标签:col cells 字母转 name 字母 range ace load log
我们在python中引入openpyxl模块来操控excel文件。一个以.xlsx为扩张名的excel文件打开后叫工作簿workbook,每个工作簿可以包括多张表单worksheet,正在操作的这张表单被认为是活跃的active sheet。每张表单有行和列,行号1、2、3…,列号A、B、C...。在某一个特定行和特定列的小格子叫单元格cell。
python程序从excel文件中读数据基本遵循以下步骤:
1、import openpyxl
2、调用openpyxl模块下的load_workbook(‘你的文件名.xlsx’)函数打开excel文件,得到一个工作簿(workbook)对象wb
3、通过wb.active或wb的方法函数get_sheet_by_name(‘你想要访问的表单名称’)得到表单对象ws
4、通过索引获取单元格:ws[‘B2’]
通过表单的方法函数cell()获取单元格:ws.cell(row=1, column=2)
通过单元格的属性value,row,column,coordinate对单元格进行多方向立体式访问
5、行对象ws[10],列对象[‘C’],行切片ws[5:10]、列切片ws[‘C:D’],单元格左上角和右下角左边共同划定表单指定区域ws[‘A1‘:‘C3‘]
6、ws.max_row和ws.max_column给出数据用到的最大行和列
7、from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter, column_index_from_string引进来的两个函数实现excel表格列字母和数字的转换
工作薄中包可以获取表单对象,表单对象中获取行和列 ,行和列中获取单元格对象
excel中内容如下:
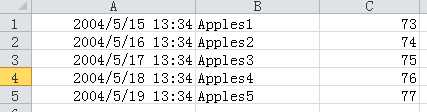
从工作薄中获取创建表单对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)# 从工作薄中获取一个表单(sheet)对象sheets = wb.sheetnamesprint(sheets, type(sheets))# 创建一个表单mySheet = wb.create_sheet(‘mySheet‘)print(wb.sheetnames)# 获取指定的表单sheet3 = wb.get_sheet_by_name(‘Sheet3‘)sheet4 = wb[‘mySheet‘]for sheet in wb: print(sheet.title) |

获取单元格对象中的信息
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)# 从表单中获取单元格的内容ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单print(ws)print(ws[‘A1‘]) # 获取A列的第一个对象print(ws[‘A1‘].value)c = ws[‘B1‘]print(‘Row {}, Column {} is {}‘.format(c.row, c.column, c.value)) # 打印这个单元格对象所在的行列的数值和内容print(‘Cell {} is {}\n‘.format(c.coordinate, c.value)) # 获取单元格对象的所在列的行数和值 |

获取指定的单元格中 值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)# 从表单中获取单元格的内容ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单print(ws.cell(row=1, column=2)) # 获取第一行第二列的单元格print(ws.cell(row=1, column=2).value)for i in range(1, 8, 2): # 获取1,3,4,7 行第二列的值 print(i, ws.cell(row=i, column=2).value) |

获取指定的行和列
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)# 从表单中获取单元格的内容ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单# 从表单中获取行和列colC = ws[‘C‘] # 获取整个C列print(colC)row6 = ws[6] # 获取第6行print(row6,type(row6)) |

遍历行和列中单元格的值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单col_range = ws[‘B:C‘]row_range = ws[2:6]for col in col_range: # 打印BC两列单元格中的值内容 for cell in col: print(cell.value)for row in row_range: # 打印 2-5行中所有单元格中的值 for cell in row: print(cell.value)for row in ws.iter_rows(min_row=1, max_row=2, max_col=2): # 打印1-2行,1-2列中的内容 for cell in row: print(cell.value) |
查看行和列的总数
import openpyxl# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单print(‘{}行 {}列‘.format(ws.max_row, ws.max_column)) |

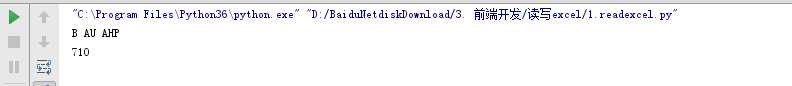
数字和字母的转换
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import openpyxlfrom openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter, column_index_from_string# 打开excel文件,获取工作簿对象wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(‘example.xlsx‘)ws = wb.active # 当前活跃的表单# 把数字转换成字母print(get_column_letter(2), get_column_letter(47), get_column_letter(900))# 把字母转换成数字print(column_index_from_string(‘AAH‘)) |
标签:col cells 字母转 name 字母 range ace load log
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ai-dev/p/12169129.html