标签:oba instance 语言环境 logformat exce strace get gre multiple
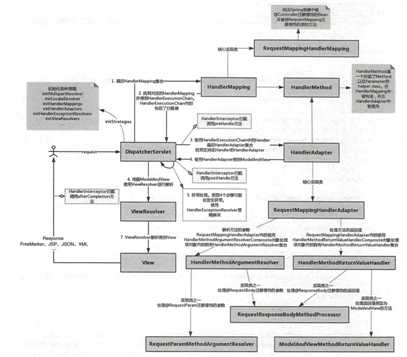
SpringMVC 的处理过程可分为如下 三步 :
首先找到 DispatcherServlet类, 寻找 init()方法。我们发现 init()方法其实在父类 HttpServletBean 中,其源码如下 :

public final void init() throws ServletException { // Set bean properties from init parameters. PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { //定位资源 BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); //加载配置信息 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘", ex); } throw ex; } } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. //完成bean的初始化 initServletBean(); }
在这段代码中调用了一个 重要的方法 : initServletBean()。 initServletBean()方法 的源码如下 :

protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Initializing Servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ? "shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" : "masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data"; logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails=‘" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails + "‘: request parameters and headers will be " + value); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms"); } }
上面这段代码主要就是初始化 IoC 容器,最终会调用 refresh()方法,前面的章节对 IoC 容器的 初始化己经讲得很详细,在此不再赘述。 我们看到,在 IoC容器初始化之后, 又调用了 onRefresh() 方法,它是在 DisptcherServlet 类中实现的 , 来看源码 :
初始化web容器:

protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { //先从 ServletContext 中获得父容器 WebApplicationContext WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); //声明子容器 WebApplicationContext wac = null; //建立子和父容器之间的关系 if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } //先去 ServletContext 中查找 Web 容器的引用是否存在 ,并创建好默认的空 IoC 容器 if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } //给上一步创建好的ioc容器赋值 if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } //处罚onRefresh()方法 if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { onRefresh(wac); } } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
我们看到,在 IoC容器初始化之后, 又调用了 onRefresh() 方法,它是在 DisptcherServlet 类中实现的 , 来看源码 :

protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } /** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { //初始化springMvc九大组件 //多文件上传的组件 initMultipartResolver(context); //初始化本地语言环境 initLocaleResolver(context); //初始化模板处理器 initThemeResolver(context); //初始化 handlerMapping initHandlerMappings(context); //初始化参数适配器 initHandlerAdapters(context); //初始化异常拦截器 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); //初始化视图预处理器 initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //初始化视图转换器 initViewResolvers(context); //初始化Flash管理器 initFlashMapManager(context); }
到这就完成了 Spring MVC 的九大组件的初始化。接下来,我们来看 URL 和 Controller 的关 系是如何建立的 。 HandlerMapping 的子类 AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping 实现了 initApplicationContext()方法,我们直接看子类中的初始化容器方法:

public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException { super.initApplicationContext(); detectHandlers(); } /** * Register all handlers found in the current ApplicationContext. * <p>The actual URL determination for a handler is up to the concrete * {@link #determineUrlsForHandler(String)} implementation. A bean for * which no such URLs could be determined is simply not considered a handler. * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException if the handler couldn‘t be registered * @see #determineUrlsForHandler(String) */ protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException { ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext(); //获取 ApplicationContext 容器中所有 Bean 的名字 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) : applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); // Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for. //遍历 beanNames, 并找到这些 Bean 对应的 URL for (String beanName : beanNames) { //查找 Bean 上的所有 URL(Controlle「 上的 URL+方法上的 URL),该方法由对应的子类实现 String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) { // URL paths found: Let‘s consider it a handler. //保存 urls 和 beanName 的对应关系,放入 Map<urls,beanName>, // 该方法在父类 AbstractUr、!Handler、Mapping 中实现 registerHandler(urls, beanName); } } if ((logger.isDebugEnabled() && !getHandlerMap().isEmpty()) || logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + getHandlerMap().size() + " mappings in " + formatMappingName()); } } /** * Determine the URLs for the given handler bean. * @param beanName the name of the candidate bean * @return the URLs determined for the bean, or an empty array if none */ // 获取 Controller 中所有方法的 URL,由子类实现,典型的模板模式 protected abstract String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName);
determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName)方法的作用是获取每个 Controller 中的 URL, 不同 的子类有不同的实现,这是典型的模板模式。因为开发中用得最多的就是用注解来配置 Controller 中的 URL. BeanNameUr!HandlerMapping 是 AbstractDetectingUr!HandlerMapping 的子类,用于处 理注解形式的 U也映射。我们这里以 BeanNameUr!HandlerMapping为例来进行分析,看看如何查 找 beanName 上所有映射的 URL。

public class BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping extends AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping { /** * Checks name and aliases of the given bean for URLs, starting with "/". */ @Override protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) { List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>(); if (beanName.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(beanName); } String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName); for (String alias : aliases) { if (alias.startsWith("/")) { urls.add(alias); } } return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls); } }
到这里 HandlerMapping 组件 己经建立了所有 URL 和 Controller 的对应关系。
在日常开发中,我们最常用的请求方式大概就是Get和Post了,Tomcat或者Jetty等web服务器在接受到请求后会调用到DispatcherServlet对应的方法

@Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
可以看到其实最终都是调用的同一个方法FrameworkServlet.processRequest():

protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //记录开始时间 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; //记录当前线程的信息 LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { //核心处理,往下看 doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException | IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally {//清除线程绑定信息 resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (failureCause != null) { this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause); } else { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing"); } else { this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request"); } } } //发送事件通知 publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } } protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); if (this.flashMapManager != null) { FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); } try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } }
运行调用是由请求触发的,所以入口为 DispatcherServlet 的核心方法 doService(), 中的核心由 doDispatch()实现,源代码如下:

protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { // 1.检查是否是文件上传的请求 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. // 11 2.取得处理当前请求的 Controll肘 ,这里也称为 Hanlder, 即处理器 // 第一步的意义就在这里体现了。这里并不是直接返回 Controll, // 而是返回 Handler、ExecutionChain 请求处理器链对象, // 该对象封装了 Handler、和 interceptor mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); // 如果 Handler 为空,则返回 404 if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. // 3. 获取处理请求的处理器适配器 HandleAdapte HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. //处理 last-modified 请求头 String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. // 4.实际处理器处理请求,返回结果视图对象 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } //结果视图对象的处理 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we‘re processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { //请求成功响应之后的方法 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }

protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { //遍历所有的handlerMapping,这里的handlemapping就是初始化阶段构造的三个 for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } //这里调用具体的handler,哪个handler能够处理就直接返回 HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; } public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { //1. 调用具体的实现去获取handler Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); //如果为空使用默认的 if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } //没有默认的返回空 if (handler == null) { return null; } // 尝试通过BeanName去获取handler if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } //2. 获取handler执行链 HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
获取具体的handler,这里以AbstractUrlHandlerMapping为例解读一下,顾明思议,这个类是根据请求url获取响应的handler的

protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { //截取url String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); //根据url寻找handler Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request); if (handler == null) { // 如果请求路径为/则使用RootHandler Object rawHandler = null; if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) { rawHandler = getRootHandler(); } if (rawHandler == null) { //使用默认 rawHandler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (rawHandler != null) { // 根据beanName尝试获取Handler if (rawHandler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) rawHandler; rawHandler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); }//校验 validateHandler(rawHandler, request); handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null); } } if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler); } else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]"); } return handler; } protected Object lookupHandler(String urlPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { // 直接根据url匹配 Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath); if (handler != null) { // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(handler, request); //封装执行链 return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, urlPath, urlPath, null); } // 正则匹配 List<String> matchingPatterns = new ArrayList<>(); for (String registeredPattern : this.handlerMap.keySet()) { if (getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern, urlPath)) { matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern); } else if (useTrailingSlashMatch()) { if (!registeredPattern.endsWith("/") && getPathMatcher().match(registeredPattern + "/", urlPath)) { matchingPatterns.add(registeredPattern +"/"); } } } String bestMatch = null; Comparator<String> patternComparator = getPathMatcher().getPatternComparator(urlPath); if (!matchingPatterns.isEmpty()) { matchingPatterns.sort(patternComparator); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Matching patterns for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + matchingPatterns); } bestMatch = matchingPatterns.get(0); } if (bestMatch != null) { handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestMatch); if (handler == null) { if (bestMatch.endsWith("/")) { handler = this.handlerMap.get(bestMatch.substring(0, bestMatch.length() - 1)); } if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Could not find handler for best pattern match [" + bestMatch + "]"); } } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } validateHandler(handler, request); String pathWithinMapping = getPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestMatch, urlPath); // There might be multiple ‘best patterns‘, let‘s make sure we have the correct URI template variables // for all of them Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables = new LinkedHashMap<>(); for (String matchingPattern : matchingPatterns) { if (patternComparator.compare(bestMatch, matchingPattern) == 0) { Map<String, String> vars = getPathMatcher().extractUriTemplateVariables(matchingPattern, urlPath); Map<String, String> decodedVars = getUrlPathHelper().decodePathVariables(request, vars); uriTemplateVariables.putAll(decodedVars); } } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("URI Template variables for request [" + urlPath + "] are " + uriTemplateVariables); } return buildPathExposingHandler(handler, bestMatch, pathWithinMapping, uriTemplateVariables); } // No handler found... return null; }
当获取到相应的handler后,查看是否存在拦截器,如果存在的话则加入执行链中

protected Object buildPathExposingHandler(Object rawHandler, String bestMatchingPattern, String pathWithinMapping, @Nullable Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) { HandlerExecutionChain chain = new HandlerExecutionChain(rawHandler); chain.addInterceptor(new PathExposingHandlerInterceptor(bestMatchingPattern, pathWithinMapping)); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(uriTemplateVariables)) { chain.addInterceptor(new UriTemplateVariablesHandlerInterceptor(uriTemplateVariables)); } return chain; }
根据handler获取匹配的handlerAdpter

protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); } //不同的handlerAdapter的判断方法不同 if (ha.supports(handler)) { return ha; } } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); } 以SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter为例,判断是否实现Controller接口 public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof Controller); }

public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response); } public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod())) { response.setHeader("Allow", getAllowHeader()); return null; } // Delegate to WebContentGenerator for checking and preparing. checkRequest(request); prepareResponse(response); // 如果需要同步session if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { return handleRequestInternal(request, response); } } } 调用Controller方法 return handleRequestInternal(request, response); }

private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; //是否包含异常信息 if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else {//异常视图处理 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { // 页面跳转处理 render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling"); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }

protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. Locale locale = (this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale()); response.setLocale(locale); View view; String viewName = mv.getViewName(); if (viewName != null) { //1.解析视图名 view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name ‘" + mv.getViewName() + "‘ in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } } else { // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView(); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } } // Delegate to the View object for rendering. if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } try { if (mv.getStatus() != null) { response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); }//2.跳转 view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘", ex); } throw ex; } }

protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.viewResolvers != null) { for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); if (view != null) { return view; } } } return null; }
具体的跳转逻辑是根据当前使用的渲染引擎决定的,比如html、jsp、Thymeleaf等,这里简单 列举一个Thymeleaf的逻辑吧

public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { this.renderFragment(this.markupSelectors, model, request, response); } protected void renderFragment(Set<String> markupSelectorsToRender, Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext(); String viewTemplateName = this.getTemplateName(); ISpringTemplateEngine viewTemplateEngine = this.getTemplateEngine(); if (viewTemplateName == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property ‘templateName‘ is required"); } else if (this.getLocale() == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property ‘locale‘ is required"); } else if (viewTemplateEngine == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property ‘templateEngine‘ is required"); } else { Map<String, Object> mergedModel = new HashMap(30); Map<String, Object> templateStaticVariables = this.getStaticVariables(); if (templateStaticVariables != null) { mergedModel.putAll(templateStaticVariables); } if (pathVariablesSelector != null) { Map<String, Object> pathVars = (Map)request.getAttribute(pathVariablesSelector); if (pathVars != null) { mergedModel.putAll(pathVars); } } if (model != null) { mergedModel.putAll(model); } ApplicationContext applicationContext = this.getApplicationContext(); RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(request, response, this.getServletContext(), mergedModel); SpringWebMvcThymeleafRequestContext thymeleafRequestContext = new SpringWebMvcThymeleafRequestContext(requestContext, request); addRequestContextAsVariable(mergedModel, "springRequestContext", requestContext); addRequestContextAsVariable(mergedModel, "springMacroRequestContext", requestContext); mergedModel.put("thymeleafRequestContext", thymeleafRequestContext); ConversionService conversionService = (ConversionService)request.getAttribute(ConversionService.class.getName()); ThymeleafEvaluationContext evaluationContext = new ThymeleafEvaluationContext(applicationContext, conversionService); mergedModel.put("thymeleaf::EvaluationContext", evaluationContext); IEngineConfiguration configuration = viewTemplateEngine.getConfiguration(); WebExpressionContext context = new WebExpressionContext(configuration, request, response, servletContext, this.getLocale(), mergedModel); String templateName; Set markupSelectors; if (!viewTemplateName.contains("::")) { templateName = viewTemplateName; markupSelectors = null; } else { IStandardExpressionParser parser = StandardExpressions.getExpressionParser(configuration); FragmentExpression fragmentExpression; try { fragmentExpression = (FragmentExpression)parser.parseExpression(context, "~{" + viewTemplateName + "}"); } catch (TemplateProcessingException var24) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid template name specification: ‘" + viewTemplateName + "‘"); } ExecutedFragmentExpression fragment = FragmentExpression.createExecutedFragmentExpression(context, fragmentExpression); templateName = FragmentExpression.resolveTemplateName(fragment); markupSelectors = FragmentExpression.resolveFragments(fragment); Map<String, Object> nameFragmentParameters = fragment.getFragmentParameters(); if (nameFragmentParameters != null) { if (fragment.hasSyntheticParameters()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parameters in a view specification must be named (non-synthetic): ‘" + viewTemplateName + "‘"); } context.setVariables(nameFragmentParameters); } } String templateContentType = this.getContentType(); Locale templateLocale = this.getLocale(); String templateCharacterEncoding = this.getCharacterEncoding(); Set processMarkupSelectors; if (markupSelectors != null && markupSelectors.size() > 0) { if (markupSelectorsToRender != null && markupSelectorsToRender.size() > 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("A markup selector has been specified (" + Arrays.asList(markupSelectors) + ") for a view that was already being executed as a fragment (" + Arrays.asList(markupSelectorsToRender) + "). Only one fragment selection is allowed."); } processMarkupSelectors = markupSelectors; } else if (markupSelectorsToRender != null && markupSelectorsToRender.size() > 0) { processMarkupSelectors = markupSelectorsToRender; } else { processMarkupSelectors = null; } response.setLocale(templateLocale); if (!this.getForceContentType()) { String computedContentType = SpringContentTypeUtils.computeViewContentType(request, templateContentType != null ? templateContentType : "text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1", templateCharacterEncoding != null ? Charset.forName(templateCharacterEncoding) : null); response.setContentType(computedContentType); } else { if (templateContentType != null) { response.setContentType(templateContentType); } else { response.setContentType("text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1"); } if (templateCharacterEncoding != null) { response.setCharacterEncoding(templateCharacterEncoding); } } viewTemplateEngine.process(templateName, processMarkupSelectors, context, response.getWriter()); } }
getHandler(processedRequest)方法实际上从 HandlerMapping中找到 U也和 Controller的对应关 系 ,也就是 Map<url,Controller>。 我们知道,最终处理请求的是 Controller 中的方法,现在只是知 道了 Controller,如何确 认 Controller 中处理请求的方法呢?继续往下看。
从 Map<urls,beanName>中取得 Controller 后,经过拦截器的预处理方法,再通过反射获取该 方法上的注解和参数,解析方法和参数上的注解,然后反射调用方法获取 Mode!AndView 结果视图。最后调用 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的 handle()中的核心代码,由 handlelntenal (request, response, handler)实现 :

protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ModelAndView mav; checkRequest(request); // Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required. if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } else { // No synchronization on session demanded at all... mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) { if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers); } else { prepareResponse(response); } } return mav; }
整个处理过程中最核心的步骤其实就是拼接 Controller 的 URL 和方法的 URL,与 Request 的 URL 进行匹配,找到匹配的方法。 在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法上。

protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { //如果请求 URL 为 http://localhost:8080/web/hello.json, 则 lookupPath=web/hello.json String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath); this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { //遍历 Controlle「 上的所有方法 , 获取 URL 匹配的方法 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
通过上面的代码分析,己经找到处理请求的 Controller 中的方法了,下面看如何解析该方法上 的参数, 井反射调用该方法。 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter的invokeHandlerMethod方法:

protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); try { WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod); if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory); invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> { String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn); return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]"; }); invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } finally { webRequest.requestCompleted(); } }
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle()最终要实现的目的是 : 完成请求 中的 参数和方法参数上数 据 的绑定 。 SpringMVC 中提供两种从请求参数到方法中参数 的绑定方式 :
Cl )通过注解进行绑定 , @RequestParamo
(2)通过参数名称进行绑定 。
通过注解进行绑定 , 只要在方法的参数前面声 明@RequestParam(”name”),就可以将请求中参
数 name 的值绑定到方法的该参数上 。
通过参数名称进行绑定的前提是必 须获取方法 中参数的名称, Java 反射只提供了获取方法参 数类型的方法, 并没有提供获取参数名称的方法。 SpringMVC解决这个问题的方法是用 asm框架 读取字节码文件。 asm 框架是一个字节码操作框架,更多介绍可以参考其宫网。 个人建议通过注 解进行绑定,如下代码所示,这样就可以省去 asm框架的读取字节码的操作。

public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { //调用。。。 Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args)); } return doInvoke(args); } /** * Get the method argument values for the current request, checking the provided * argument values and falling back to the configured argument resolvers. * <p>The resulting array will be passed into {@link #doInvoke}. * @since 5.1.2 */ protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters(); if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) { return EMPTY_ARGS; } Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length]; for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i]; parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs); if (args[i] != null) { continue; } if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) { throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver")); } try { args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory); } catch (Exception ex) { // Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled... if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String exMsg = ex.getMessage(); if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) { logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg)); } } throw ex; } } return args; }
标签:oba instance 语言环境 logformat exce strace get gre multiple
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/heqiyoujing/p/12209878.html