CrawlSpider类
通过下面的命令可以快速创建 CrawlSpider模板 的代码:
scrapy genspider -t crawl tencent tencent.com
CrawSpider是Spider的派生类,Spider类的设计原则是只爬取start_url列表中的网页,而CrawlSpider类定义了一些规则(rule)来提供跟进link的方便的机制,从爬取的网页中获取link并继续爬取的工作更适合。
CrawSpider源码详细解析
class CrawlSpider(Spider): rules = () def __init__(self, *a, **kw): super(CrawlSpider, self).__init__(*a, **kw) self._compile_rules() #首先调用parse()来处理start_urls中返回的response对象 #parse()则将这些response对象传递给了_parse_response()函数处理,并设置回调函数为parse_start_url() #设置了跟进标志位True #parse将返回item和跟进了的Request对象 def parse(self, response): return self._parse_response(response, self.parse_start_url, cb_kwargs={}, follow=True) #处理start_url中返回的response,需要重写 def parse_start_url(self, response): return [] def process_results(self, response, results): return results #从response中抽取符合任一用户定义‘规则‘的链接,并构造成Resquest对象返回 def _requests_to_follow(self, response): if not isinstance(response, HtmlResponse): return seen = set() #抽取之内的所有链接,只要通过任意一个‘规则‘,即表示合法 for n, rule in enumerate(self._rules): links = [l for l in rule.link_extractor.extract_links(response) if l not in seen] #使用用户指定的process_links处理每个连接 if links and rule.process_links: links = rule.process_links(links) #将链接加入seen集合,为每个链接生成Request对象,并设置回调函数为_repsonse_downloaded() for link in links: seen.add(link) #构造Request对象,并将Rule规则中定义的回调函数作为这个Request对象的回调函数 r = Request(url=link.url, callback=self._response_downloaded) r.meta.update(rule=n, link_text=link.text) #对每个Request调用process_request()函数。该函数默认为indentify,即不做任何处理,直接返回该Request. yield rule.process_request(r) #处理通过rule提取出的连接,并返回item以及request def _response_downloaded(self, response): rule = self._rules[response.meta[‘rule‘]] return self._parse_response(response, rule.callback, rule.cb_kwargs, rule.follow) #解析response对象,会用callback解析处理他,并返回request或Item对象 def _parse_response(self, response, callback, cb_kwargs, follow=True): #首先判断是否设置了回调函数。(该回调函数可能是rule中的解析函数,也可能是 parse_start_url函数) #如果设置了回调函数(parse_start_url()),那么首先用parse_start_url()处理response对象, #然后再交给process_results处理。返回cb_res的一个列表 if callback: #如果是parse调用的,则会解析成Request对象 #如果是rule callback,则会解析成Item cb_res = callback(response, **cb_kwargs) or () cb_res = self.process_results(response, cb_res) for requests_or_item in iterate_spider_output(cb_res): yield requests_or_item #如果需要跟进,那么使用定义的Rule规则提取并返回这些Request对象 if follow and self._follow_links: #返回每个Request对象 for request_or_item in self._requests_to_follow(response): yield request_or_item def _compile_rules(self): def get_method(method): if callable(method): return method elif isinstance(method, basestring): return getattr(self, method, None) self._rules = [copy.copy(r) for r in self.rules] for rule in self._rules: rule.callback = get_method(rule.callback) rule.process_links = get_method(rule.process_links) rule.process_request = get_method(rule.process_request) def set_crawler(self, crawler): super(CrawlSpider, self).set_crawler(crawler) self._follow_links = crawler.settings.getbool(‘CRAWLSPIDER_FOLLOW_LINKS‘, True)
CrawlSpider继承于Spider类,除了继承过来的属性外(name、allow_domains),还提供了新的属性和方法:
LinkExtractors
Link Extractors 的目的很简单: 提取链接?
每个LinkExtractor有唯一的公共方法是 extract_links(),它接收一个 Response 对象,并返回一个 scrapy.link.Link 对象。
Link Extractors要实例化一次,并且 extract_links 方法会根据不同的 response 调用多次提取链接?
class scrapy.linkextractors.LinkExtractor( allow = (), deny = (), allow_domains = (), deny_domains = (), deny_extensions = None, restrict_xpaths = (), tags = (‘a‘,‘area‘), attrs = (‘href‘), canonicalize = True, unique = True, process_value = None )
主要参数:
-
allow:满足括号中“正则表达式”的值会被提取,如果为空,则全部匹配。 -
deny:与这个正则表达式(或正则表达式列表)不匹配的URL一定不提取。 -
allow_domains:会被提取的链接的domains。 -
deny_domains:一定不会被提取链接的domains。 -
restrict_xpaths:使用xpath表达式,和allow共同作用过滤链接
rules
在rules中包含一个或多个Rule对象,每个Rule对爬取网站的动作定义了特定操作。如果多个rule匹配了相同的链接,则根据规则在本集合中被定义的顺序,第一个会被使用。
class scrapy.spiders.Rule( link_extractor, callback = None, cb_kwargs = None, follow = None, process_links = None, process_request = None )
主要参数:
-
link_extractor:是一个Link Extractor对象,用于定义需要提取的链接。 -
callback: 从link_extractor中每获取到链接时,参数所指定的值作为回调函数,该回调函数接受一个response作为其第一个参数。注意:当编写爬虫规则时,避免使用parse作为回调函数。由于CrawlSpider使用parse方法来实现其逻辑,如果覆盖了 parse方法,crawl spider将会运行失败。
-
follow:是一个布尔(boolean)值,指定了根据该规则从response提取的链接是否需要跟进。 如果callback为None,follow 默认设置为True ,否则默认为False。 -
process_links:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用,从link_extractor中获取到链接列表时将会调用该函数。该方法主要用来过滤。 -
process_request:指定该spider中哪个的函数将会被调用, 该规则提取到每个request时都会调用该函数。 (用来过滤request)
CrawlSpider 版本写腾讯职位招聘

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy class TencentItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # 职位名 positionname = scrapy.Field() # 详情连接 positionlink = scrapy.Field() # 职位类别 positionType = scrapy.Field() # 招聘人数 peopleNum = scrapy.Field() # 工作地点 workLocation = scrapy.Field() # 发布时间 publishTime = scrapy.Field()

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import json class TencentPipeline(object): def __init__(self): self.filename = open("tencent.json", "w") def process_item(self, item, spider): text = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii = False) + ",\n" self.filename.write(text.encode("utf-8")) return item def close_spider(self, spider): self.filename.close()
tencent.py
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import scrapy # 导入CrawlSpider类和Rule from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule # 导入链接规则匹配类,用来提取符合规则的连接 from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor from TencentSpider.items import TencentItem class TencentSpider(CrawlSpider): name = "tencent" allow_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"] start_urls = ["http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"] # Response里链接的提取规则,返回的符合匹配规则的链接匹配对象的列表 pagelink = LinkExtractor(allow=("start=\d+")) rules = [ # 获取这个列表里的链接,依次发送请求,并且继续跟进,调用指定回调函数处理 Rule(pagelink, callback = "parseTencent", follow = True) ] # 指定的回调函数 def parseTencent(self, response): for each in response.xpath("//tr[@class=‘even‘] | //tr[@class=‘odd‘]"): item = TencentItem() # 职位名称 item[‘positionname‘] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/text()").extract()[0] # 详情连接 item[‘positionlink‘] = each.xpath("./td[1]/a/@href").extract()[0] # 职位类别 item[‘positionType‘] = each.xpath("./td[2]/text()").extract()[0] # 招聘人数 item[‘peopleNum‘] = each.xpath("./td[3]/text()").extract()[0] # 工作地点 item[‘workLocation‘] = each.xpath("./td[4]/text()").extract()[0] # 发布时间 item[‘publishTime‘] = each.xpath("./td[5]/text()").extract()[0] yield item
settings.py可以设置保存日志

通过在setting.py中进行以下设置可以被用来配置logging: LOG_ENABLED 默认: True,启用logging LOG_ENCODING 默认: ‘utf-8‘,logging使用的编码 LOG_FILE 默认: None,在当前目录里创建logging输出文件的文件名 LOG_LEVEL 默认: ‘DEBUG‘,log的最低级别 LOG_STDOUT 默认: False 如果为 True,进程所有的标准输出(及错误)将会被重定向到log中。例如,执行 print "hello" ,其将会在Scrapy log中显示。

Scrapy提供5层logging级别: CRITICAL - 严重错误(critical) ERROR - 一般错误(regular errors) WARNING - 警告信息(warning messages) INFO - 一般信息(informational messages) DEBUG - 调试信息(debugging messages)
# 保存日志信息的文件名 LOG_FILE = "tencentlog.log" # 保存日志等级,低于|等于此等级的信息都被保存 LOG_LEVEL = "DEBUG"
案例实战
爬取问政平台 “http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=” 投诉信息
每页的帖子
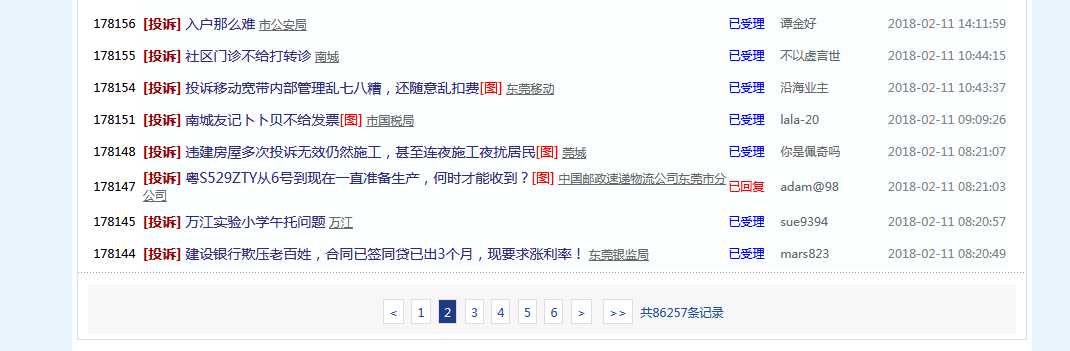
帖子里面的内容
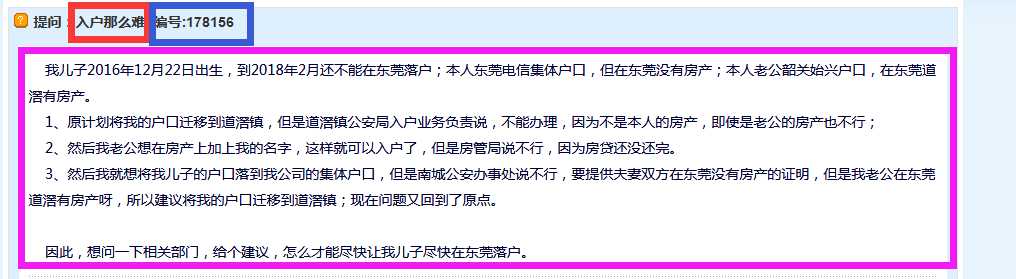
===《《《我们要爬取的是所有页的全部帖子的投诉主题、编号和内容===》》》
分别用Spider类和CrawlSpiders类两种方法实现

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy class NewdongguanItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # 标题 title = scrapy.Field() # 编号 number = scrapy.Field() # 内容 content = scrapy.Field() # 链接 url = scrapy.Field()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule from newdongguan.items import NewdongguanItem class DongdongSpider(CrawlSpider): name = ‘dongdong‘ allowed_domains = [‘wz.sun0769.com‘] start_urls = [‘http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=‘] # 每一页的匹配规则 pagelink = LinkExtractor(allow=("type=4")) # 每一页里的每个帖子的匹配规则 contentlink = LinkExtractor(allow=(r"/html/question/\d+/\d+.shtml")) rules = ( # 本案例的url被web服务器篡改,需要调用process_links来处理提取出来的url Rule(pagelink, process_links = "deal_links"), Rule(contentlink, callback = "parse_item") ) # links 是当前response里提取出来的链接列表 def deal_links(self, links): for each in links: each.url = each.url.replace("?","&").replace("Type&","Type?") return links def parse_item(self, response): item = NewdongguanItem() # 标题 item[‘title‘] = response.xpath(‘//div[contains(@class, "pagecenter p3")]//strong/text()‘).extract()[0] # 编号 item[‘number‘] = item[‘title‘].split(‘ ‘)[-1].split(":")[-1] # 内容,先使用有图片情况下的匹配规则,如果有内容,返回所有内容的列表集合 content = response.xpath(‘//div[@class="contentext"]/text()‘).extract() # 如果没有内容,则返回空列表,则使用无图片情况下的匹配规则 if len(content) == 0: content = response.xpath(‘//div[@class="c1 text14_2"]/text()‘).extract() item[‘content‘] = "".join(content).strip() else: item[‘content‘] = "".join(content).strip() # 链接 item[‘url‘] = response.url yield item

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import codecs import json class NewdongguanPipeline(object): def __init__(self): # 创建一个文件 self.filename = codecs.open("donggguan.json", "w", encoding = "utf-8") def process_item(self, item, spider): # 中文默认使用ascii码来存储,禁用后默认为Unicode字符串 content = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) + "\n" self.filename.write(content) return item def close_spider(self, spider): self.filename.close()
用Spider类写的方法
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from newdongguan.items import NewdongguanItem class DongdongSpider(scrapy.Spider): name = ‘xixi‘ allowed_domains = [‘wz.sun0769.com‘] url = ‘http://wz.sun0769.com/index.php/question/questionType?type=4&page=‘ offset = 0 start_urls = [url + str(offset)] def parse(self, response): # 每一页里的所有帖子的链接集合 links = response.xpath(‘//div[@class="greyframe"]/table//td/a[@class="news14"]/@href‘).extract() # 迭代取出集合里的链接 for link in links: # 提取列表里每个帖子的链接,发送请求放到请求队列里,并调用self.parse_item来处理 yield scrapy.Request(link, callback = self.parse_item) # 页面终止条件成立前,会一直自增offset的值,并发送新的页面请求,调用parse方法处理 if self.offset <= 71160: self.offset += 30 # 发送请求放到请求队列里,调用self.parse处理response yield scrapy.Request(self.url + str(self.offset), callback = self.parse) # 处理每个帖子的response内容 def parse_item(self, response): item = NewdongguanItem() # 标题 item[‘title‘] = response.xpath(‘//div[contains(@class, "pagecenter p3")]//strong/text()‘).extract()[0] # 编号 item[‘number‘] = item[‘title‘].split(‘ ‘)[-1].split(":")[-1] # 内容,先使用有图片情况下的匹配规则,如果有内容,返回所有内容的列表集合 content = response.xpath(‘//div[@class="contentext"]/text()‘).extract() # 如果没有内容,则返回空列表,则使用无图片情况下的匹配规则 if len(content) == 0: content = response.xpath(‘//div[@class="c1 text14_2"]/text()‘).extract() item[‘content‘] = "".join(content).strip() else: item[‘content‘] = "".join(content).strip() # 链接 item[‘url‘] = response.url # 交给管道 yield item
爬取的结果:

python爬虫入门(八)Scrapy框架之CrawlSpider类
标签:main 合规 rate 并发 匹配 ror 没有 原则 判断
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gaidy/p/12095778.html

