标签:ber for 含义 循环 表示 说明 into 存储过程 declare
数据表使用的是orcale数据库自带的SCOTT用户下的表,主要使用就是EMP(雇员表)和DEPT(部门表),表中有部分数据。
这个用户默认是锁定的,需要登录有DBA权限的用户对他进行解锁,解锁语句如下
alter user scott account unlock;
解锁完之后就可以进行登录和使用,如果安装时没有设置scott用户的密码时,默认密码是tiger
ROWNUM:表示行号,实际上此是一个列,但是这个列是一个伪列,此列可以在每张表中出现。
例子:根据rownum获取emp表中的前三条数据
select rownum,emp.* from emp where rownum <=3
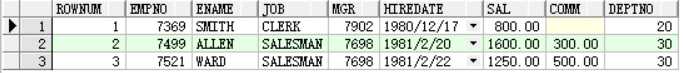
rownum不支持大于号(>)的操作
当我们想获取中间的几条数据的时候,可以使用子查询来进行分页效果
第一种分页方式(效率最高)
select * from (select rownum pnum,emp.* from emp) p where p.pnum>0 and p.pnum<3
第二种分页方式
select * from (select rownum pnum,p1.* from emp p1 where rownum<3) p2 where p2.pnum >0
第三种
select * from (select rownum pnum,p1.* from (select * from emp)p1 where rownum <3) p2 where p2.pnum >0
视图就是封装了一条复杂查询的语句。
语法:
CREATE VIEW 视图名称 AS 子查询
创建一个视图,只保留empno,ename两列数据
创建视图的用户必须要有DBA的权限
create view emp_view as (select empno,ename from emp);
查看视图和查看表的语句是一样的,只不过把表名换成了视图名
视图不用于保存数据,对视图进行DML操作,其实操作的就是真实的物理表,所以我们可以把视图设置成只读的
语法
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW 视图名称 AS 子查询 WITH READ ONLY
删除索引
DROP VIEW 视图名称
PLSQL 是Oracle 对sql 语言的过程化扩展,指在SQL 命令语言中增加了过程处理语句(如分支、循环等),使 SQL 语言具有过程处理能力。把 SQL 语言的数据操纵能力与过程语言的数据处理能力结合起来,使得PLSQL 面向过程但比过程语言简单、高效、灵活和实用。
程序语法:
declare 说明部分 (变量说明,游标申明,例外说明 ) begin 语句序列(DML 语句)… exception 例外处理语句 End;
--常量 declare empname varchar(255) :=‘天雁‘; begin dbms_output.put_line(empname); end;
declare emprec emp.ename%type; --引用某一张表中的某一列 begin select t.ename into emprec from emp t where t.empno = 7369; dbms_output.put_line(emprec); end;
declare p emp%rowtype; --记录了一张表 begin select * into p from emp t where t.empno = 7369; dbms_output.put_line(p.ename || ‘ ‘ || p.sal); end;
语法 1: IF 条件 THEN 语句 1; 语句 2; END IF; 语法 2: IF 条件 THEN 语句序列 1; ELSE 语句序列 2; END IF; 语法 3: IF 条件 THEN 语 句 ; ELSIF 语句 THEN 语句;
例子
declare mynum number := # --&num从控制台接受一个number类型的值 begin if mynum < 5 then dbms_output.put_line(‘输入的值小于5‘); elsif mynum >=5 and mynum<=10 then dbms_output.put_line(‘输入的值在5和10之间‘); elsif mynum >10 then dbms_output.put_line(‘输入的值大于10‘); end if; end;
WHILE total <= 25000 LOOP .. . total : = total + salary; END LOOP;
例子:输出一到十
declare pcount number := 1; begin while pcount<=10 loop dbms_output.put_line(pcount); pcount :=pcount+1; end loop; end;
Loop EXIT [when 条件]; …… End loop
例子:输出一到十
declare pcount number := 1; begin loop exit when pcount>10; --终止循环的条件,当条件满足时终止 dbms_output.put_line(pcount); pcount :=pcount+1; end loop; end;
FOR I IN 1 . . 3 LOOP 语句序列 ; END LOOP ;
输出1到100
declare pcount number := 1; begin for pcount in 1..100 loop --自己进行+1操作 dbms_output.put_line(pcount); end loop; end;
游标的含义
在写 java 程序中有集合的概念,那么在 pl/sql 中也会用到多条记录,这时候我们就要用到游标, 游标可以存储查询返回的多条数据。
在PL/SQL块中执行SELECT、INSERT、DELETE和UPDATE语句时,ORACLE会在内存中为其分配上下文区(Context Area),即缓冲区。游标是指向该区的一个指针,或是命名一个工作区(Work Area),或是一种结构化数据类型。它为应用等量齐观提供了一种对具有多行数据查询结果集中的每一行数据分别进行单独处理的方法,是设计嵌入式SQL语句的应用程序的常用编程方式。
语法:
CURSOR 游标名 [ (参数名 数据类型,参数名 数据类型,...)] IS SELECT 语句;
--游标的使用步骤
--1.声明游标 CURSOR 游标名 [ (参数名 数据类型,参数名 数据类型,...)] IS SELECT 语句;
--2.打开游标 open 游标名
--3.取一行游标的值:fetch 游标名 into 变量名
--4.关闭游标: close 游标名
declare cursor myemp is select * from emp;--声明 pemp emp%Rowtype; begin open myemp;--打开 loop fetch myemp into pemp; --循环读取每一条记录放到记录变量中 exit when myemp%notfound; --循环终止条件 dbms_output.put_line(pemp.ename); end loop; close myemp; --关闭 end;
存储过程(Stored Procedure)是在大型数据库系统中,一组为了完成特定功能的 SQL 语句集,经编译后存储在数据库中,用户通过指定存储过程的名字并给出参数(如果该存储过程带有参数)来 执行它。存储过程是数据库中的一个重要对象,任何一个设计良好的数据库应用程序都应该用到存 储过程。
语法:
create [or replace] PROCEDURE 过程名[(参数名 in/out 数据类型)] AS begin PLSQL 子程序体; End; 或者 create [or replace] PROCEDURE 过程名[(参数名 in/out 数据类型)] is begin PLSQL 子程序体; End 过程名;
创建一个名为helloworld存储过程
create or replace procedure helloworld is begin dbms_output.put_line(‘helloworld‘); end helloworld;
进行调用helloworld
begin helloworld; end;
标签:ber for 含义 循环 表示 说明 into 存储过程 declare
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yjc1605961523/p/12170804.html