标签:long class 思路 ons pos mamicode 操作 version 删除节点
成员变量
// 比较器
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//红黑树的根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root = null;
//红黑树的大小
/**
* The number of entries in the tree
*/
private transient int size = 0;
//修改的次数,用于线程安全的快速失败
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;put 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
//如果红黑树不存在,先构建一个红黑树
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
//通过传入的比较器,找到合适的元素位置插入
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
//如果 comparator 为 null,则使用 key 的自然顺序进行比较,这要求 key 必须实现 comparable 接口
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
//调整红黑树,使得红黑树平衡
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}get 方法
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}我们直接看 getEntry 方法。
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
//通过传入的比较器进行比较,比较方法和下面的使用默认比较器没有区别
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
//使用 compareTo 方法,从根节点开始进行比较
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}remove 方法
public V remove(Object key) {
//找到需要删除的节点
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
//删除节点并且平衡红黑树
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}TreeMap 使用红黑树按照 key 的顺序(自然顺序或者自定义顺序)来使得键值对有序存储,但是只能在单线程下使用。多线程环境下想要使键值对按照 key 的顺序来存储,则需要使用 ConcurrentSkipListMap。
ConcrurrentSkipListMap 底层使通过跳表来实现的。跳表是一个链表,通过使用“跳跃式”的查找的方式使得插入,读取数据的时间复杂度变成了 O(longn)。
跳表(SkipList):使用“空间换时间”的算法。在查询上跟平衡树的复杂度一致,因此是平衡数的替代方法。在 redis 的 ZSET 中有应用。因为链表不能像数组那样随机访问,只能从头一个个遍历。跳表为节点设置了快速访问的指针,不同于一个个遍历,而是可以跨节点进行访问,这也是跳表名字的含义。
数据结构如下:
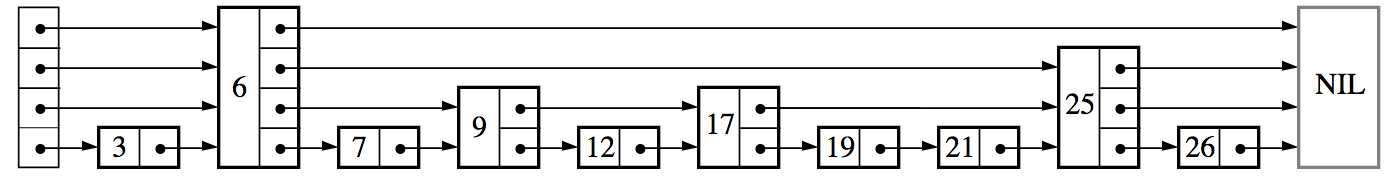
那么问题来了,如何决定每个节点的高度那?
当插入一个数据,随机获得节点的高度,没错,就是随机。每涨一层的概率为 p。这个概率人为设置,一般为 0.25 或者 0.5, 则海洋层数越高的节点就越少。
如何搜索?
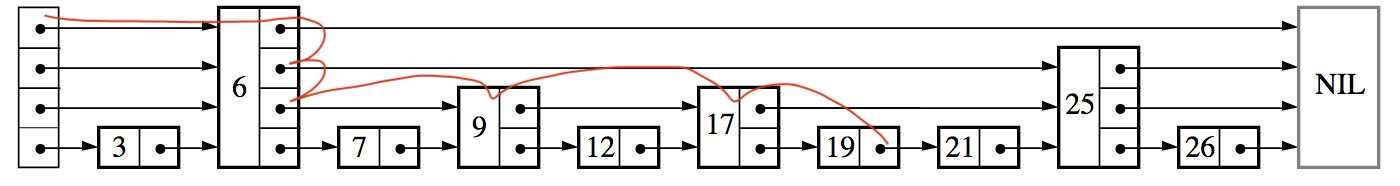
可以看到高层级的节点相当于一个快速通道,让搜索进行了节点的跳跃,而不是一个个的遍历。
插入
插入的思路是要找到插入的点,并且在遍历的同时,记录下需要更新的层数,在最后进行处理。
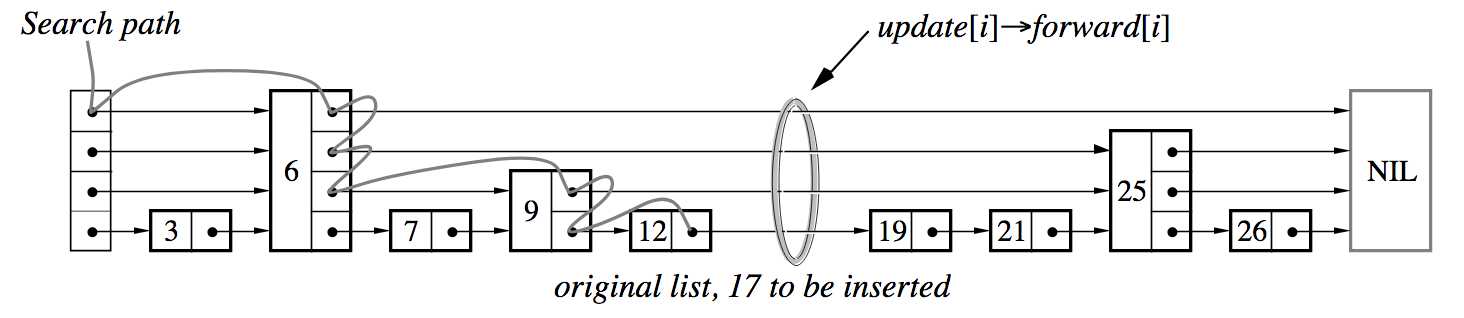
假如插入 17,并且 17 节点随机获得层数是 2。这样节点 9 的第二层需要指向新的节点 17,12 的第一层也要指向 17。
删除
删除方法的思路也是一样,需要记录搜索过程中每一层最后i贝纳利的节点。在找到要删除的节点后,把每一层中指向删除节点的指针指向被删除节点每层的后续指针。
了解了 SkipList 的原理之后,我们来分析一下 ConcurrentSkipListMap 的源码。
插入
private V doPut(K kkey, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);
for (;;) {
// 找到key的前继节点
Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);
// 设置n为“key的前继节点的后继节点”,即n应该是“插入节点”的“后继节点”
Node<K,V> n = b.next;
for (;;) {
if (n != null) {
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
// 如果两次获得的b.next不是相同的Node,说明已经被更改了,就跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。
if (n != b.next)
break;
// v是“n的值”
Object v = n.value;
// 当n的值为null(意味着其它线程删除了n);此时删除b的下一个节点,然后跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。
if (v == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
// 如果其它线程删除了b;则跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。
if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deleted
break;
// 比较key和n.key
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) {
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value))
return (V)v;
else
break; // restart if lost race to replace value
}
// else c < 0; fall through
}
// 新建节点(对应是“要插入的键值对”)
Node<K,V> z = new Node<K,V>(kkey, value, n);
// 设置“b的后继节点”为z
if (!b.casNext(n, z))
break; // 多线程情况下,break才可能发生(其它线程对b进行了操作)
// 随机获取一个level,每个节点的层数都是随机的。
// 然后在“第1层”到“第level层”的链表中都插入新建节点
int level = randomLevel();
if (level > 0)
insertIndex(z, level);
return null;
}
}
}删除
final V doRemove(Object okey, Object value) {
Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(okey);
for (;;) {
// 找到“key的前继节点”
Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);
// 设置n为“b的后继节点”(即若key存在于“跳表中”,n就是key对应的节点)
Node<K,V> n = b.next;
for (;;) {
if (n == null)
return null;
// f是“当前节点n的后继节点”
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
// 如果两次读取到的“b的后继节点”不同(其它线程操作了该跳表),则返回到“外层for循环”重新遍历。
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
// 如果“当前节点n的值”变为null(其它线程操作了该跳表),则返回到“外层for循环”重新遍历。
Object v = n.value;
if (v == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
// 如果“前继节点b”被删除(其它线程操作了该跳表),则返回到“外层for循环”重新遍历。
if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deleted
break;
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c < 0)
return null;
if (c > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
// 以下是c=0的情况
if (value != null && !value.equals(v))
return null;
// 设置“当前节点n”的值为null
if (!n.casValue(v, null))
break;
// 设置“b的后继节点”为f
if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f))
findNode(key); // Retry via findNode
else {
// 清除“跳表”中每一层的key节点
findPredecessor(key); // Clean index
// 如果“表头的右索引为空”,则将“跳表的层次”-1。
if (head.right == null)
tryReduceLevel();
}
return (V)v;
}
}
}private Node<K,V> findNode(Comparable<? super K> key) {
for (;;) {
// 找到key的前继节点
Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);
// 设置n为“b的后继节点”(即若key存在于“跳表中”,n就是key对应的节点)
Node<K,V> n = b.next;
for (;;) {
// 如果“n为null”,则跳转中不存在key对应的节点,直接返回null。
if (n == null)
return null;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
// 如果两次读取到的“b的后继节点”不同(其它线程操作了该跳表),则返回到“外层for循环”重新遍历。
if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read
break;
Object v = n.value;
// 如果“当前节点n的值”变为null(其它线程操作了该跳表),则返回到“外层for循环”重新遍历。
if (v == null) { // n is deleted
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deleted
break;
// 若n是当前节点,则返回n。
int c = key.compareTo(n.key);
if (c == 0)
return n;
// 若“节点n的key”小于“key”,则说明跳表中不存在key对应的节点,返回null
if (c < 0)
return null;
// 若“节点n的key”大于“key”,则更新b和n,继续查找。
b = n;
n = f;
}
}
}可以发现:ConcurrentSkipListMap 的线程安全原理 与非阻塞队列 ConcurrentBlockingQueue 的原理一样,通过底层的插入,删除的 CAS 原子性操作,通过死循环不断获取最新的节点指针来保证不会出现竞态条件。
Java 集合框架(七):TreeMap 和 ConcurrentSkipListMap
标签:long class 思路 ons pos mamicode 操作 version 删除节点
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/paulwang92115/p/12184845.html