标签:static 属性 成员变量 发展 setname The 第一个 c++ val
一:面向对象----Object
在Java中引入了对象和类的概念
-
对象是一个变量--------具体的东西;
-
类就是类型(是规范,是定义),从万千对象中抽取共性;
-
类规定了对象应该有的属性内容和方法;
-
对象就是类的具体实现,是活生生的;
-
例如:土豆丝菜谱是类,一盘土豆丝就是对象
-
从程序员的发展角度来理解,OO-Oriented Object是对OP—Oriented Procedure的一种改造。
-
OP面向过程更强调方法和动作,所有的变量是被动参与进来的,没有自主决定权
-
OO面向对象属于每个对象的。能否实现由每个对象说的算,有主人翁精神
OP代码实例:
-
public class OpExample {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
int a,b,c;
-
a = 1;
-
b = 2;
-
c = add(a,b);
-
System.out.println(c);
-
}
-
public static int add(int m,int n) {
-
return m+n;
-
}
-
OO实例:
-
public class OoExample {
-
private int a;
-
public void set(int a) {
-
this.a = a;
-
}
-
public int add(int b) {
-
return this.a+b;
-
}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
int b = 5;
-
OoExample obj = new OoExample();
-
obj.set(10);
-
System.out.println(obj.add(b));
-
}
-
-
}
二:Reference和基本类型
对象基本定义:
类型 变量名 = new 类型(参数)
A obj = new A(形参) int a=new int(5)等价与 int a=5
A obj1 = new A() A obj2 = new A()
以上有个对象,它们的类型都是A,但是两个不同的对象,在内存中有不同的存放的地址。因此没有完全两个对象是相同的
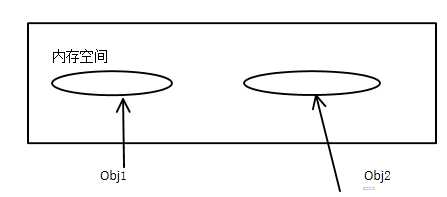
Obj可以看做是内存中一个对象的句柄,在C/C++中称为指针,在Java中是Reference。
对象赋值是Reference赋值,基本类型是直接拷贝。下面两个例子就是区分两者的区别。
-
public class Reference {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
int num1 = 5 ;
-
int num2= num1;
-
System.out.println("num1: "+num1+", num2: "+num2);
-
num2 = 10;
-
System.out.println("num1: "+num1+", num2: "+num2);
-
Mynumber obj1 = new Mynumber();
-
Mynumber obj2 = new Mynumber();
-
System.out.println(obj1.num);
-
System.out.println(obj2.num);
-
System.out.println("=========接下来输出新值===========");
-
obj2 = obj1;
-
obj2.num = 10;
-
System.out.println(obj1.num);
-
System.out.println(obj2.num);
-
}
-
}
-
public class Mynumber {
-
int num =5 ;
-
}
输出结果:
-
num1: 5, num2: 5
-
num1: 5, num2: 10
-
5
-
5
-
=========接下来输出新值===========
-
10
-
10
基本类型是值的copy,num2被num1赋值为5,所以内存num1和num2分别指向的就是内存中不同的地方,但是值都是5。当num2赋值为10时,num1的值不变。
Reference赋值就是第二种情况,obj2被obj1赋予值,这个时候,obj1和obj2作为指针都是指向内存中同一地址,任何一个值被初始化改变,两者都会改变。
有一个同样的例子可以证明:
-
public class ArguementPassing {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
int a =1; int b = 2;
-
swap(a,b);
-
System.out.println("a is: "+a+", b is: "+b);
-
Mynumber obj1 = new Mynumber();
-
Mynumber obj2 = new Mynumber();
-
obj2.num = 10;
-
swap(obj1,obj2);
-
System.out.println("obj1 is "+obj1.num+", obj2 is "+obj2.num);
-
}
-
public static void swap(int m,int n) {
-
int s = m;
-
m = n;
-
n = m;
-
}
-
public static void swap(Mynumber obj3, Mynumber obj4) {
-
int s = obj3.num;
-
obj3.num = obj4.num;
-
obj4.num = s;
-
}
-
}
输出结果:
-
a is: 1, b is: 2
-
obj1 is 10, obj2 is 5
三:数据初始化
New出对象后,内部属性值默认是多少?
-
public class Initialization {
-
boolean v1;// boolean v1 = new b
-
byte v2;
-
char v3;
-
double v4;
-
long v5;
-
int v6 ;
-
float v7;
-
short v8;
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
Initialization obj = new Initialization();
-
System.out.println("the value of boolean is "+obj.v1);
-
System.out.println("the value of byte is "+obj.v2);
-
System.out.println("the value of char is "+obj.v3);
-
System.out.println("the value of double is "+obj.v4);
-
System.out.println("the value of long is "+obj.v5);
-
System.out.println("the value of int is "+obj.v6);
-
System.out.println("the value of float is "+obj.v7);
-
System.out.println("the value of short is "+obj.v8);
-
}
-
}
输出结果:
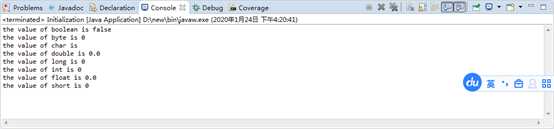
同时有一点需要注意:类的成员变量,javac会直接赋值,但是对于函数内部的局部变量不会给默认值,需要初始化后才能使用。
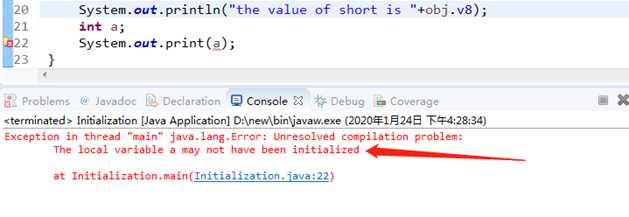 函数内部的a没有初始化赋值,直接报错了。
函数内部的a没有初始化赋值,直接报错了。
四:构造函数
根据第三节,成员变量是有默认值的。我们希望对象在创建的时候就能自定义赋值,这就需要构造函数去自定义赋值。
- Java构造函数的名称必须和类名一致,且没有返回值—也不能写void
- 每个变量都是有生命周期的,它是只能存储在离他最近的一个{}中---参考LifeCycle.java
- 当变量被创建时,变量将暂居内存;当变量消亡时,系统将回收内存。Java具有自动回收机制,当变量退出生命周期后,Jvm将自动回收所分配的对象的内存。所以不需要析构函数去释放内存(析构函数----C语言特性)
代码实例:
-
public class LifeCycle {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
int a = 0; // a在main函数中都是active
-
for(int i = 0; i<5;i++) { // i只存活在for循环中
-
int k =0;
-
k++;
-
}
-
if(a>0) {
-
Object obj1 = new Object();
-
System.out.println("a is positive"); // obj1 只存活在if分支
-
}
-
else {
-
Object obj2 = new Object();
-
System.out.println("a is no positive");// Obj2只存活在else分支
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
每个Java类都有构造函数,如果没有显示的构造函数,Java类将会产生一个空的无形参构造函数
-
每个子类的构造函数的第一句话,都默认调用父类的无参数构造函数super(),除非子类的构造函数第一句话是super,而且super语句必须放在第一条------这个在后面的系列四补充
-
一个类一个有多个构造函数,只要形参不同即可
-
class MyPairNumber{
-
int m,n;
-
public MyPairNumber() {m = 0;n=0;}
-
public MyPairNumber(int a) {m=a;n=0;}
-
public MyPairNumber(int a,int b) {m = a; m = b;}
-
}
-
public class Constructor {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
MyPairNumber obj1 = new MyPairNumber();
-
MyPairNumber obj2 = new MyPairNumber(10);
-
MyPairNumber obj3 = new MyPairNumber(11, 12);
-
System.out.println("obj1 has "+obj1.m+obj1.n);
-
System.out.println("obj2 has "+obj2.m+obj2.n);
-
System.out.println("obj3 has "+obj3.m+obj1.n);
-
-
}
-
-
}
三个构造函数里面根据三个形参不同来调用。
五:信息隐藏和this
面向对象有一个法则:信息隐藏
----类的成员属性是私有的,private,为避免通过对象.属性的方法来调用
----类的方法是公有的 public,通过方法修改成员属性的值,通过get和set方法来操作,可以使用Java IDE直接生成----具体方法大家自行百度
-
public class Perpson {
-
private int age;
-
private String name;
-
public int getAge() {
-
return age;
-
}
-
public void setAge(int age) {
-
this.age = age;
-
}
-
public String getName() {
-
return name;
-
}
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
this.name = name;
-
}
-
}
如上图程序,我们可以通过obj.setName方法去给Name属性赋值。
其实涉及到this,this.变量可以获取类变量的值;
This负责指向本类中的成员----成员变量和成员方法
This可以代替本类中的构造函数
-
public class MyPairNumber {
-
private int m;
-
private int n;
-
public int getM() {
-
return m;
-
}
-
public void setM(int m) {
-
this.m = m;//this代替成员变量
-
}
-
public int getN() {
-
return n;
-
}
-
public void setN(int n) {
-
this.n = n;
-
}
-
public MyPairNumber() {
-
this(0, 0);
-
}
-
public MyPairNumber(int m) {
-
this(m, 0); //This代替构造函数会调用23行
-
}
-
public MyPairNumber(int m, int n) {
-
this.m = m;
-
this.n= n;
-
}
-
public int sum() {
-
return this.add(m,n); //this代替成员方法 可省略
-
}
-
public int add(int a, int b){
-
return a+b;
-
}
-
}
执行以下程序,传入参数5,会调用19行构造函数,19行会调用23行构造函数,得到m n的值,系统输入调用sum方法,sum方法体调用add方法
-
public class ThisTest {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
MyPairNumber obj = new MyPairNumber(5);
-
-
System.out.println(obj.sum());
-
}
-
-
}
{Java初级系列三}----面向对象和类
标签:static 属性 成员变量 发展 setname The 第一个 c++ val
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yblecs/p/12234882.html


 函数内部的a没有初始化赋值,直接报错了。
函数内部的a没有初始化赋值,直接报错了。