标签:ace 之间 比较 tostring ast i++ 可变 创建 字符串连接
API(Application Programming Interface),应用程序编程接口。Java API是JDK中提供给我们使用的类的说明文档。即jdk包里边写好的类,这些类将底层的代码实现封装了起来,我们不需要关心这些类是如何实现的,只需要学习这些类如何使用即可。所以我们可以通过查询API的方式,来学习Java提供的类,并得知如何使用它们。
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList就是一个常用集合类,我们可以调用调用这个类的方法来进行业务操作,不需要我们自己去实现一个集合功能。下面介绍一些常用的类。
1.String类
String s1 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1);
String s1 = "abc"; s1 += "d"; System.out.println(s1); // "abcd" // 值不变,不是说变量s1不能变,是字符串"abc"不变,内存中有"abc","abcd"两个对象,s1从指向"abc",改变指向,指向了"abcd"。 String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "abc"; // 内存中只有一个"abc"对象被创建,同时被s1和s2共享。
java.lang包下的类不需要导入,可直接使用。创建String对象时,根据具体需要,调用构造方法创建
构造方法:
// 无参构造 String str = new String(); // 通过字符数组构造 char chars[] = {‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘}; String str2 = new String(chars); // 通过字节数组构造 byte bytes[] = { 97, 98, 99 }; String str3 = new String(bytes);
public class String_Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建字符串对象 String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "hello"; String s3 = "HELLO"; // boolean equals(Object obj):比较字符串的内容是否相同 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); //boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比较字符串的内容是否相同,忽略大小写 System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // true System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s3)); // true } }
public class String_Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "helloworld"; // int length():获取字符串的长度,其实也就是字符个数 System.out.println(s.length()); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // String concat (String str):将将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾. String s = "helloworld"; String s2 = s.concat("**hello"); System.out.println(s2);// helloworld**hello // char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符 System.out.println(s.charAt(0)); System.out.println(s.charAt(1)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // int indexOf(String str):获取str在字符串对象中第一次出现的索引,没有返回‐1 System.out.println(s.indexOf("l")); System.out.println(s.indexOf("owo")); System.out.println(s.indexOf("ak")); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // String substring(int start):从start开始截取字符串到字符串结尾 System.out.println(s.substring(0)); System.out.println(s.substring(5)); System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // String substring(int start,int end):从start到end截取字符串。含start,不含end。 System.out.println(s.substring(0, s.length())); System.out.println(s.substring(3,8)); } }
public class String_Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "abcde"; // char[] toCharArray():把字符串转换为字符数组 char[] chs = s.toCharArray(); for(int x = 0; x < chs.length; x++) { System.out.println(chs[x]); } System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // byte[] getBytes ():把字符串转换为字节数组 byte[] bytes = s.getBytes(); for(int x = 0; x < bytes.length; x++) { System.out.println(bytes[x]); } System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐"); // 替换字母it为大写IT String str = "itcast"; String replace = str.replace("it", "IT"); System.out.println(replace); // ITcast } }
public class String_Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建字符串对象 String s = "aa|bb|cc"; String[] strArray = s.split("|"); // ["aa","bb","cc"] for(int x = 0; x < strArray.length; x++) { System.out.println(strArray[x]); // aa bb cc } } }
2.Arrays类
public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义int 数组 int[] arr = {2,34,35,4,657,8,69,9}; // 打印数组,输出地址值 System.out.println(arr); // [I@2ac1fdc4 // 数组内容转为字符串 String s = Arrays.toString(arr); // 打印字符串,输出内容 System.out.println(s); // [2, 34, 35, 4, 657, 8, 69, 9] }
public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义int 数组 int[] arr = {24, 7, 5, 48, 4, 46, 35, 11, 6, 2}; System.out.println("排序前:"+ Arrays.toString(arr)); // 排序前:[24, 7, 5, 48, 4, 46, 35, 11, 6, 2] // 升序排序 Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println("排序后:"+ Arrays.toString(arr));// 排序后:[2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 11, 24, 35, 46, 48] }
3.ArrayList类
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
public class Demo01ArrayListMethod { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建集合对象 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); //添加元素 list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); list.add("java"); //public E get(int index):返回指定索引处的元素 System.out.println("get:"+list.get(0)); System.out.println("get:"+list.get(1)); System.out.println("get:"+list.get(2)); //public int size():返回集合中的元素的个数 System.out.println("size:"+list.size()); //public E remove(int index):删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素 System.out.println("remove:"+list.remove(0)); //遍历输出 for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){ System.out.println(list.get(i)); } } }
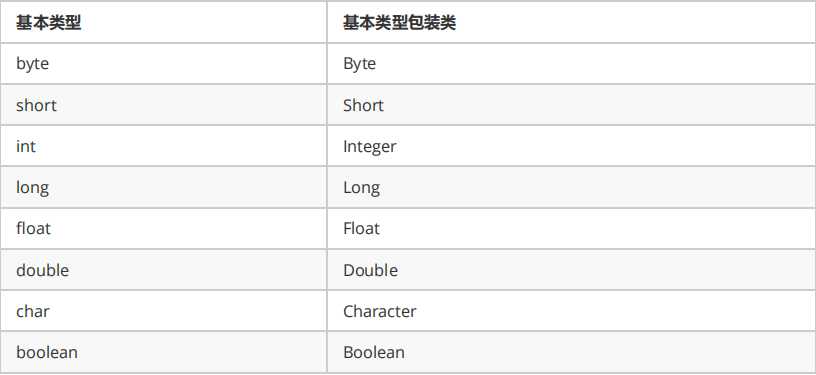
4.基本类型包装类
5.Random类
构造方法
Random r = new Random();
//1. 导包 import java.util.Random; public class Demo01_Random { public static void main(String[] args) { //2. 创建键盘录入数据的对象 Random r = new Random(); for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){ //3. 随机生成一个数据 int number = r.nextInt(10); //4. 输出数据 System.out.println("number:"+ number); } } }
6.Math类
double d1 = Math.abs(‐5); //d1的值为5
double d1 = Math.ceil(3.3); //d1的值为 4.0
double d1 = Math.floor(3.3); //d1的值为3.0
long d1 = Math.round(5.5); //d1的值为6.0
标签:ace 之间 比较 tostring ast i++ 可变 创建 字符串连接
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zxxfz/p/12067951.html