标签:取出 算法 指针变量 otto lock 插入 block 链式 convert
栈是一种应用特别广泛的数据结构,是一种典型的数据结构,实现后悔和回退功能.本实例为:将任意十进制转变为任意进制进行表示。由于进制转换中转换过程中存在取余倒序很好的契合栈"先进后出"的特点,故使用栈存储结构进行实现
★栈(stack):只能在一端插入和删除的线性表,又称为“先进后出”的线性表,或“后进先出”的线性表。
★栈顶(top):允许进行插入,删除操作的一端,又称为表尾。
★栈底(bottom):是固定端,又称为表头。
★空栈:当表中没有元素时称空栈。
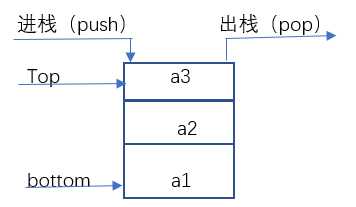
和线性表类似,栈也有多种存储表示方法
1.1顺序栈1
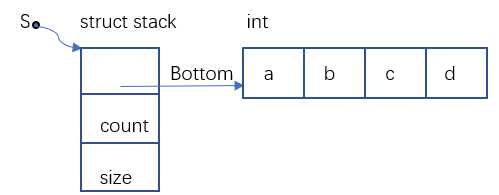
1.2顺序栈2
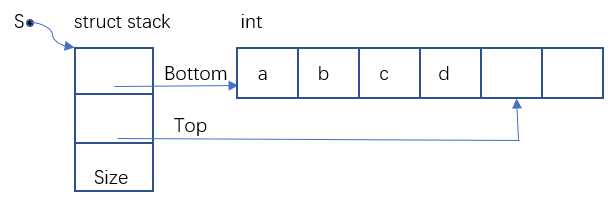
2.1链式栈
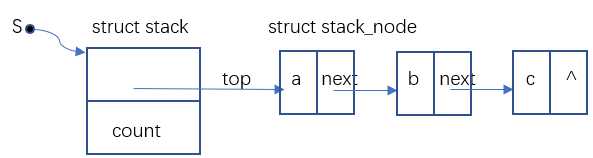
struct stack stack_init();//初始化栈存储空间
void stack_free(struct stack s);//释放内存空间
void stack_clear(struct stack s);//清空内存空间的数据元素
int stack_isempty(struct stack s);//判断存储空间的数据元素是否为空
int stack_count(struct stack s); //返回栈中数据元素个数
void stack_push(struct stack s,int e); //压栈
int stack_pop(struct stack s); //将栈中元素弹出来
int stack_top(struct stack s); //返回栈顶元素
Stack.h
#ifndef __STACK_H__
#define __STACK_H__
Struct stack;
Struct stack *stack_init();
Void stack_free(struct stack *s);
Void stack_clear(struct stack *s);
Int stack_isempty(struct stack *s);
Int stack_count(struct stack *s);
Void stack_push(struct stack *s,int e);
Int stack_pop(struct stack *s);
Int stack_top(struct stack *s);
#endifMain.c
//将任意十进制转换为八进制表示
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "stack.h"
void convert10toD(int n,int d);
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
//定义指针变量s指向stack类型的结构体
struct stack *s=NULL;
//初始化栈空间
s=stack_init();
//将3/5/6依次入栈
stack_push(s,3);
stack_push(s,5);
stack_push(s,6);
//栈顶元素
printf("The top elememnt is %d.\n",stack_top(s));
printf("The array isempty %d.\n",stack_isempty(s));
//将栈中元素依次取出
while(!stack_isempty(s)){
printf("The element is %d.\n",stack_pop(s));
}
stack_free(s);
printf("\n\n");
//将10进制数在158装换为8进制
convert10toD(158,8);
return 0;
}
void convert10toD(int n,int d)
{
struct stack *s=NULL;
s=stack_init();
int k;
//逐级取余,依次入栈
while(n>0){
k=n%d;
stack_push(s,k);
n=n/d;
}
//将栈中元素取出(由于栈"先进后出"的特点完成倒序)
while(!stack_isempty(s)){
printf("%d\n",stack_pop(s));
}
stack_free(s);
return;
}Stack.c
结构①
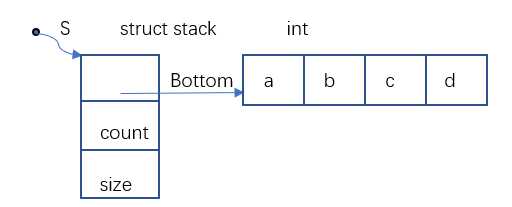
//顺序栈
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "stack.h"
//定义数组初始长度为1,每次增加1
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 1
#define STACK_INCR_SIZE 1
//定义一级结构,botton用于指向栈底(用来存放数组的首地址),count用来记录栈中数据元素的个数,size用于记录定义栈结构(栈结构中数组)的长度
struct stack{
int *bottom;
int count;
int size;
};
//初始化栈存储结构
struct stack *stack_init()
{
struct stack *s=NULL;
s=(struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if(s==NULL) return NULL;
assert(s!=NULL);
s->bottom=NULL;
s->count=0;
s->size=0;
s->bottom=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
if(s->bottom==NULL){
free(s);
return NULL;
}
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
//将栈中元素清零
memset(s->bottom,0,sizeof(int)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
s->size=STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return s;
}
void stack_free(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
free(s->bottom);
free(s);
}
void stack_clear(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
s->count=0;
}
int stack_isempty(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
return (s->count==0);
}
int stack_count(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
return s->count;
}
void stack_push(struct stack *s,int e)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
//如果栈空间不够,使用realloc()函数进行扩容操作
if(s->count==s->size){
s->bottom=(int *)realloc(s->bottom,sizeof(int)*(s->size+STACK_INCR_SIZE));
s->size+=STACK_INCR_SIZE;
}
s->bottom[s->count]=e;
//每添加一个数据元素,s->count指向新元素后面一个空的位置,方便下次存储
s->count++;
return;
}
//将栈中数据元素弹出
int stack_pop(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
int result=-1;
result=s->bottom[s->count-1];
s->count--;
return result;
}
//取出栈定元素
int stack_top(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
return s->bottom[s->count-1];
}结构②
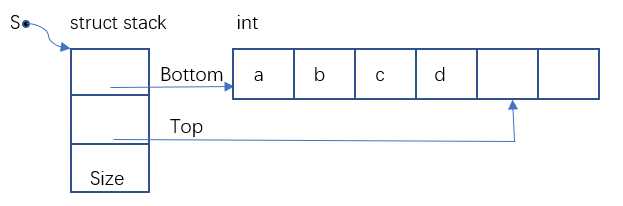
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "stack.h"
#define STACK_INIT_SIZE 1
#define STACK_INCR_SIZE 1
//定义结构体作为一级结构,bottom指向栈底,top指向栈顶下一个内存空间,size记录定义的栈空间的长度
struct stack{
int *bottom;
int *top;
int size;
};
struct stack *stack_init()
{
struct stack *s=NULL;
s=(struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if(s==NULL) return NULL;
assert(s!=NULL);
s->bottom=NULL;
s->top=NULL;
s->size=0;
s->bottom=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
if(s->bottom==NULL){
free(s);
return NULL;
}
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
memset(s->bottom,0,sizeof(int)*STACK_INIT_SIZE);
s->top=s->bottom;
s->size=STACK_INIT_SIZE;
return s;
}
void stack_free(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s->top!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
free(s->bottom);
free(s);
}
void stack_clear(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
//让栈顶指针指向栈底实现清除功能
s->top=s->bottom;
}
int stack_isempty(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
return (s->top==s->bottom);
}
int stack_count(struct stack *s)
{
ssert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
//栈顶指针减去栈底指针得到栈中有多少个数据元素
return s->top-s->bottom;
}
void stack_push(struct stack *s,int e)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
if((s->top-s->bottom)==s->size){
s->bottom=(int*)realloc(s->bottom,sizeof(int)*(s->size+STACK_INCR_SIZE));
s->size+=STACK_INCR_SIZE;
}
//添加数据到栈顶
*(s->top)=e;
s->top++;
return;
}
int stack_pop(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
int result=-1;
result=*(s->top-1);
s->top--;
return result;
}
int stack_top(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s->bottom!=NULL);
assert(s!=NULL);
return *(s->top-1);
}结构③
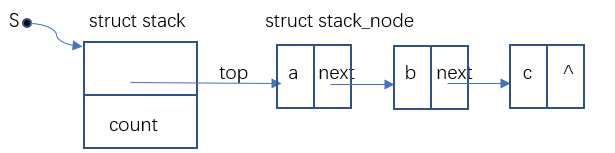
//链式栈
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "stack.h"
//定义结构体作为数据节点,data用来存放数据,next用来存放下一个数据节点的首地址
struct stack_node{
int data;
struct stack_node *next;
};
//定义一级结构,top用来存放数据节点的地址,count用来记录栈结构共包含多少数据节点
struct stack{
struct stack_node *top;
int count;
};
struct stack *stack_init()
{
struct stack *s=NULL;
s=(struct stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
if(s==NULL) return NULL;
assert(s!=NULL);
s->top=NULL;
s->count=0;
return s;
}
void stack_free(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
struct stack_node *p=NULL;
//逐级将数据节点释放
while(s&&s->top!=NULL){
p=s->top;
p=p->next;
free(p);
}
free(s);
}
void stack_clear(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
struct stack_node *p=NULL;
while(s&&s->top!=NULL){
p=s->top;
s->top=p->next;
free(p);
}
s->count=0;
}
int stack_isempty(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
return (s->count==0);
}
int stack_count(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
return s->count;
}
void stack_push(struct stack *s,int e)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
//定义结构体指针变量node指向stack_node结构体类型的数据
struct stack_node *node=NULL;
//node指向新开辟的stack_node结构体类型大小的存储空间
node=(struct stack_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stack_node));
if(node==NULL) {
perror("malloc struct error\n");
exit(0);
}
//将数据元素e赋到结构体中
node->data=e;
node->next=NULL;
//将数据节点添加到链上
node->next=s->top;
s->top=node;
s->count++;
return;
}
int stack_pop(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
int result=-1;
struct stack_node *node=NULL;
//将数据节点断开
node=s->top;
s->top=node->next;
s->count--;
//取出数据节点中的数据元素
result=node->data;
return result;
}
int stack_top(struct stack *s)
{
assert(s!=NULL);
return s->top->data;
}六. 编译结果
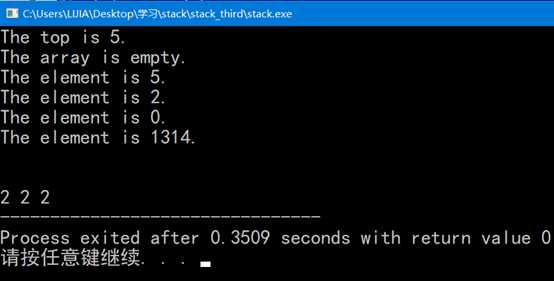
标签:取出 算法 指针变量 otto lock 插入 block 链式 convert
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/miaowulj/p/12237920.html