标签:style 方便 string 构造 控制 str close 输出流 write
平时我们在控制台打印输出,是调用print方法和println方法完成的,这两个方法都来自于java.io.PrintStream类,该类能够方便地打印各种数据类型的值,是一种便捷的输岀方式。
PrintStream类,为其他输出流添加了功能,使他们能够方便的打印各种数据值表示格式。
PrintStream类的特点:
PrintStream(String fileName) // 使用指定的文件名创建一个新的打印流。
PrintStream extends OutputStream
1、public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException; // 将指定的字节输出流。 2、public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException{...}; // 将b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。 3、public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException{...}; // 从指定的字节数组写入len字节,从偏移量off开始输出到此输出流。 4、public void flush() throws IOException{}; // 刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。 5、public void close() throws IOException {}; // 关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。
说明:
如果使用继承父类的write方法写数据,那么查询数据的时候,会查询编码表。
如果使用自身特有的print方法、println方法写数据,那么写的数据会原样输出。
举例:往print.txt空文件中写入数据
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintStream; public class DemoPrintStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { // 创建PrintStream对象,传入输出的路径,路径需要存在,否则会抛出FileNotFoundException异常 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("/Users/liyihua/IdeaProjects/Study/src/view/study/demo37/print"); // 使用父类OutputStream的write方法,写入数据 ps.write(97); // 使用自身特有的方法,写入数据 ps.print(97); // 释放资源 ps.close(); } }
print.txt文件内容如下:
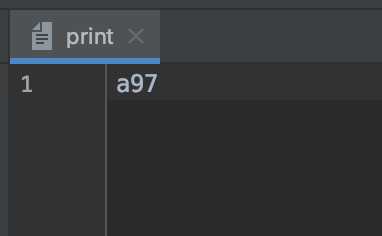
数据a是使用父类中的write方法写入的。数据97是使用自身特有方法写入的。
分析:输出语句,默认是在控制台输出,使用System.setOut方法,可以改变输出语句的目的地。
static void setOut(PrintStream out) // 将输出语句的目的地,改变为参数中传递的打印流的目的地。 参数: PrintStream out:打印流对象
代码实现:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintStream; public class DemoSetOut { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { // 在控制台输出 System.out.println("我是在控制台输出的!!!"); // 在空的setOut.txt文件中输出 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("/Users/liyihua/IdeaProjects/Study/src/view/study/demo37/setOut"); System.setOut(ps); System.out.println("我是在setOut.txt文件中输出的!!!"); // 释放资源 ps.close(); } }
控制台输出:
我是在控制台输出的!!!
setOut.txt文件内容:
我是在setOut.txt文件中输出的!!!
标签:style 方便 string 构造 控制 str close 输出流 write
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/liyihua/p/12275339.html