标签:一个 http read 开始 准备 ati exce main adb
首先介绍线程的五种状态:
新生态:New Thread()
就绪态:准备抢CPU时间片
运行态:抢到了CPU时间片
阻塞态:放弃已经抢到的CPU时间片,且暂时不参与争抢
死亡态:Run运行完了之后
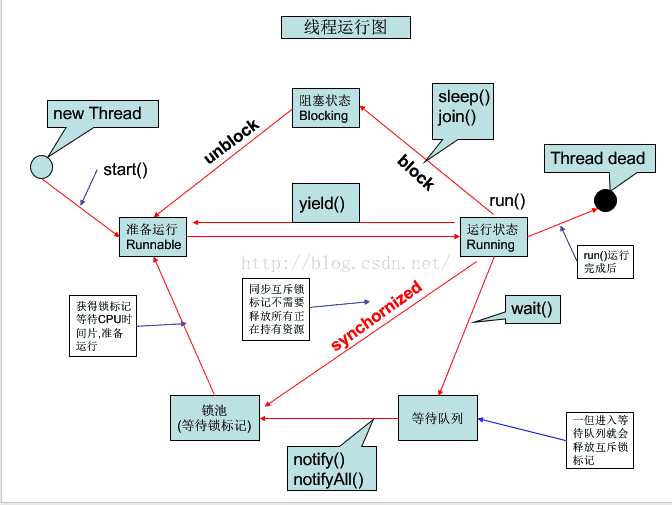
接下来介绍三种方法:线程的阻塞,线程的优先级设置,线程的礼让
1 public class MutliThreadDemo4 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 threadBlock();
4 //threadPriority();
5 //threadYield();
6
7 }
8 /**
9 * 线程的阻塞
10 */
11 private static void threadBlock() {
12 //创建Runnable接口实现类的对象
13 Runnable r = () -> {
14 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
16 //线程休眠(由运行状态到阻塞状态,时间过了回到就绪态,重新争抢),直观上表现为停顿打印
17 try {
18 Thread.sleep(1000);
19 }catch(InterruptedException e){
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }
22 }
23 };
24 //实例化
25 new Thread(r, "甲").start();
26 }
27
28 /**
29 * 线程的优先级
30 */
31 private static void threadPriority() {
32
33 Runnable r = () -> {
34 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
35 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
36 }
37 };
38 Thread t1 = new Thread(r, "甲");
39 Thread t2 = new Thread(r, "乙");
40
41 //设置优先级,必须在开始执行(start)之前
42 //设置线程的优先级,只是修改这个线程可以去抢到CPU时间片的概率。
43 //并不是优先级高的线程一定能抢到CPU时间片
44 //优先级的设置,是一个整数(0,10]的整数,默认是5
45 t1.setPriority(10);
46 t2.setPriority(1);
47
48 t1.start();
49 t2.start();
50
51 }
52 /**
53 * 线程的礼让
54 */
55 private static void threadYield() {
56 //线程释放自己的CPU资源,由运行状态,回到就绪状态
57 //匿名内部类
58 Runnable r = new Runnable() {
59 public void run() {
60 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
61 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
62 if (i == 3) {
63 Thread.yield();
64 }
65 }
66 }
67 };
68 Thread thread1 = new Thread(r, "thread-1");
69 Thread thread2 = new Thread(r, "thread-2");
70
71 thread1.start();
72 thread2.start();
73 }
74 }
标签:一个 http read 开始 准备 ati exce main adb
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ggrrbb/p/12289677.html