numpy 模块
numpy 模块主要用来做数据分析,对numpy数组 进行科学运算
主要方法和常用属性,都是用numpy 生成的对象.出来的
import numpy as np
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| T | 数组的转置,行和列一一对应,重构,每行2个元素 |
| dtype | 数组元素的数据类型(int32 和 float64) |
| size | 数组元素的个数 |
| ndim | 数组的维数 |
| shape | 数组的维度大小(有几行几列) |
| astype | 数据类型转换 |
| 常用方法 | 描述 |
| 元素切分 | [:,:] 表示行和列 |
| 逻辑取值 | 取出用numpy生成的数组对象 > 4的元素 |
| 赋值 | 取出用numpy生成的数组对象的索引值 = 0 |
| 数组横向合并 | 行和行合并,列和列合并 |
| 数组垂直合并 | 相当于list update,直接添加元素 |
| 数组函数 | 描述 |
| np.array() | 将列表转换为数组,可选择是否制定dtype |
| np.ones() | 传入行数和列数,值都为1 |
| np.zeros() | 传入行数和列数,值都为0 |
| np.eye() | 输入行数和列数,对角值为1 |
| np.arange() | 和列表的range方法一样,支持浮点数 |
| np.linspace() | 类似arange(),第三个参数为数组长度 |
| np.empty() | 创建一个元素全随机的数组 |
| np.reshape() | 重塑形状 |
| 数组运算 | 与数组函数联用 +-*/ 数字 |
| 生成随机数(常用) | np.random.rand(x,y) |
| np.random.random(x,y) | |
| np.random.choice(x,y) | |
| np.random.shuffle(x,y) | |
| numpy数学 统计方法 | 描述 |
| sum | 求和 |
| cumsum | 累加求和 |
| mean | 求平均数 |
| std | 求标准差 |
| var | 求方差 |
| min | 求最小值 |
| max | 求最大值 |
| argmin | 求最小值索引 |
| argmax | 求最大值索引 |
| sort | 排序 |
以下代码具体解释
lt1 = [1,2,3]
lt2 = [4,5,6]
lt = []
# 如果我们想要对这两个列表内数据相乘,我们可以用for循环
for i in range(len(lt1)):
lt.append(lt1[i] * lt2[i])
print(lt)
import numpy as np
# 利用numpy 进行矩阵计算 更方便
arr1 = np.array([1,2,3])
arr2 = np.array([4,5,6])
print(arr1 * arr2)
## [ 4 10 18]
# numpy 创建 numpy 数组 --》 可变的数据类型
# 一维数组 通常不使用,创建的数组没有,
arr = np.array([1,2,3])
print(arr)
# [1 2 3]
# 二维数组
arr = np.array([
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
])
print(arr)
# [[1 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
# 三维数组 通常不使用
arr = np.array([
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
])
print(arr)
# [[1 2 3]
# [4 5 6]
# [7 8 9]]
# numpy 数组的属性 特性
arr = np.array([
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
])
# T数组的转置,行列互换
print(arr, "\n",arr.T)
# [[1 4]
# [2 5]
# [3 6]]
# dtype 数组元素的数据类型,
# numpy数组是属于python解释器的,
# int32 float64 属于numpy数组
print(arr.dtype)
# int32
# size 数组元素的个数
print(arr.size)
# 6
# ndim 数据的维数
print(arr.ndim)
# 2
# shape 数据的纬度大小(以元组形式)
print(arr.shape)
# (2, 3)
# astype 类型转换 为int32
arr = arr.astype(np.float64)
print(arr)
# [[1. 2. 3.]
# [4. 5. 6.]]
# 切片numpy数组
arr = np.array([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
])
print(arr[:,:]) # :行,:列
# [[1 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
print(arr[0,0])
# 1
print(arr[1,2])
# 6
print(arr[:,-2:])
# [[2 3]
# [5 6]]
# 逻辑取值
print(arr[arr > 4])
# [[2 3]
# [5 6]]
# [5 6]
# 赋值
arr[0,0] = 0
print(arr)
# [[0 2 3]
# [4 5 6]]
# 数组合并
arr1 = np.array([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
])
arr2 = np.array([
[7, 8, 9],
[‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘]
])
# 横向合并
print(np.hstack((arr1,arr2)))
# [[‘1‘ ‘2‘ ‘3‘ ‘7‘ ‘8‘ ‘9‘]
# [‘4‘ ‘5‘ ‘6‘ ‘a‘ ‘b‘ ‘c‘]]
# 垂直合并
print(np.vstack((arr1,arr2)))
# [[‘1‘ ‘2‘ ‘3‘]
# [‘4‘ ‘5‘ ‘6‘]
# [‘7‘ ‘8‘ ‘9‘]
# [‘a‘ ‘b‘ ‘c‘]]
# 默认以列合并 #axis = 0 0表示列,1表示行
print(np.concatenate((arr1,arr2),axis=1))
# [[‘1‘ ‘2‘ ‘3‘ ‘7‘ ‘8‘ ‘9‘]
# [‘4‘ ‘5‘ ‘6‘ ‘a‘ ‘b‘ ‘c‘]]
# 通过函数创建numpy数组
print(np.ones((2,3)))
# [[1. 1. 1.]
# [1. 1. 1.]]
print(np.zeros((2,3)))
# [[0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0.]]
print(np.eye(3,3))
# [0. 1. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1.]]
print(np.linspace(1,100,10))
# [ 1. 12. 23. 34. 45. 56. 67. 78. 89. 100.]
print(np.arange(2,10))
# [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
# 重构形状
arr1 = np.zeros((2,6)) #
print(arr1.reshape((3,4))) # 重构形状必须相乘的 相等
# [[0. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 0. 0.]]
# numpy 数组运算
# +-*/
arr = np.ones((3,4)) * 4
print(arr)
# [[4. 4. 4. 4.]
# [4. 4. 4. 4.]
# [4. 4. 4. 4.]]
arr = np.ones((3,4)) + 4
print(arr)
# [[5. 5. 5. 5.]
# [5. 5. 5. 5.]
# [5. 5. 5. 5.]]
# numpy 数组运算函数 了解——————-
print(np.sin(arr))
# [[-0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427]
# [-0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427]
# [-0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427 -0.95892427]]
# 矩阵运算 -- 点乘
arr1 = np.array([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
])
arr2 = np.array([
[1, 2],
[4, 5],
[6, 7]
])
print(np.dot(arr1,arr2))
# [[27 33]
# [60 75]]
# 求逆
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [9, 8, 9]])
print(np.linalg.inv(arr))
# [[ 0.5 -1. 0.5 ]
# [-3. 3. -1. ]
# [ 2.16666667 -1.66666667 0.5 ]]
# numpy 数组数学和统计方法
arr = np.array([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
])
print(np.sum(arr[:,:]))
# 21
# 生成随机数
print(np.random.rand(3,4))
# [[0.76654824 0.23510842 0.79989748 0.93094884]
# [0.97155472 0.29956374 0.27754847 0.91103403]
# [0.43714323 0.7549109 0.14547903 0.20511579]]
print(np.random.random((3,4)))
# [[0.91673193 0.15218486 0.32976182 0.41812734]
# [0.33360061 0.20190749 0.48689467 0.46679115]
# [0.12490532 0.50441629 0.95525997 0.5402791 ]]
# 针对一维 随机选择数字
print(np.random.choice([1,2,3],1))
# [1]
# 追对某一范围
print(np.random.randint(1,100,(3,4)))
# [[33 40 93 18]
# [80 65 64 51]
# [66 6 83 10]]
matplotlib 模块
matplotlib 模块 就是用来画图的
# 条形图
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
# 设置字体,不然画出来会乱码
font = FontProperties(fname=r"C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc")
# 设置背景
plt.style.use("ggplot")
# 定义 行 列 信息
clas = ["3班","4班","5班","6班"]
students = [50,55,45,60]
clas_index = range(len(clas))
# 开始画
plt.bar(clas_index,students,color="darkblue")
plt.xlabel("学生",FontProperties=font)
plt.xlabel("学生人数",FontProperties=font)
plt.title("班级-学生人数",FontProperties=font,Fontsize=25,fontweight=20)
plt.xticks(clas_index,clas,FontProperties=font)
# 展示
plt.show()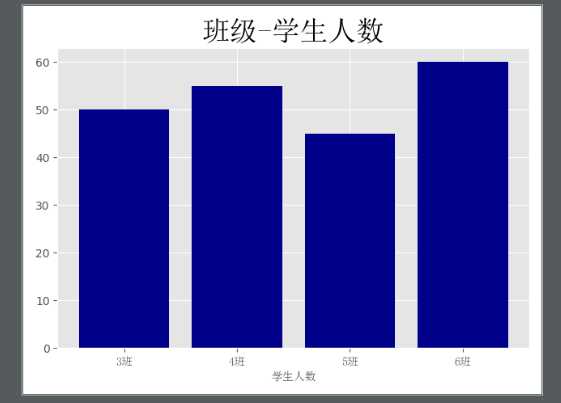
# 直方图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
# 设置字体,不然画出来会乱码
font = FontProperties(fname=r"C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc")
plt.style.use("ggplot")
# 生成随机数对象
x1 = np.random.randn(10000)
x2 = np.random.randn(10000)
# 生成画布
fig = plt.figure()
# 每行每列
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
ax1.hist(x1,bins=50,color="darkblue")
ax2.hist(x2,bins=50,color="y")
fig.suptitle("两个正太分布",FontProperties=font,fontsize=20)
ax1.set_title("x1的正态分布",FontProperties=font)
ax2.set_title("x2的正态分布",FontProperties=font)
# 展示
plt.show()
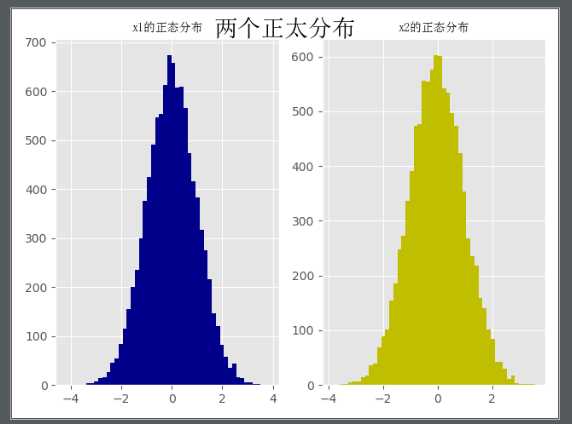
# 折线图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
# 设置字体,不然画出来会乱码
font = FontProperties(fname=r"C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc")
plt.style.use("ggplot")
np.random.seed(10)
x1 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x2 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x3 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
x4 = np.random.randn(40).cumsum()
plt.plot(x1,color="r",linestyle="-",marker="o",label="红圆线")
plt.plot(x2,color="y",linestyle="--",marker="*",label="黄虚线")
plt.plot(x3,color="b",linestyle="-.",marker="s",label="蓝方线")
plt.plot(x4,color="black",linestyle=":",marker="s",label="黑方线")
plt.legend(loc="best",prop=font)
# 展示
plt.show()
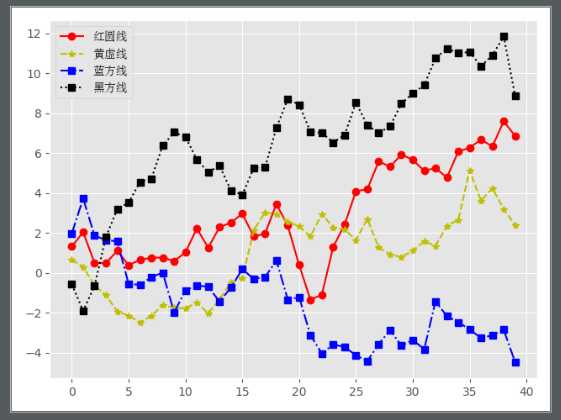
# 散点图 + 直线图
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 约定俗成
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties # 修改字体
# 设置字体,不然画出来会乱码
font = FontProperties(fname=‘C:\Windows\Fonts\simsun.ttc‘)
plt.style.use(‘ggplot‘)
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
x = np.arange(20)
y = x ** 2
x2 = np.arange(20)
y2 = x2 ** 2
ax1.scatter(x,y,color="r",label="红")
ax2.scatter(x2,y2,color="b",label="蓝")
ax1.plot(x,y)
ax2.plot(x2,y2)
fig.suptitle("两张图",FontProperties=font,fontsize=15)
ax1.set_title("散点图",FontProperties=font)
ax2.set_title("折线图",FontProperties=font)
ax1.legend(prop=font)
# 展示
plt.show()
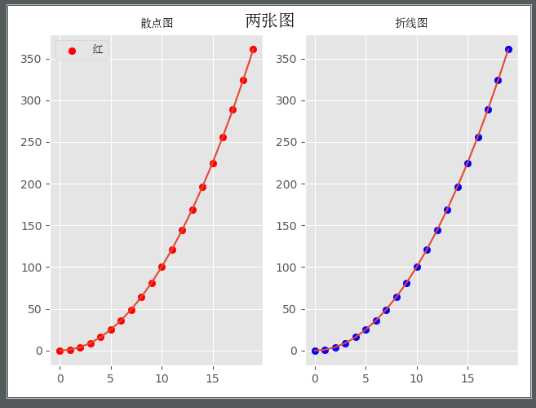
pandas 模块
pandas 模块 操作excel/json/sql/ini/csv文件的
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(10)
# 生成6个月份
index = pd.date_range("2019-01-01",periods=6,freq="M")
print(index)
columns = ["c1","c2","c3","c4"]
# 生成随机数
val = np.random.randn(6,4)
df = pd.DataFrame(index=index,columns=columns,data=val)
print(df)
# c1 c2 c3 c4
# 2019-01-31 1.331587 0.715279 -1.545400 -0.008384
# 2019-02-28 0.621336 -0.720086 0.265512 0.108549
# 2019-03-31 0.004291 -0.174600 0.433026 1.203037
# 2019-04-30 -0.965066 1.028274 0.228630 0.445138
# 2019-05-31 -1.136602 0.135137 1.484537 -1.079805
# 2019-06-30 -1.977728 -1.743372 0.266070 2.384967
# 保存成 xlsx 文件
df.to_excel("date_c.xlsx")
# 读出文件
df = pd.read_excel("date_c.xlsx",index_col=[0])
print(df)
# c1 c2 c3 c4
# 2019-01-31 1.331587 0.715279 -1.545400 -0.008384
# 2019-02-28 0.621336 -0.720086 0.265512 0.108549
# 2019-03-31 0.004291 -0.174600 0.433026 1.203037
# 2019-04-30 -0.965066 1.028274 0.228630 0.445138
# 2019-05-31 -1.136602 0.135137 1.484537 -1.079805
# 2019-06-30 -1.977728 -1.743372 0.266070 2.384967
###############
print(df.index)
print(df.columns)
print(df.values)
print(df[[‘c1‘, ‘c2‘]])
# 按照index取值
# print(df[‘2019-01-31‘])
print(df.loc[‘2019-01-31‘])
print(df.loc[‘2019-01-31‘:‘2019-05-31‘])
# 按照values取值
print(df)
print(df.iloc[0, 0])
df.iloc[0, :] = 0
print(df)