFSCREEN
int ColorSpaceConversion(MInt32 format, IplImage* img, ASVLOFFSCREEN& offscreen)
{
switch (format) //原始图像颜色格式
{
case ASVL_PAF_I420:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] >> 1;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[2] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] >> 1;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.i32Height * offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[2] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.i32Height * offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * 5 / 4;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_YUYV:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_NV12:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * offscreen.i32Height;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_NV21:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * offscreen.i32Height;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_RGB24_B8G8R8:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_DEPTH_U16:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_GRAY:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img->width;
offscreen.i32Height = img->height;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img->widthStep;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = (MUInt8*)img->imageData;
break;
default:
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
Mat 转 ASVLOFFSCREEN
int ColorSpaceConversion(MInt32 format, cv::Mat img, ASVLOFFSCREEN& offscreen)
{
switch (format) //原始图像颜色格式
{
case ASVL_PAF_I420:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] >> 1;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[2] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] >> 1;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.i32Height * offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[2] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.i32Height * offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * 5 / 4;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_YUYV:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_NV12:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * offscreen.i32Height;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_NV21:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[1] = offscreen.pi32Pitch[0];
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[1] = offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] + offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] * offscreen.i32Height;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_RGB24_B8G8R8:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_DEPTH_U16:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
break;
case ASVL_PAF_GRAY:
offscreen.u32PixelArrayFormat = (unsigned int)format;
offscreen.i32Width = img.cols;
offscreen.i32Height = img.rows;
offscreen.pi32Pitch[0] = img.step;
offscreen.ppu8Plane[0] = img.data;
break;
default:
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
举例说明
这里引用了虹软官网文档中的示例,但使用了上述的图像格式转换方法。
//opencv方式裁剪图片
void CutIplImage(IplImage* src, IplImage* dst, int x, int y)
{
CvSize size = cvSize(dst->width, dst->height);//区域大小
cvSetImageROI(src, cvRect(x, y, size.width, size.height));//设置源图像ROI
cvCopy(src, dst); //复制图像
cvResetImageROI(src);//源图像用完后,清空ROI
}
IplImage* originalImg = cvLoadImage("1280 x 720.jpg");
//图像裁剪,宽度做四字节对齐,若能保证图像是四字节对齐这步可以不用做
IplImage* img = cvCreateImage(cvSize(originalImg->width - originalImg->width % 4, originalImg->height), IPL_DEPTH_8U, originalImg->nChannels);
CutIplImage(originalImg, img, 0, 0);
//图像数据以结构体形式传入,对更高精度的图像兼容性更好
ASF_MultiFaceInfo detectedFaces = { 0 };
ASVLOFFSCREEN offscreen = { 0 };
//IplImage 转 ASVLOFFSCREEN
ColorSpaceConversion(ASVL_PAF_RGB24_B8G8R8, img, offscreen);
if (img)
{
MRESULT res = ASFDetectFacesEx(handle, &offscreen, &detectedFaces);
if (MOK != res)
{
printf("ASFDetectFacesEx failed: %d\n", res);
}
else
{
// 打印人脸检测结果
for (int i = 0; i < detectedFaces.faceNum; i++)
{
printf("Face Id: %d\n", detectedFaces.faceID[i]);
printf("Face Orient: %d\n", detectedFaces.faceOrient[i]);
printf("Face Rect: (%d %d %d %d)\n",
detectedFaces.faceRect[i].left, detectedFaces.faceRect[i].top,
detectedFaces.faceRect[i].right, detectedFaces.faceRect[i].bottom);
}
}
//释放图像内存,这里只是做人脸检测,若还需要做特征提取等处理,图像数据没必要释放这么早
cvReleaseImage(&img);
}
cvReleaseImage(&originalImg);
个人总结 :通过研究发现V3.0 版本SDK使用老接口也是可以正常使用的,新接口对更高字节对齐的图像兼容性更好。
Demo可在虹软人脸识别开放平台下载
标签:code mui cte enc 检测 gray 处理 EDA 特征提取
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14633836/2458136