标签:using ssi man 代码 添加 queue mem pop else
spfa算法是对bellman-ford算法的优化,bellman-ford算法遍历每一条边,不断的迭代更新。但是注意到,有许多边的值是不变的,也就是说不需要更新,所以spfa算法基于这一点进行优化,只有值变小的点才有机会去更新其他点。所以我们用一个队列来存储可以更新其他点的点。
1 1.初始化 2 while 队列不空 3 { 4 2.取队头; 5 3.标记不在队列中 6 4.更新其他点 7 }
1.初始化需要初始化dis数组为正无穷,将第一个点dis置为0,将第一个点加入队列,并标记在队列中。
2.当队列不空时取队头元素,并将其标记置为不在队列中。
3.需要注意的是spfa中的st数组是标记该点是否在队列中,与dijkstra算法中的st数组作用不同,dijkstra算法中的st数组是在出队时标记已经用过,所以只会标记一次。而spfa数组的元素是可以多次入队的。
4.由于spfa算法是bellman-ford算法的优化,所以spfa算法是可以处理带负权边的单源最短路算法,而dijkstra是只能处理正权边的单源最短路算法。
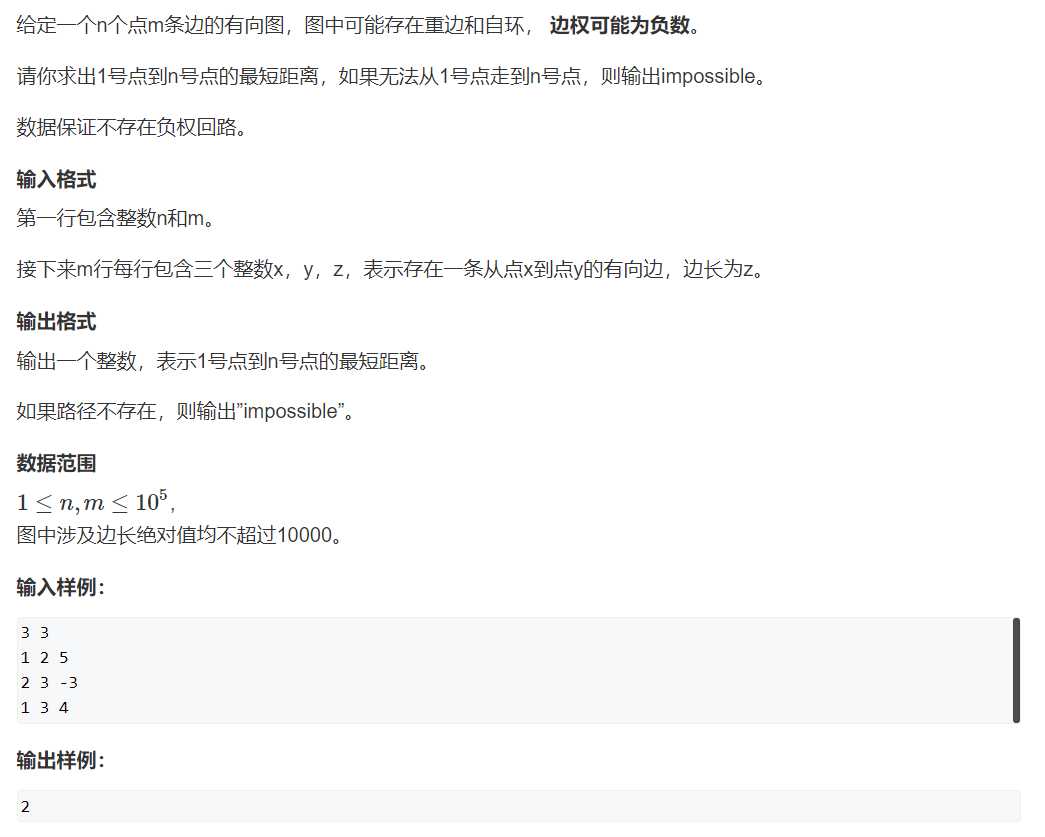
1 #include <cstring> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <queue> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 const int N = 1e5+10; 9 10 int n, m; 11 int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx; 12 int dis[N]; 13 bool st[N]; 14 15 void add(int a, int b, int c) 16 { 17 e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ; 18 } 19 20 int spfa() 21 { 22 memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);//初始化dis正无穷 23 dis[1] = 0;//将第一个点置为0 24 25 queue<int> q; 26 q.push(1);//将第一个点加入队列 27 st[1] = true;//标记已在队列中 28 29 while (q.size()) 30 { 31 int t = q.front(); 32 q.pop(); 33 34 st[t] = false;//从队列中取出,不在队列中 35 36 for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) 37 { 38 int j = e[i]; 39 if (dis[j] > dis[t] + w[i]) 40 { 41 dis[j] = dis[t] + w[i]; 42 if (!st[j])//只有不在队列中才要将其添加到队列中 43 { 44 q.push(j); 45 st[j] = true; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 51 return dis[n]; 52 } 53 54 int main() 55 { 56 cin >> n >> m; 57 58 memset(h, -1, sizeof h); 59 60 while (m -- ) 61 { 62 int a, b, c; 63 cin >> a >> b >> c; 64 add(a, b, c); 65 } 66 67 int t = spfa(); 68 69 if (t == 0x3f3f3f3f) puts("impossible"); 70 else cout << t << endl; 71 72 return 0; 73 }
标签:using ssi man 代码 添加 queue mem pop else
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/1-0001/p/12229954.html