标签:bst 数组 eth http end string tin print mamicode
概念:集合是java中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据。
集合和数组有什么区别:
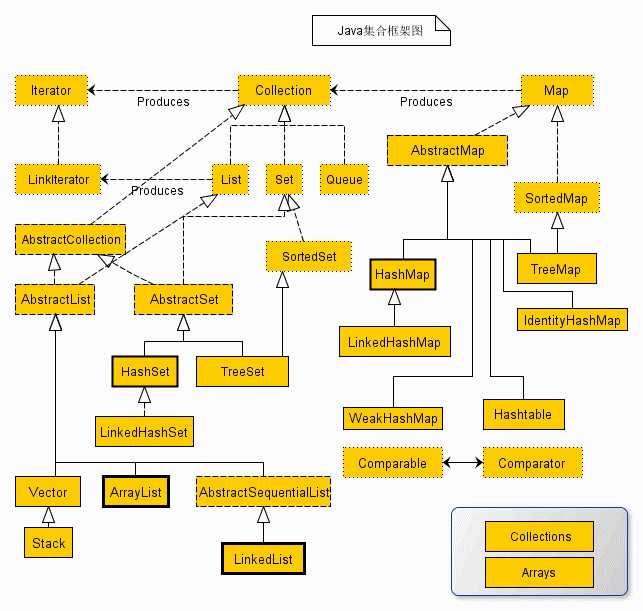
Collection接口:定义的是所有单列集合中共性的方法,所有单列集合都可以使用共性方法,没有带索引的方法
1 Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>(); 2 System.out.println(coll); //[] 3 4 coll.add("s1"); 5 coll.add("s2"); 6 coll.add("s3"); 7 coll.add("s4"); 8 coll.remove("s1"); 9 10 System.out.println(coll.isEmpty()); //false 11 System.out.println(coll.contains("s2")); //true 12 System.out.println(coll.size()); //3 13 System.out.println(coll); //[s2, s3, s4] 14 15 Object[] arr = coll.toArray(); 16 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 17 System.out.print(arr[i] + ","); //s2,s3,s4, 18 } 19 System.out.println(); 20 21 coll.clear(); 22 System.out.println(coll.size()); //0
两个常用方法:
Iterator迭代器我们无法正常使用,需要使用Iterator接口的实现类,Collection接口中iterator()方法返回迭代器对象的实现类Iterator<E> iterator()。
迭代器使用步骤:
1 Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator(); 2 3 while (it.hasNext()){ 4 System.out.println(it.next()); 5 }
JDK1.5之后出现的新特性,所有的单列集合都可以使用增强for循环
格式:
for(集合/数组的数据类型 变量名:集合名/数组名){
}
1 for (Object s : arr 2 ) { 3 System.out.println(s); 4 } 5 6 for (String s : coll 7 ) { 8 System.out.println(s); 9 }
泛型类:
语法:修饰符 class 类名<代表泛型的变量>{ }
1 class TestClass<E>{ 2 private E name; 3 4 public E getName(){ 5 return name; 6 } 7 8 public void setName(E name){ 9 this.name = name; 10 } 11 }
泛型方法:
语法:修饰符 <代表泛型的变量> 返回值类型 方法名(参数){ }
1 class TestMethod{ 2 public <E> void show1(E e){ 3 System.out.println(e.getClass()); 4 } 5 6 public <E> E show2(E e){ 7 return e; 8 } 9 10 }
泛型接口:
语法:修饰符 interface 接口名<代表泛型的变量>{ }
1 interface TestInterface<E>{ 2 3 public abstract void add(E e); 4 5 public abstract E getE(); 6 }
泛型通配符:
1 public static void testExtends(Collection<? extends Number> coll) { 2 System.out.println("coll中的元素只能是Number或Number的子类"); 3 } 4 5 public static void testSuper(Collection<? super Number> coll) { 6 System.out.println("coll中的元素只能是Number或Number的父类"); 7 } 8 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 Collection<Integer> coll1 = new ArrayList<>(); 13 Collection<Number> coll2 = new ArrayList<>(); 14 Collection<Object> coll3 = new ArrayList<>(); 15 16 testExtends(coll1); 17 testExtends(coll2); 18 testSuper(coll2); 19 testSuper(coll3); 20 21 }
标签:bst 数组 eth http end string tin print mamicode
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhihaospace/p/12116159.html