标签:列表 argument com def 地方 nbsp 计算 不包含 作品
1.对CD类的派生练习。基类CD类存储作者和作品号等信息,派生类Classic额外增加一格“主要作品”的信息。主函数使用拷贝构造函数、按引用传递参数的函数和指针来测试基类和派生类的功能。
注意继承类和基类的权限关系、初始化成员列表的使用。
class.h
#ifndef _CLASS_H_ #define _CLASS_H_ #include <iostream> using std::cin; using std::cout; class CD { private: char performers[20] = {}; //初始化为空,不然输出一堆烫 char label[20] = {}; int selections; double playtime; public: CD(const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x); //自定义构造函数 CD(const CD & d); //拷贝构造函数 CD(); //默认构造函数 virtual ~CD(); virtual void Report()const; virtual CD & operator = (const CD & d); }; class Classic :public CD { private: char collection[50] = {}; public: Classic(const char *c, const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x); Classic(); ~Classic(); void Report()const; Classic & operator = (const Classic & d); }; #endif
DefineClass.cpp
#include "class.h" CD::CD(const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x) { for (int i = 0; s1[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { performers[i] = s1[i]; } for (int i = 0; s2[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { label[i] = s2[i]; } selections = n; playtime = x; } CD::CD(const CD & d) { for (int i = 0; d.performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { performers[i] = d.performers[i]; } for (int i = 0; d.label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { label[i] = d.label[i]; } selections = d.selections; playtime = d.playtime; } CD::CD() { } CD::~CD() { } void CD::Report()const { cout << "Performers: "; for (int i = 0; performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << performers[i]; } cout << "\n"; cout << "Label: "; for (int i = 0; label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << label[i]; } cout << "\n"; cout << "Selections: " << selections << "\n"; cout << "Playtime: " << playtime << "\n"; } CD & CD::operator=(const CD & d) { for (int i = 0; d.performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { performers[i] = d.performers[i]; } for (int i = 0; d.label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { label[i] = d.label[i]; } selections = d.selections; playtime = d.playtime; return *this; } //derived class Classic::Classic(const char *c, const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x):CD(s1,s2,n,x) { for (int i = 0; c[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { collection[i] = c[i]; } } Classic::Classic() { } Classic::~Classic() { } void Classic::Report()const { CD::Report(); cout << "Collection: "; for (int i = 0; collection[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << collection[i]; } cout << "\n\n"; } Classic & Classic::operator = (const Classic & d) { CD::operator=(d); for (int i = 0; d.collection[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { collection[i] = d.collection[i]; } return *this; }
main.cpp
#include "class.h" void Bravo(const CD & disk); int main() { CD c1("Beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5); Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17); CD *pcd = &c1; cout << "Using Object directly:\n"; c1.Report(); c2.Report(); cout << "Using type cd * pointer to objects:\n"; pcd->Report(); pcd = &c2; pcd->Report(); cout << "Calling a function with a cd reference argument:\n"; Bravo(c1); Bravo(c2); cout << "Testing assignment:\n"; Classic copy; copy = c2; copy.Report(); //pause cin.get(); return 0; } void Bravo(const CD & disk) { disk.Report(); }
2.以上题为基础。存储的字符数组用使用动态分配内存。
我初始化对象的时候把两个字符成员都设为了空指针,做题的过程中,了解到了空指针不能被赋值。其它需要注意的地方见注释。
ClassCD.h
#ifndef _CLASSCD_ #define _CLASSCD_ #include <iostream> using std::cout; using std::cin; //Base Class Declare class CD { private: char *performers = nullptr; char *label = nullptr; int selections; double playtime; public: CD(const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x); //自定义构造函数 CD(const CD & d); //拷贝构造函数 CD(); //默认构造函数 virtual ~CD(); virtual void Report()const; virtual CD & operator = (const CD & d); }; //Base Class Define CD::CD(const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x) { //根据s1和s2的长度分配内存 //strlen()计算的长度不包含终止符‘\0‘ //为了不影响report()的执行,分配的内存长度+1,使其包含‘\0‘ performers = new char[strlen(s1)+1]; for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(s1)+1); i++) { performers[i] = s1[i]; } label = new char[strlen(s2)+1]; for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(s2)+1); i++) { label[i] = s2[i]; } selections = n; playtime = x; } CD::CD() { selections = 0; playtime = 0; } CD::CD(const CD & d) { int count; //对象分配内存的成员不是空指针才会赋值,防止内存访问混乱 if (d.performers != nullptr) { //获取等号右边的类里面分配的长度 for (count = 0; d.performers[count] != ‘\0‘; count++) { ; } //根据它的长度来分配自身的长度,加上‘\0‘一位 performers = new char[count + 1]; //给自身成员变量赋值,取到终止符后停止 for (int i = 0; d.performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { performers[i] = d.performers[i]; if (d.performers[i + 1] == ‘\0‘) { performers[i + 1] = ‘\0‘; break; } } } //以下同理 if (d.label != nullptr) { for (count = 0; d.label[count] != ‘\0‘; count++) { ; } label = new char[count + 1]; for (int i = 0; d.label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { label[i] = d.label[i]; if (d.label[i + 1] == ‘\0‘) { label[i + 1] = ‘\0‘; break; } } } selections = d.selections; playtime = d.playtime; } CD::~CD() { //是空指针,说明从未分配过内存,不需要释放 //不是空指针,说明分配了内存,需要释放 if (performers != nullptr) { delete[] performers; } if (label != nullptr) { delete[] label; } } void CD::Report()const { //对象分配内存的成员不是空指针才会打印,防止内存访问混乱 cout << "Performers: "; if (performers != nullptr) { for (int i = 0; performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << performers[i]; } } cout << "\n"; cout << "Label: "; if (label != nullptr) { for (int i = 0; label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << label[i]; } } cout << "\n"; cout << "Selections: " << selections << "\n"; cout << "Playtime: " << playtime << "\n"; } CD & CD::operator=(const CD & d) { int count; //对象分配内存的成员不是空指针才会赋值,防止内存访问混乱 if (d.performers != nullptr) { //获取等号右边的类里面分配的长度 for (count = 0; d.performers[count] != ‘\0‘; count++) { ; } //根据它的长度来分配自身的长度,加上‘\0‘一位 performers = new char[count + 1]; //给自身成员变量赋值,取到终止符后停止 for (int i = 0; d.performers[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { performers[i] = d.performers[i]; if (d.performers[i + 1] == ‘\0‘) { performers[i + 1] = ‘\0‘; break; } } } //以下同理 if (d.label != nullptr) { for (count = 0; d.label[count] != ‘\0‘; count++) { ; } label = new char[count + 1]; for (int i = 0; d.label[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { label[i] = d.label[i]; if (d.label[i + 1] == ‘\0‘) { label[i + 1] = ‘\0‘; break; } } } selections = d.selections; playtime = d.playtime; return *this; } //Derived Class Declare class Classic :public CD { private: char *collection = nullptr; public: Classic(const char *c, const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x); Classic(); ~Classic(); void Report()const; Classic & operator = (const Classic & d); }; //Derived Class Define Classic::Classic(const char *c, const char *s1, const char*s2, int n, double x) :CD(s1, s2, n, x) { collection = new char[strlen(c) + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(c) + 1); i++) { collection[i] = c[i]; } } Classic::Classic() { } Classic::~Classic() { if (collection != nullptr) { delete[] collection; } } void Classic::Report()const { CD::Report(); cout << "Collection: "; if (collection != nullptr) { for (int i = 0; collection[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << collection[i]; } } cout << "\n\n"; } Classic & Classic::operator = (const Classic & d) { CD::operator=(d); int count; if (d.collection != nullptr) { for (count = 0; d.collection[count] != ‘\0‘; count++) { ; } collection = new char[count + 1]; for (int i = 0; d.collection[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { collection[i] = d.collection[i]; if (d.collection[i + 1] == ‘\0‘) { collection[i + 1] = ‘\0‘; break; } } } return *this; } #endif
main.cpp
#include "ClassCD.h" void Bravo(const CD & disk); int main() { CD c1("Beatles", "Capitol", 14, 35.5); Classic c2 = Classic("Piano Sonata in B flat, Fantasia in C", "Alfred Brendel", "Philips", 2, 57.17); CD *pcd = &c1; cout << "Using Object directly:\n"; c1.Report(); c2.Report(); cout << "Using type cd * pointer to objects:\n"; pcd->Report(); pcd = &c2; pcd->Report(); cout << "Calling a function with a cd reference argument:\n"; Bravo(c1); Bravo(c2); cout << "Testing assignment:\n"; Classic copy; copy = c2; copy.Report(); //pause cin.get(); return 0; } void Bravo(const CD & disk) { disk.Report(); }
3.不想使用原题所以没用,目的是练习抽象基类的继承。
所谓抽象基类,就是把定义的基类之中的虚成员函数声明为纯虚的(virtual修饰的函数后面加个 = 0),那么这个基类就只能用于继承,而不能实例化。一旦在代码里试图去实例化,编译之前就会提示“不允许使用抽象类型XXX的对象”。
抽象基类是抽象出一系列对象的共性的做法,方便派生出许多相似的对象。 需要注意,基类定义的纯虚函数不给出定义,而由所有派生类给出自己的定义。
下面是自己简单的练习。定义一个MovingObject的抽象基类,nowwhere()显示当前目标的位置,set_speed()设定目标的速度。从MovingObject派生出Car和Plane对象,各自的构造函数、析构函数、nowwhere()和set_speed()方法都不同。Car类会在坐标轴上按上下左右四个方向移动,Plane类指定一个目标地点,用动态数组的方式存储和打印该地点。
class.h
#ifndef _CLASS_H_ #define _CLASS_H_ #include <iostream> #include <string> using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::string; /* Abstract Base Class */ class MovingObject { protected: double x; double y; double v; string name; public: MovingObject(); virtual ~MovingObject(); virtual void nowwhere() = 0; //pure virtual function virtual void set_speed(unsigned int vv) = 0; //pure virtual function }; MovingObject::MovingObject() { } MovingObject::~MovingObject() { } /* Derived Class A */ class Car :public MovingObject { public: enum car_direction { UP = 0, DOWN, LEFT, RIGHT, RESET }drive_to; private: public: Car(); Car(const double xx, const double yy); ~Car(); void move(car_direction drive_to,double t); void nowwhere(); void set_speed(unsigned int vv); }; Car::Car() { name = "car"; x = 0; y = 0; v = 30; cout << "A new car constructed.\n"; } Car::Car(const double xx, const double yy) { name = "car"; x = xx; y = yy; v = 30; cout << "A new car constructed.\n"; } Car::~Car() { cout << "Car decontructed\n"; } void Car::move(car_direction drive_to = RESET,double t = 0) { switch (drive_to) { case(UP): { cout << "The car‘s moving up, " << "with " << v << " m/s in " << t << " s.\n"; y = y + v * t; break; } case(DOWN): { cout << "The car‘s moving down, " << "with " << v << " m/s in " << t << " s.\n"; y = y - v * t; break; } case(LEFT): { cout << "The car‘s moving left, " << "with " << v << " m/s in " << t << " s.\n"; x = x - v * t; break; } case(RIGHT): { cout << "The car‘s moving right, " << "with " << v << " m/s in " << t << " s.\n"; x = x + v * t; break; } case(RESET): { cout << "The car‘s at (0,0).\n"; x = 0; y = 0; v = 1; break; } default: { break; } } } void Car::nowwhere() { cout << name << " is at (" << x << "," << y << ").\n"; } void Car::set_speed(unsigned int vv) { v = vv; } /* Derived Class B */ class Plane:public MovingObject { private: char *flywhere; public: Plane(); ~Plane(); void nowwhere(); void set_speed(unsigned int vv); }; Plane::Plane() { flywhere = new char[20]; char wishplace[20] = {}; v = 180; cout << "A plane just arrived.\n"; cout << "Assign one destination you wish: "; cin >> wishplace; for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(wishplace)+1); i++) { flywhere[i] = wishplace[i]; } } Plane::~Plane() { cout << "Plane deconstructed.\n"; delete[] flywhere; } void Plane::nowwhere() { cout << "The plane‘s flying at " << v << " m/s.\n"; cout << "Finally it arrived at "; for (int i = 0; flywhere[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << flywhere[i]; } cout << ".\n"; } void Plane::set_speed(unsigned int vv) { cout << "Changing speed to (150~250): "; if ((vv >= 150) && (vv <= 250)) { v = vv; } else { cout << "Invalid speed! (Current: " << v << " m/s.)"; } } #endif
main.cpp
#include "Class.h" int main() { Car car1; car1.move(Car::UP,10); car1.nowwhere(); Plane plane1; plane1.set_speed(180); plane1.nowwhere(); //pause cin.get(); cin.get(); return 0; }
输出结果:
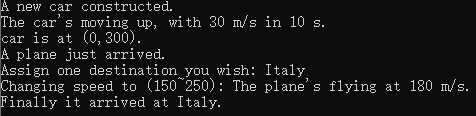
4.派生练习。定义存储酒相关信息的类和派生类。
对原题问题的回答:
(a)见代码。
(b)Port有所有默认参数的构造函数和默认构造函数冲突了。
(c)运算符=重载的函数应用的对象算不同的类型,运算符<<重载的函数是友元函数,友元函数不归属于类,也不能被继承,所以不需要声明为虚。
(d)见代码。
Class.h
#ifndef _CLASS_H_ #define _CLASS_H_ #include <iostream> using std::ostream; using std::cout; using std::cin; //Base Class class Port { private: char * brand; char style[20]; //tawny,ruby,vintage... int bottles; public: Port(const char *br, const char *st, int b); //重新定义,去掉默认参数,防止与默认构造函数重复 Port(); //创建的默认构造函数 Port(const Port & p); virtual ~Port() { delete[]brand; } Port & operator = (const Port & p); Port & operator += (int b); //add bottles Port & operator -= (int b); int BottleCount()const { return bottles; } virtual void show()const; friend ostream & operator << (ostream & os, const Port & p); }; Port::Port(const char *br, const char *st, int b = 0) { brand = new char[strlen(br) + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(br) + 1); i++) { brand[i] = br[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(st) + 1); i++) { style[i] = st[i]; } bottles = b; } Port::Port() { brand = new char[20]; brand[0] = ‘\0‘; style[0] = ‘\0‘; bottles = 0; } Port::Port(const Port & p) { for (int i = 0; i<strlen(p.brand)+1; i++) { brand[i] = p.brand[i]; } for (int i = 0; p.style[i]!=‘\0‘; i++) { style[i] = p.style[i]; } bottles = p.bottles; } Port & Port::operator = (const Port & p) { for (int i = 0; i<strlen(p.brand)+1; i++) { brand[i] = p.brand[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < strlen(p.style) + 1; i++) { style[i] = p.style[i]; } bottles = p.bottles; return *this; } Port & Port::operator += (int b) { bottles += b; return *this; } Port & Port::operator -= (int b) { bottles -= b; return *this; } void Port::show()const { cout << "Brand:"; for (int i = 0; brand[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << brand[i]; } cout << "\n"; cout << "Kind:"; for (int i = 0; style[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << style[i]; } cout << "\n"; cout << "Bottles:" << bottles << "\n"; } ostream & operator << (ostream & os, const Port & p) { os << "Brand:"; for (int i = 0; p.brand[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << p.brand[i]; } os << "\n"; os << "Kind:"; for (int i = 0; p.style[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { os << p.style[i]; } os << "\n"; os << "Bottles:" << p.bottles << "\n"; return os; } //Derived Class class VintagePort :public Port { private: char *nickname; int year; public: VintagePort(); VintagePort(const char * br, int b, const char *nn, int y); VintagePort(VintagePort & vp); ~VintagePort() { delete[]nickname; } VintagePort & operator = (const VintagePort & vp); void show() const; friend ostream & operator << (ostream & os, const VintagePort & vp); }; VintagePort::VintagePort() { nickname = new char[20]; nickname[0] = ‘\0‘; year = 0; } VintagePort::VintagePort(const char * br, int b, const char *nn, int y):Port(br,"none",b) { nickname = new char[strlen(nn) + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < strlen(nn) + 1; i++) { nickname[i] = nn[i]; } year = y; } VintagePort::VintagePort(VintagePort & vp) { for (int i = 0; i < strlen(vp.nickname) + 1; i++) { nickname[i] = vp.nickname[i]; } year = vp.year; } void VintagePort::show()const { Port::show(); cout << "Nickname:"; for (int i = 0; nickname[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { cout << nickname[i]; } cout << "\n"; cout << "Year:" << year; cout << "\n"; } VintagePort & VintagePort::operator = (const VintagePort & vp) { Port::operator=(vp); for (int i = 0; i < strlen(vp.nickname) + 1; i++) { nickname[i] = vp.nickname[i]; } year = vp.year; return *this; } ostream & operator << (ostream & os, const VintagePort & vp) { cout << "Nickname:"; for (int i = 0; vp.nickname[i] != ‘\0‘; i++) { os << vp.nickname[i]; } os << "\n"; os << "Year:" << vp.year; os << "\n"; return os; } #endif
main.cpp
#include "Class.h" int main() { cout << "-- p1 using default constructor -- \n"; Port p1; p1.show(); cout << "-- p2 using custom constructor -- \n"; Port p2("Gallo", "vintage", 20); p2.show(); cout << "-- p2 add 20 bottles -- \n"; p2 += 20; p2.show(); cout << "-- copy p2 -> p1 -- \n"; p1 = p2; p1.show(); cout << "-- cout << p1 -- \n"; cout << p1; cout << "-- vp1 using default constructor -- \n"; VintagePort vp1; vp1.show(); cout << "-- vp2 using custom constructor -- \n"; VintagePort vp2("Ruby", 10, "pussy", 1998); vp2.show(); cout << "-- copy vp2 -> vp1 -- \n"; p1 = p2; vp1 = vp2; vp1.show(); cout << "-- copy p2 -> p1 -- \n"; p1 = p2; cout << vp2; cout << "-- cout << vp1 -- \n"; cout << vp1; //pause cin.get(); return 0; }
标签:列表 argument com def 地方 nbsp 计算 不包含 作品
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/banmei-brandy/p/12005387.html