标签:noi 参考 abs svi ref ssis put atoi 吞吐量




1 package java.util.concurrent; 2 3 /** 4 * 带有缓存的线程池 5 */ 6 public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { 7 return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 8 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 9 new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); 10 }
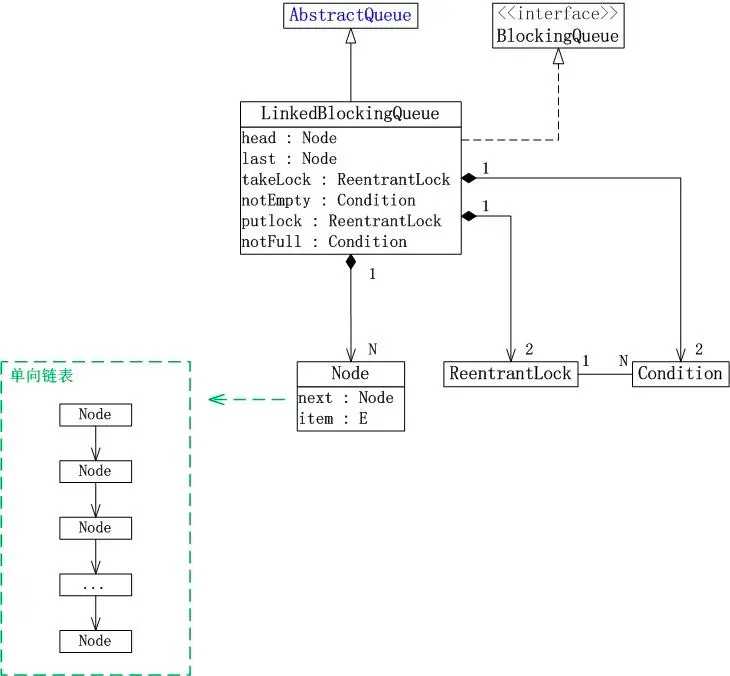
1 // 容量 2 private final int capacity; 3 4 // 当前数量 5 private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); 6 7 // 链表的表头 8 transient Node<E> head; 9 10 // 链表的表尾 11 private transient Node<E> last; 12 13 // 用于控制删除元素的【取出锁】和锁对应的【非空条件】 14 private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock(); 15 private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition(); 16 17 // 用于控制添加元素的【插入锁】和锁对应的【非满条件】 18 private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock(); 19 private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
1 // 创建一个容量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingQueue 2 LinkedBlockingQueue() 3 4 // 创建一个容量是 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的 LinkedBlockingQueue,最初包含给定 collection 的元素,元素按该 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序添加 5 LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) 6 7 // 创建一个具有给定(固定)容量的 LinkedBlockingQueue 8 LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) 9 10 // 从队列彻底移除所有元素 11 void clear() 12 13 // 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超出此队列的容量),在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则返回 false 14 boolean offer(E e) 15 16 // 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部,如有必要,则等待指定的时间以使空间变得可用 17 boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 18 19 // 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null 20 E peek() 21 22 // 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 23 E poll() 24 25 // 获取并移除此队列的头部,在指定的等待时间前等待可用的元素(如果有必要) 26 E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 27 28 // 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部,如有队列满,则等待空间变得可用 29 void put(E e) 30 31 // 返回理想情况下(没有内存和资源约束)此队列可接受并且不会被阻塞的附加元素数量 32 int remainingCapacity() 33 34 // 从此队列移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在) 35 boolean remove(Object o) 36 37 // 返回队列中的元素个数 38 int size() 39 40 // 获取并移除此队列的头部,在元素变得可用之前一直等待(如果有必要) 41 E take()
1 /** 2 * 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部(如果立即可行且不会超出此队列的容量) 3 * 在成功时返回 true,如果此队列已满,则返回 false 4 * 如果使用了有容量限制的队列,推荐使用add方法,add方法在失败的时候只是抛出异常 5 */ 6 public boolean offer(E e) { 7 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 8 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 9 if (count.get() == capacity) 10 // 如果队列已满,则返回false,表示插入失败 11 return false; 12 int c = -1; 13 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); 14 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; 15 // 获取 putLock 16 putLock.lock(); 17 try { 18 // 再次对【队列是不是满】的进行判断,如果不是满的,则插入节点 19 if (count.get() < capacity) { 20 enqueue(node); // 在队尾插入节点 21 c = count.getAndIncrement(); // 当前节点数量+1,并返回插入之前节点数量 22 if (c + 1 < capacity) 23 // 如果在插入元素之后,队列仍然未满,则唤醒notFull上的等待线程 24 notFull.signal(); 25 } 26 } finally { 27 // 释放 putLock 28 putLock.unlock(); 29 } 30 if (c == 0) 31 // 如果在插入节点前,队列为空,那么插入节点后,唤醒notEmpty上的等待线程 32 signalNotEmpty(); 33 return c >= 0; 34 }
下面来看看 put(E e) 的源码:
1 /** 2 * 将指定元素插入到此队列的尾部,如有队列满,则等待空间变得可用 3 * 4 * @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc} 5 * @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc} 6 */ 7 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 8 if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException(); 9 10 int c = -1; 11 Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e); 12 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; 13 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 14 putLock.lockInterruptibly(); // 可中断地获取 putLock 15 try { 16 // count 变量是被 putLock 和 takeLock 保护起来的,所以可以真实反映队列当前的容量情况 17 while (count.get() == capacity) { 18 notFull.await(); 19 } 20 enqueue(node); // 在队尾插入节点 21 c = count.getAndIncrement(); // 当前节点数量+1,并返回插入之前节点数量 22 if (c + 1 < capacity) 23 // 如果在插入元素之后,队列仍然未满,则唤醒notFull上的等待线程 24 notFull.signal(); 25 } finally { 26 putLock.unlock(); // 释放 putLock 27 } 28 if (c == 0) 29 // 如果在插入节点前,队列为空,那么插入节点后,唤醒notEmpty上的等待线程 30 signalNotEmpty(); 31 }
1 /** 2 * 通知一个等待的take。该方法应该仅仅从put/offer调用,否则一般很难锁住takeLock 3 */ 4 private void signalNotEmpty() { 5 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 6 takeLock.lock(); // 获取 takeLock 7 try { 8 notEmpty.signal(); // 唤醒notEmpty上的等待线程,意味着现在可以获取元素了 9 } finally { 10 takeLock.unlock(); // 释放 takeLock 11 } 12 }
1 /** 2 * 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 3 */ 4 public E poll() { 5 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 6 if (count.get() == 0) 7 return null; 8 E x = null; 9 int c = -1; 10 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 11 takeLock.lock(); // 获取 takeLock 12 try { 13 if (count.get() > 0) { 14 x = dequeue(); // 获取队头元素,并移除 15 c = count.getAndDecrement(); // 当前节点数量-1,并返回移除之前节点数量 16 if (c > 1) 17 // 如果在移除元素之后,队列中仍然有元素,则唤醒notEmpty上的等待线程 18 notEmpty.signal(); 19 } 20 } finally { 21 takeLock.unlock(); // 释放 takeLock 22 } 23 if (c == capacity) 24 // 如果在移除节点前,队列是满的,那么移除节点后,唤醒notFull上的等待线程 25 signalNotFull(); 26 return x; 27 }
1 /** 2 * 取出并返回队列的头。若队列为空,则一直等待 3 */ 4 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 5 E x; 6 int c = -1; 7 final AtomicInteger count = this.count; 8 final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock; 9 // 获取 takeLock,若当前线程是中断状态,则抛出InterruptedException异常 10 takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); 11 try { 12 // 若队列为空,则一直等待 13 while (count.get() == 0) { 14 notEmpty.await(); 15 } 16 x = dequeue(); // 从队头取出元素 17 c = count.getAndDecrement(); // 取出元素之后,节点数量-1;并返回移除之前的节点数量 18 if (c > 1) 19 // 如果在移除元素之后,队列中仍然有元素,则唤醒notEmpty上的等待线程 20 notEmpty.signal(); 21 } finally { 22 takeLock.unlock(); // 释放 takeLock 23 } 24 25 if (c == capacity) 26 // 如果在取出元素之前,队列是满的,就在取出元素之后,唤醒notFull上的等待线程 27 signalNotFull(); 28 return x; 29 }
1 /** 2 * 唤醒notFull上的等待线程,只能从 poll 或 take 调用 3 */ 4 private void signalNotFull() { 5 final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock; 6 putLock.lock(); // putLock 上锁 7 try { 8 notFull.signal(); // 唤醒notFull上的等待线程,意味着可以插入元素了 9 } finally { 10 putLock.unlock(); // putLock 解锁 11 } 12 }
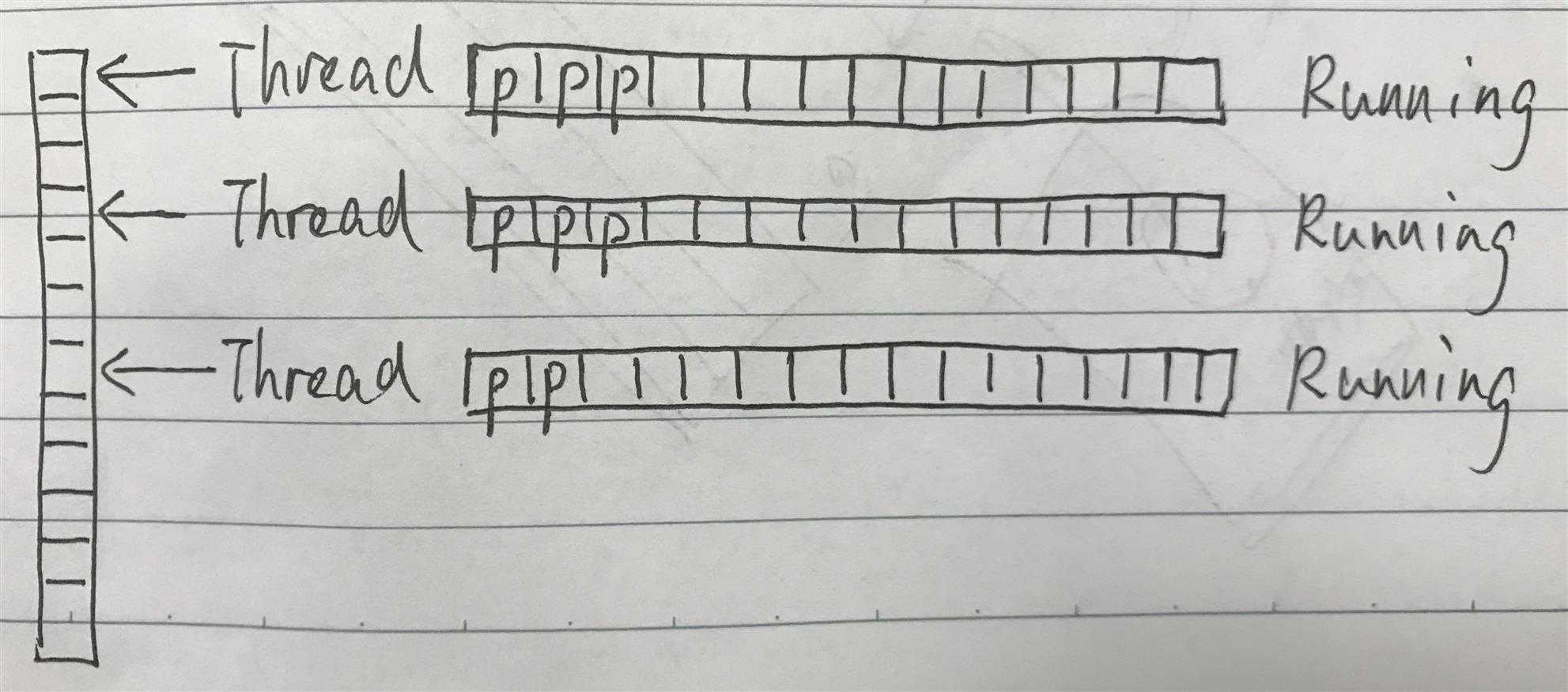
1 package cn.com.gkmeteor.threadpool.utils; 2 3 @Component 4 public class ThreadPoolUtil implements InitializingBean { 5 6 public static int POOL_SIZE = 10; 7 8 @Autowired 9 private ThreadExecutorService threadExecutorService; // 具体的线程处理类 10 11 private List<ThreadWithQueue> threadpool = new ArrayList<>(); 12 13 /** 14 * 在所有基础属性初始化完成后,初始化当前类 15 * 16 * @throws Exception 17 */ 18 @Override 19 public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { 20 for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) { 21 ThreadWithQueue threadWithQueue = new ThreadWithQueue(i, threadExecutorService); 22 this.threadpool.add(threadWithQueue); 23 } 24 } 25 }
1 public static int POOL_SIZE = 10; // 线程池容量 2 index = (++index) % POOL_SIZE; // index 是当前选中的线程下标
1 package cn.com.gkmeteor.threadpool.utils; 2 3 import cn.com.gkmeteor.threadpool.service.ThreadExecutorService; 4 import org.slf4j.Logger; 5 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 6 7 import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; 8 9 /** 10 * 带有【参数阻塞队列】的线程 11 */ 12 public class ThreadWithQueue extends Thread { 13 14 public static int CAPACITY = 10; 15 16 private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ThreadWithQueue.class); 17 18 private BlockingQueue<String> queue; 19 20 private ThreadExecutorService threadExecutorService; // 线程运行后的业务逻辑处理 21 22 private String threadName; 23 24 public String getThreadName() { 25 return threadName; 26 } 27 28 public void setThreadName(String threadName) { 29 this.threadName = threadName; 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 构造方法 34 * 35 * @param i 第几个线程 36 * @param threadExecutorService 线程运行后的业务逻辑处理 37 */ 38 public ThreadWithQueue(int i, ThreadExecutorService threadExecutorService) { 39 queue = new java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue<>(CAPACITY); 40 threadName = "Thread(" + i + ")"; 41 42 this.threadExecutorService = threadExecutorService; 43 44 this.start(); 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * 将参数放到线程的参数队列中 49 * 50 * @param param 参数 51 * @return 52 */ 53 public String paramAdded(String param) { 54 String result = ""; 55 if(queue.offer(param)) { 56 logger.info("参数已入队,{} 目前参数个数 {}", this.getThreadName(), queue.size()); 57 result = "参数已加入线程池,等待处理"; 58 } else { 59 logger.info("队列已达最大容量,请稍后重试"); 60 result = "线程池已满,请稍后重试"; 61 } 62 return result; 63 } 64 65 public synchronized int getQueueSize() { 66 return queue.size(); 67 } 68 69 @Override 70 public void run() { 71 while (true) { 72 try { 73 String param = queue.take(); 74 logger.info("{} 开始运行,参数队列中还有 {} 个在等待", this.getThreadName(), this.getQueueSize()); 75 if (param.startsWith("contact")) { 76 threadExecutorService.doContact(param); 77 } else if (param.startsWith("user")) { 78 threadExecutorService.doUser(param); 79 } else { 80 logger.info("参数无效,不做处理"); 81 } 82 logger.info("{} 本次处理完成", this.getThreadName()); 83 } catch (Exception e) { 84 e.printStackTrace(); 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 }
了解了链接阻塞队列的底层方法后,使用起来就底气十足。具体来说:
使用 LinkedBlockingQueue 实现简易版线程池
标签:noi 参考 abs svi ref ssis put atoi 吞吐量
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gkmeteor/p/12228672.html