标签:argument empty 运行 command 脚本 pac sem equal i++
在项目开发中,经常碰到map转实体对象或者对象转map的场景,工作中,很多时候我们可能比较喜欢使用第三方jar包的API对他们进行转化,而且用起来也还算方便,比如像fastJson就可以轻松实现map和对象的互转,但这里,我想通过反射的方式对他们做转化,也算是对反射的学习和研究吧;
1、map转对象;
主要思路,将map中的key-value取出来,然后和给定的对象去匹配,为了使工具方法更具通用性,直接通过反射的方式将给定对象的属性获取到,然后调用反射相关的API和map中的key-value进行匹配即可,下面直接上代码,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
|
/** * 利用反射将map集合封装成bean对象 * * @param params * @param clazz * @return */ public static <T> T mapToBean(Map<String, Object> map, Class<?> clazz) throws Exception { Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); if (map != null && !map.isEmpty() && map.size() > 0) { for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : map.entrySet()) { String propertyName = entry.getKey(); // 属性名 Object value = entry.getValue(); // 属性值 String setMethodName = "set" + propertyName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + propertyName.substring(1); Field field = getClassField(clazz, propertyName); //获取和map的key匹配的属性名称 if (field == null){ continue; } Class<?> fieldTypeClass = field.getType(); value = convertValType(value, fieldTypeClass); try { clazz.getMethod(setMethodName, field.getType()).invoke(obj, value); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return (T) obj; } /** * 根据给定对象类匹配对象中的特定字段 * @param clazz * @param fieldName * @return */ private static Field getClassField(Class<?> clazz, String fieldName) { if (Object.class.getName().equals(clazz.getName())) { return null; } Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : declaredFields) { if (field.getName().equals(fieldName)) { return field; } } Class<?> superClass = clazz.getSuperclass(); //如果该类还有父类,将父类对象中的字段也取出 if (superClass != null) { //递归获取 return getClassField(superClass, fieldName); } return null; } /** * 将map的value值转为实体类中字段类型匹配的方法 * @param value * @param fieldTypeClass * @return */ private static Object convertValType(Object value, Class<?> fieldTypeClass) { Object retVal = null; if (Long.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName()) || long.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName())) { retVal = Long.parseLong(value.toString()); } else if (Integer.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName()) || int.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName())) { retVal = Integer.parseInt(value.toString()); } else if (Float.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName()) || float.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName())) { retVal = Float.parseFloat(value.toString()); } else if (Double.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName()) || double.class.getName().equals(fieldTypeClass.getName())) { retVal = Double.parseDouble(value.toString()); } else { retVal = value; } return retVal; } |
我们写一个测试方法来验证一下上述代码,我提前建好了一个实体类productInfo,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
public class ProductInfo { private Long id; private String name; private Double price; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Double price) { this.price = price; } public ProductInfo(Long id, String name, Double price) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.price = price; } public ProductInfo() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "ProductInfo [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; }} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>(); param.put("id", 12232); param.put("name", "banana"); param.put("price", 12.25); ProductInfo info = mapToBean(param, ProductInfo.class); System.out.println(info.getName()); } |
运行main函数,查看结果,可以看到控制台已经成功打印出结果,
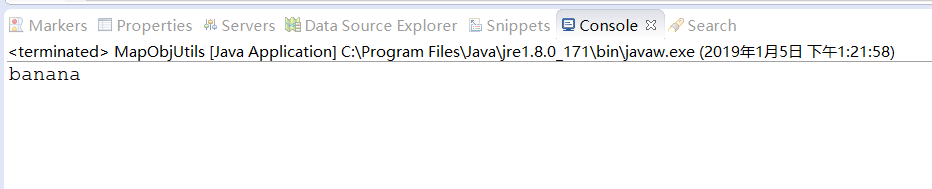
2、对象转map,
思路,同上述的分析类似,这不过这里需要反过来,给定一个待转化的实体类,通过反射,将实体类中的字段名称和字段值获取到,然后一一设置到map的key-value中,下面看代码,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
/** * 对象转map * @param obj * @return */ private static Map<String, Object> objToMap(Object obj) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Field[] fields = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); // 获取f对象对应类中的所有属性域 for (int i = 0, len = fields.length; i < len; i++) { String varName = fields[i].getName(); varName = varName.toLowerCase(); // 将key置为小写,默认为对象的属性 try { boolean accessFlag = fields[i].isAccessible(); // 获取原来的访问控制权限 fields[i].setAccessible(true); // 修改访问控制权限 Object o = fields[i].get(obj); // 获取在对象f中属性fields[i]对应的对象中的变量 if (o != null){ map.put(varName, o.toString()); } fields[i].setAccessible(accessFlag); // 恢复访问控制权限 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } return map; } |
下面写个测试方法,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>(); param.put("id", 12232); param.put("name", "banana"); param.put("price", 12.25); ProductInfo info = mapToBean(param, ProductInfo.class); System.out.println(info.getName()); System.out.println("---------------------"); Map<String, Object> map = objToMap(info); System.out.println("对象转map后的结果 : " + map); } |
运行,查看控制台的输出结果,说明已经成功转化,
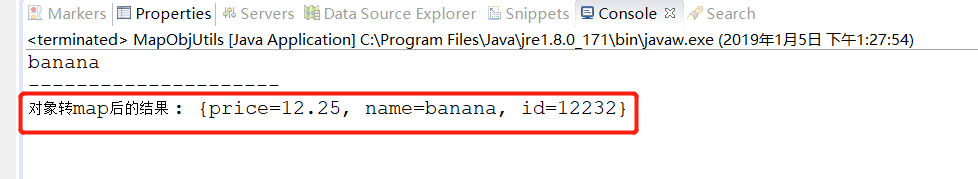
以上,就是map和对象之间实现互相转化的工具类,各位今后工作中如有需要可直接拿去使用,不足之处,敬请见谅哈!也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
https://blog.csdn.net/u011191463/article/details/60579191
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22596931/article/details/86637540
https://www.jb51.net/article/167715.htm
标签:argument empty 运行 command 脚本 pac sem equal i++
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/leijiangtao/p/12076110.html