标签:pup style 包含 ast span 访问 serial item 控制
Stack简介
Stack是栈。它的特性是:先进后出(FILO, First In Last Out)。
java工具包中的Stack是继承于Vector(矢量队列)的,由于Vector是通过数组实现的,这就意味着,Stack也是通过数组实现的,而非链表。当然,我们也可以将LinkedList当作栈来使用!在“Java 集合系列06之 Vector详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例”中,已经详细介绍过Vector的数据结构,这里就不再对Stack的数据结构进行说明了。
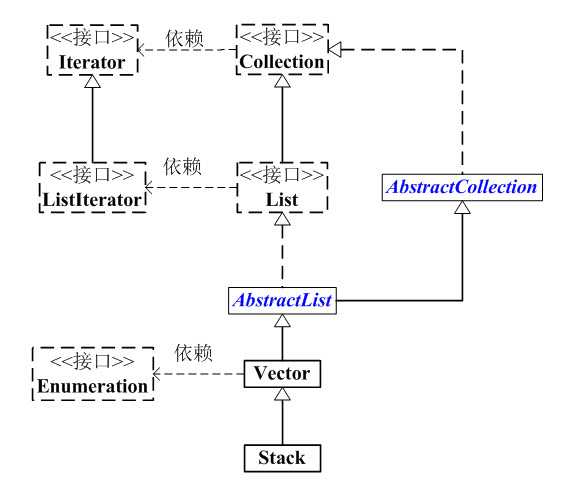
Stack的继承关系
java.lang.Object ? java.util.AbstractCollection<E> ? java.util.AbstractList<E> ? java.util.Vector<E> ? java.util.Stack<E> public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {}
Stack和Collection的关系如下图:
Stack的构造函数
Stack只有一个默认构造函数,如下:
Stack()
Stack的API
Stack是栈,它常用的API如下:
boolean empty() synchronized E peek() synchronized E pop() E push(E object) synchronized int search(Object o)
由于Stack和继承于Vector,因此它也包含Vector中的全部API。
Stack的源码非常简单,下面我们对它进行学习。
1 package java.util; 2 3 public 4 class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> { 5 // 版本ID。这个用于版本升级控制,这里不须理会! 6 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L; 7 8 // 构造函数 9 public Stack() { 10 } 11 12 // push函数:将元素存入栈顶 13 public E push(E item) { 14 // 将元素存入栈顶。 15 // addElement()的实现在Vector.java中 16 addElement(item); 17 18 return item; 19 } 20 21 // pop函数:返回栈顶元素,并将其从栈中删除 22 public synchronized E pop() { 23 E obj; 24 int len = size(); 25 26 obj = peek(); 27 // 删除栈顶元素,removeElementAt()的实现在Vector.java中 28 removeElementAt(len - 1); 29 30 return obj; 31 } 32 33 // peek函数:返回栈顶元素,不执行删除操作 34 public synchronized E peek() { 35 int len = size(); 36 37 if (len == 0) 38 throw new EmptyStackException(); 39 // 返回栈顶元素,elementAt()具体实现在Vector.java中 40 return elementAt(len - 1); 41 } 42 43 // 栈是否为空 44 public boolean empty() { 45 return size() == 0; 46 } 47 48 // 查找“元素o”在栈中的位置:由栈底向栈顶方向数 49 public synchronized int search(Object o) { 50 // 获取元素索引,elementAt()具体实现在Vector.java中 51 int i = lastIndexOf(o); 52 53 if (i >= 0) { 54 return size() - i; 55 } 56 return -1; 57 } 58 }
总结:
(01) Stack实际上也是通过数组去实现的。
执行push时(即,将元素推入栈中),是通过将元素追加的数组的末尾中。
执行peek时(即,取出栈顶元素,不执行删除),是返回数组末尾的元素。
执行pop时(即,取出栈顶元素,并将该元素从栈中删除),是取出数组末尾的元素,然后将该元素从数组中删除。
(02) Stack继承于Vector,意味着Vector拥有的属性和功能,Stack都拥有。
下面我们通过实例学习如何使用Stack
1 import java.util.Stack; 2 import java.util.Iterator; 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 /** 6 * @desc Stack的测试程序。测试常用API的用法 7 * 8 * @author skywang 9 */ 10 public class StackTest { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 Stack stack = new Stack(); 14 // 将1,2,3,4,5添加到栈中 15 for(int i=1; i<6; i++) { 16 stack.push(String.valueOf(i)); 17 } 18 19 // 遍历并打印出该栈 20 iteratorThroughRandomAccess(stack) ; 21 22 // 查找“2”在栈中的位置,并输出 23 int pos = stack.search("2"); 24 System.out.println("the postion of 2 is:"+pos); 25 26 // pup栈顶元素之后,遍历栈 27 stack.pop(); 28 iteratorThroughRandomAccess(stack) ; 29 30 // peek栈顶元素之后,遍历栈 31 String val = (String)stack.peek(); 32 System.out.println("peek:"+val); 33 iteratorThroughRandomAccess(stack) ; 34 35 // 通过Iterator去遍历Stack 36 iteratorThroughIterator(stack) ; 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * 通过快速访问遍历Stack 41 */ 42 public static void iteratorThroughRandomAccess(List list) { 43 String val = null; 44 for (int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) { 45 val = (String)list.get(i); 46 System.out.print(val+" "); 47 } 48 System.out.println(); 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * 通过迭代器遍历Stack 53 */ 54 public static void iteratorThroughIterator(List list) { 55 56 String val = null; 57 for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext(); ) { 58 val = (String)iter.next(); 59 System.out.print(val+" "); 60 } 61 System.out.println(); 62 } 63 64 }
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5 the postion of 2 is:4 1 2 3 4 peek:4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
标签:pup style 包含 ast span 访问 serial item 控制
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuexiaoyun/p/12056967.html