标签:data oat int sum 可靠性 art frame 发动机 日期
Python高级应用程序设计任务要求
用Python实现一个面向主题的网络爬虫程序,并完成以下内容:
(注:每人一题,主题内容自选,所有设计内容与源代码需提交到博客园平台)
一、主题式网络爬虫设计方案(15分)
1.主题式网络爬虫名称
瓜子二手车网站数据爬取
2.主题式网络爬虫爬取的内容与数据特征分析
品牌、车型、年月、公里数、售价
爬取内容:基本参数、发动机参数、底盘及制动、安全配置、外部配置、内部配置
3.主题式网络爬虫设计方案概述(包括实现思路与技术难点)
爬取瓜子二手车数据实现思路:使用requests库爬取数据、生成所有需要抓取的URL,对所有目标链接进行数据抓取,存储数据
爬取瓜子二手车数据技术难点:瓜子二手车网运用的反爬虫措施主要有js混淆,根据发送的原始header和js混淆生成特定的cookie才能访问到网站。
deal_head.py处理的数js混淆和生成特定的header。原始header的user-agent必须是使用电脑相同的平台(windows、linux),不一致返回不了有效的cookie。
二、主题页面的结构特征分析(15分)
1.主题页面的结构特征
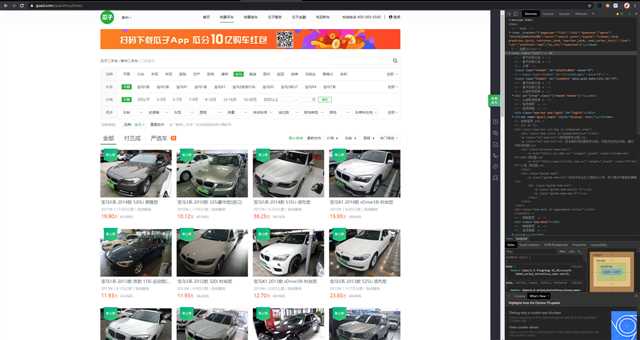
2.Htmls页面解析
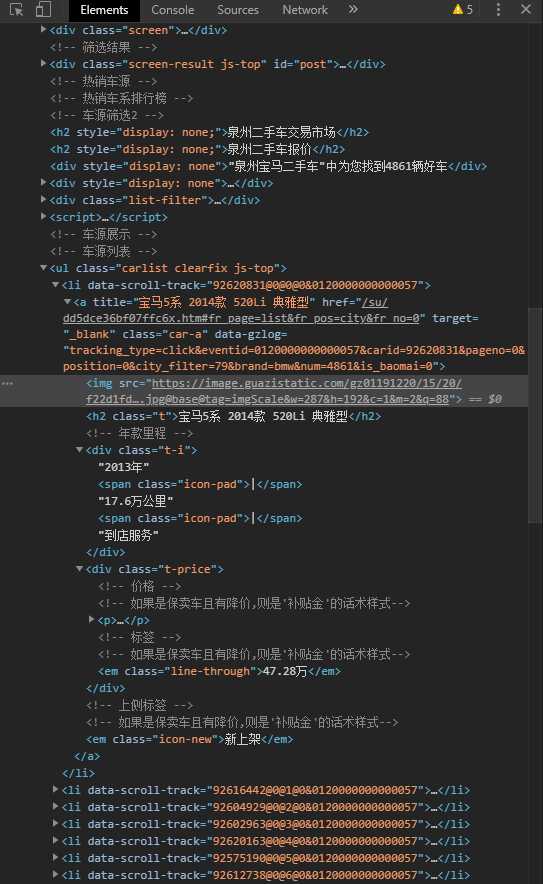
主题页面为瓜子二手车网站宝马检索结果的HTML代码,需要的信息保存在carlist选择器属性的标签中
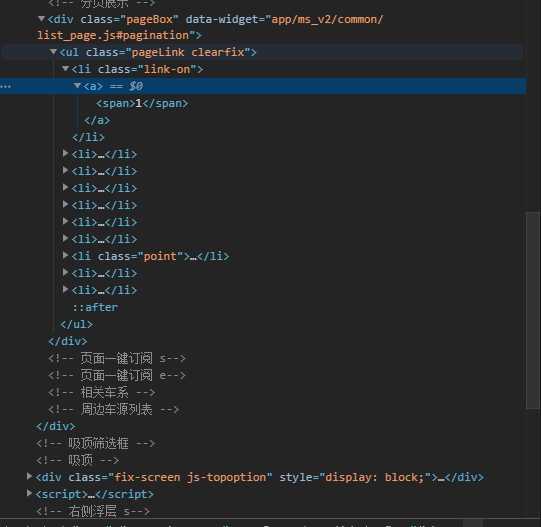
页数内容在该结构中,以此分析如何按页爬取所需要的数据
3.节点(标签)查找方法与遍历方法
(必要时画出节点树结构)
<html>→<ul class="carlist">→<li class="data">
三、网络爬虫程序设计(60分)
爬虫程序主体要包括以下各部分,要附源代码及较详细注释,并在每部分程序后面提供输出结果的截图。
1.数据爬取与采集
# 导入第三方包 import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import time # 设置伪头 headers = { ‘Accept‘:‘*/*‘, ‘Accept-Encoding‘:‘gzip, deflate, br‘, ‘Accept-Language‘:‘zh-CN,zh;q=0.8‘, ‘Connection‘:‘keep-alive‘, ‘User-Agent‘:‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/61.0.3163.79 Safari/537.36‘ } # 二手车主页的链接 url = ‘https://www.guazi.com/quanzhou/bmw/‘ # 发出抓取链接的请求并进一步解析 res = requests.get(url, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 抓取二手车品牌名称及对应的链接 car_brands = soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘brand-name‘}) car_brands = [j for i in car_brands for j in i] brands = [i.text for i in car_brands] urls = [‘https://www.guazi.com/quanzhou/bmw/‘ + i[‘href‘] for i in car_brands] # 生成所需抓取的目标链接 target_urls = [] target_brands = [] for b,u in zip(brands,urls): # 抓取各品牌二手车主页下的所有页码 res = requests.get(u, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 查询出页数 if len(soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘the-pages‘})) == 0: pages = 1 else: pages = int([page.text for page in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘the-pages‘})[0].findAll(‘a‘)][-2]) time.sleep(3) for i in range(1,pages + 1): target_brands.append(b) target_urls.append(u+‘?page=‘+str(i)+‘#pagetag‘) # 构建空列表,用于数据的存储 brand = [] title = [] boarding_time = [] km = [] discharge = [] sec_price = [] new_price = [] # 对每个链接发生请求 for b,u in zip(target_brands,target_urls):
res = requests.get(u, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 每页车子的数量 N = len([i.findAll(‘a‘)[0][‘title‘] for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_details‘})]) try: # 车品牌 brands = (b+‘-‘)*N brand.extend(brands.split(‘-‘)[:-1]) # 车名称 title.extend([i.findAll(‘a‘)[0][‘title‘] for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_details‘})]) # 二手车的上牌时间、行驶里程数等信息 info = [i.findAll(‘li‘) for i in soup.findAll(‘ul‘,{‘class‘:‘ul_news‘})] boarding_time.extend([i[0].text[4:] for i in info]) km.extend([i[1].text[4:] for i in info]) discharge.extend([i[3].text[4:] for i in info]) sec_price.extend([float(i.findAll(‘h2‘)[0].text[:-1]) for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_price‘})]) new_price.extend([i.findAll(‘p‘)[0].text.split(‘\xa0‘)[0][5:].strip() for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_price‘})]) except IndexError: pass # 每4秒停顿一次 time.sleep(4) # 数据导出 import pandas as pd cars_info = pd.DataFrame([brand,title,boarding_time,km,discharge,sec_price,new_price]).T cars_info = cars_info.rename(columns={0:‘Brand‘,1:‘Name‘,2:‘Boarding_time‘,3:‘Km‘,4:‘Discharge‘,5:‘Sec_price‘,6:‘New_price‘}) cars_info.to_csv(‘second_cars_info.csv‘, index=False)
2.对数据进行清洗和处理
# 导入第三方模块 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from nbconvert.exporters import python from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 可视化的中文处理 plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = ‘Microsoft YaHei‘ plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘] = False # 设置风格 plt.style.use(‘ggplot‘) # 读取数据 cars = pd.read_csv(‘second_cars_info.csv‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) # 取出上牌时间变量中的年和月 cars[‘year‘] = cars.Boarding_time.str[:4].astype(‘int‘) month = cars.Boarding_time.str.findall(‘年(.*?)月‘) # print(month.head(10)) # 由于month是列表构成的序列,所以需要非列表化,再序列化 month = pd.Series([i[0] for i in month]).astype(‘int‘) cars[‘month‘] = month # print(month.head(10)) # 计算上牌日期距离2017年10月份的月数 cars[‘diff_months‘] = (2017 - cars.year) * 12 + (10 - cars.month) + 1 # 显示数据的前5行 cars.head(5) # 剔除“万公里”三个字 cars[‘Km_new‘] = cars.Km.str[:-3] # 数值类型转换 cars.Km_new = cars.Km_new.astype(‘float‘) # “百公里内”的样本量 N = np.sum(cars.Km == ‘百公里内‘) Ratio = N / cars.shape[0] # 将“百”字替换为0.005 cars.Km_new.replace(‘百‘, ‘0.005‘, inplace=True) # 数据类型转换 cars.Km_new = cars.Km_new.astype(‘float‘) cars.head() # 删除字段中的“万”字 cars[‘New_price_new‘] = cars.New_price.str[:-1] # “暂无”的样本量 N = np.sum(cars.New_price == ‘暂无‘) Ratio = N / cars.shape[0] cars = cars.loc[cars.New_price != ‘暂无‘, :] # 数据类型的转换 cars.New_price_new = cars.New_price_new.astype(‘float‘) cars.head() # 数据集的概览信息 cars.describe()
3.文本分析(可选):jieba分词、wordcloud可视化
4.数据分析与可视化
(例如:数据柱形图、直方图、散点图、盒图、分布图、数据回归分析等)
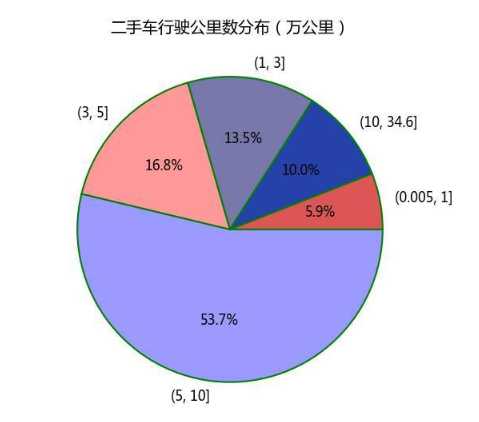
# 行驶公里数饼状图 km_min = cars.Km_new.min() km_max = cars.Km_new.max() # 切割数据片段 km_cuts = pd.cut(cars.Km_new, bins=[km_min, 1, 3, 5, 10, km_max]) km_stats = km_cuts.value_counts() km_stats # 绘制饼图 # 将横、纵坐标轴标准化处理 plt.axes(aspect=‘equal‘) # 提取出索引作为标签 labels = km_stats.index # 自定义颜色 colors = [‘#9999ff‘, ‘#ff9999‘, ‘#7777aa‘, ‘#2442aa‘, ‘#dd5555‘] # 绘制饼图 plt.pie(km_stats.values, labels=labels, colors=colors, # 设置颜色 autopct=‘%.1f%%‘, # 设置百分比的格式,这里保留一位小数 counterclock=False, # 设置为顺时针方向显示图形 wedgeprops={‘linewidth‘: 1.5, ‘edgecolor‘: ‘green‘}, # 设置饼图内外边界的属性值 textprops={‘fontsize‘: 12, ‘color‘: ‘k‘} # 设置文本标签的属性值 ) # 添加图标题 plt.title(‘二手车行驶公里数分布(万公里)‘) # 显示图形 plt.show()
5.数据持久化
数据导出为CSV文件实现数据持久化操作
# 数据导出 import pandas as pd cars_info = pd.DataFrame([brand,title,boarding_time,km,discharge,sec_price,new_price]).T cars_info = cars_info.rename(columns={0:‘Brand‘,1:‘Name‘,2:‘Boarding_time‘,3:‘Km‘,4:‘Discharge‘,5:‘Sec_price‘,6:‘New_price‘}) cars_info.to_csv(‘second_cars_info.csv‘, index=False)
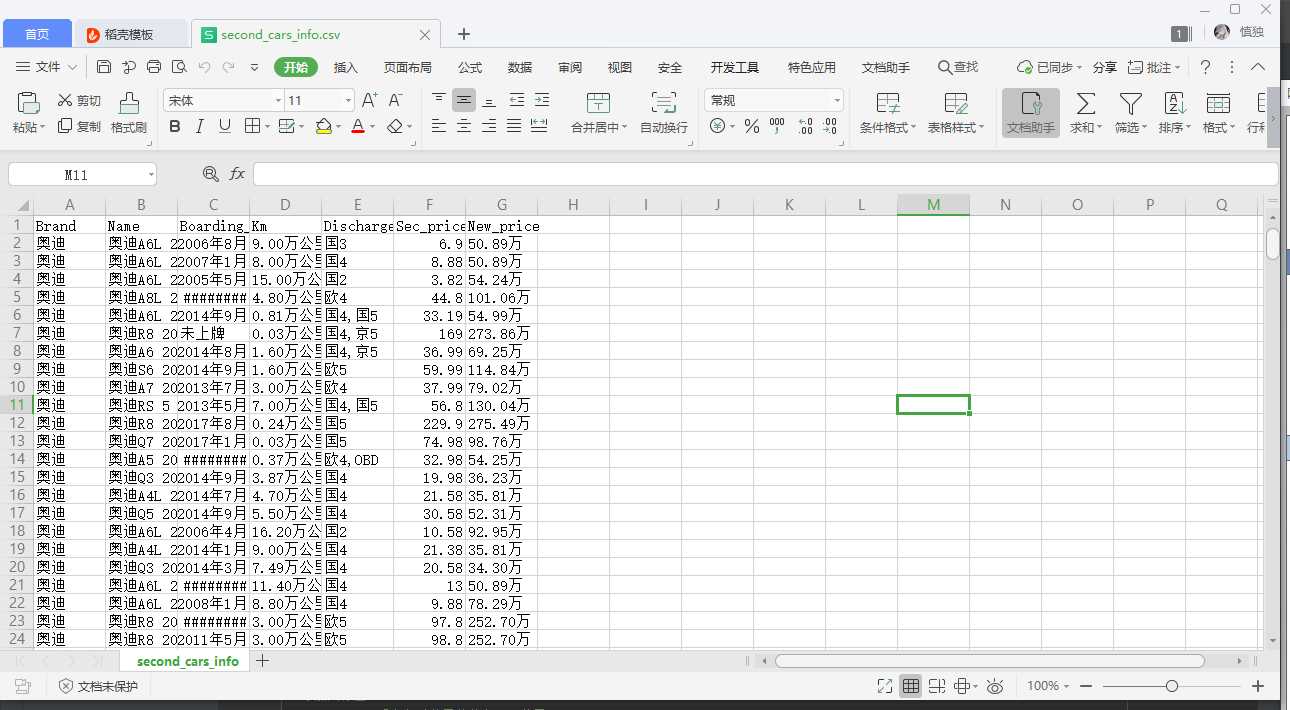
6.附完整程序代码
# 导入第三方包 import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import time # 设置伪头 headers = { ‘Accept‘:‘*/*‘, ‘Accept-Encoding‘:‘gzip, deflate, br‘, ‘Accept-Language‘:‘zh-CN,zh;q=0.8‘, ‘Connection‘:‘keep-alive‘, ‘User-Agent‘:‘Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/61.0.3163.79 Safari/537.36‘ } # 二手车主页的链接 url = ‘https://www.guazi.com/quanzhou/bmw/‘ # 发出抓取链接的请求并进一步解析 res = requests.get(url, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 抓取二手车品牌名称及对应的链接 car_brands = soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘brand-name‘}) car_brands = [j for i in car_brands for j in i] brands = [i.text for i in car_brands] urls = [‘https://www.guazi.com/quanzhou/bmw/‘ + i[‘href‘] for i in car_brands] # 生成所需抓取的目标链接 target_urls = [] target_brands = [] for b,u in zip(brands,urls): # 抓取各品牌二手车主页下的所有页码 res = requests.get(u, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 查询出页数 if len(soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘the-pages‘})) == 0: pages = 1 else: pages = int([page.text for page in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘the-pages‘})[0].findAll(‘a‘)][-2]) time.sleep(3) for i in range(1,pages + 1): target_brands.append(b) target_urls.append(u+‘?page=‘+str(i)+‘#pagetag‘) # 构建空列表,用于数据的存储 brand = [] title = [] boarding_time = [] km = [] discharge = [] sec_price = [] new_price = [] # 对每个链接发生请求 for b,u in zip(target_brands,target_urls): res = requests.get(u, headers = headers).text soup = BeautifulSoup(res,‘html.parser‘) # 每页车子的数量 N = len([i.findAll(‘a‘)[0][‘title‘] for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_details‘})]) try: # 车品牌 brands = (b+‘-‘)*N brand.extend(brands.split(‘-‘)[:-1]) # 车名称 title.extend([i.findAll(‘a‘)[0][‘title‘] for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_details‘})]) # 二手车的上牌时间、行驶里程数等信息 info = [i.findAll(‘li‘) for i in soup.findAll(‘ul‘,{‘class‘:‘ul_news‘})] boarding_time.extend([i[0].text[4:] for i in info]) km.extend([i[1].text[4:] for i in info]) discharge.extend([i[3].text[4:] for i in info]) sec_price.extend([float(i.findAll(‘h2‘)[0].text[:-1]) for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_price‘})]) new_price.extend([i.findAll(‘p‘)[0].text.split(‘\xa0‘)[0][5:].strip() for i in soup.findAll(‘div‘,{‘class‘:‘item_price‘})]) except IndexError: pass # 每4秒停顿一次 time.sleep(4) # 数据导出 import pandas as pd cars_info = pd.DataFrame([brand,title,boarding_time,km,discharge,sec_price,new_price]).T cars_info = cars_info.rename(columns={0:‘Brand‘,1:‘Name‘,2:‘Boarding_time‘,3:‘Km‘,4:‘Discharge‘,5:‘Sec_price‘,6:‘New_price‘}) cars_info.to_csv(‘second_cars_info.csv‘, index=False)
# 导入第三方模块 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from nbconvert.exporters import python from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 可视化的中文处理 plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = ‘Microsoft YaHei‘ plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘] = False # 设置风格 plt.style.use(‘ggplot‘) # 读取数据 cars = pd.read_csv(‘second_cars_info.csv‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) # 取出上牌时间变量中的年和月 cars[‘year‘] = cars.Boarding_time.str[:4].astype(‘int‘) month = cars.Boarding_time.str.findall(‘年(.*?)月‘) # print(month.head(10)) # 由于month是列表构成的序列,所以需要非列表化,再序列化 month = pd.Series([i[0] for i in month]).astype(‘int‘) cars[‘month‘] = month # print(month.head(10)) # 计算上牌日期距离2017年10月份的月数 cars[‘diff_months‘] = (2017 - cars.year) * 12 + (10 - cars.month) + 1 # 显示数据的前5行 cars.head(5) # 剔除“万公里”三个字 cars[‘Km_new‘] = cars.Km.str[:-3] # 数值类型转换 cars.Km_new = cars.Km_new.astype(‘float‘) # “百公里内”的样本量 N = np.sum(cars.Km == ‘百公里内‘) Ratio = N / cars.shape[0] # 将“百”字替换为0.005 cars.Km_new.replace(‘百‘, ‘0.005‘, inplace=True) # 数据类型转换 cars.Km_new = cars.Km_new.astype(‘float‘) cars.head() # 删除字段中的“万”字 cars[‘New_price_new‘] = cars.New_price.str[:-1] # “暂无”的样本量 N = np.sum(cars.New_price == ‘暂无‘) Ratio = N / cars.shape[0] cars = cars.loc[cars.New_price != ‘暂无‘, :] # 数据类型的转换 cars.New_price_new = cars.New_price_new.astype(‘float‘) cars.head() # 数据集的概览信息 cars.describe() # 行驶公里数的饼图展现 km_min = cars.Km_new.min() km_max = cars.Km_new.max() # 指定任意的切割点,将数据分段 km_cuts = pd.cut(cars.Km_new, bins=[km_min, 1, 3, 5, 10, km_max]) km_stats = km_cuts.value_counts() # 绘制饼图 # 将横、纵坐标轴标准化处理. plt.axes(aspect=‘equal‘) # 提取出索引作为标签 labels = km_stats.index # 自定义颜色 colors = [‘#9999ff‘, ‘#ff9999‘, ‘#7777aa‘, ‘#2442aa‘, ‘#dd5555‘] # 绘制饼图 plt.pie(km_stats.values, labels=labels, colors=colors, # 设置颜色 autopct=‘%.1f%%‘, # 设置百分比的格式,这里保留一位小数 counterclock=False, # 设置为顺时针方向显示图形 wedgeprops={‘linewidth‘: 1.5, ‘edgecolor‘: ‘green‘}, # 设置饼图内外边界的属性值 textprops={‘fontsize‘: 12, ‘color‘: ‘k‘} # 设置文本标签的属性值 ) # 添加图标题 plt.title(‘二手车行驶公里数分布(万公里)‘) # 显示图形 plt.show()
四、结论(10分)
1.经过对主题数据的分析与可视化,可以得到哪些结论?
在瓜子二手车网站中行驶5到10万公里里程的车所占比例最多为53.7%,车的里程数与二手价格成反比,瓜子二手车网站提供给用户的数据较多,有车型,行车价格,二手车价格,里程数,上牌日期等。
2.对本次程序设计任务完成的情况做一个简单的小结。
让我更加熟悉python的诸多爬取方法,让我认识到了BeautifulSoup以及matplotlib爬取的可靠性,应对瓜子二手车网站的防爬手段我也试过多种方法找到了用js混淆,根据发送的原始header和js混淆生成特定的cookie访问到网站进行爬取。
标签:data oat int sum 可靠性 art frame 发动机 日期
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/louis20161822/p/12072462.html