标签:计时 png 加载 自动 代码 获得 class 图片 val
一、强制等待sleep()
‘‘‘ 设置固定休眠时间,单位为秒。 由python的time包提供, 导入 time 包后就可以使用。 缺点:不智能,使用太多的sleep会影响脚本运行速度。 ‘‘‘ import time sleep(10) #等待10秒
二、隐式等待:implicitly_wait()
‘‘‘ 由webdriver提供的方法,一旦设置,这个隐式等待会在WebDriver对象实例的整个生命周期起作用,
它不针对某一个元素,是全局元素等待,即在定位元素时,需要等待页面全部元素加载完成,才会执行下一个语句。
如果超出了设置时间的则抛出异常。 ‘‘‘ driver.implicitly_wait(10) #隐式等待10秒
需要特别说明的是:隐性等待对整个driver的周期都起作用,所以只要设置一次即可,有人把隐性等待当成了sleep在用,走哪儿都来一下…
三、显示等待:WebDriverWait()
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait WebDriverWait(driver,timeout,poll_frequency=0.5,ignored_exceptions=None) ‘‘‘ driver: 传入WebDriver实例,即我们上例中的driver timeout: 超时时间,等待的最长时间(同时要考虑隐性等待时间) poll_frequency: 调用until或until_not中的方法的间隔时间,默认是0.5秒 ignored_exceptions: 忽略的异常,如果在调用until或until_not的过程中抛出这个元组中的异常,则不中断代码,继续等待,
如果抛出的是这个元组外的异常,则中断代码,抛出异常。默认只有NoSuchElementException。
until method: 在等待期间,每隔一段时间调用这个传入的方法,直到返回值不是False message: 如果超时,抛出TimeoutException,将message传入异常
until_not 与until相反,until是当某元素出现或什么条件成立则继续执行,until_not是当某元素消失或什么条件不成立则继续执行,参数也相同,不再赘述。 ‘‘‘
看了以上内容基本上很清楚了,调用方法如下:
WebDriverWait(driver, 超时时长, 调用频率, 忽略异常).until(可执行方法, 超时时返回的信息)
可执行方法包含:
expected_conditions是selenium的一个模块,其中包含一系列可用于判断的条件:
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
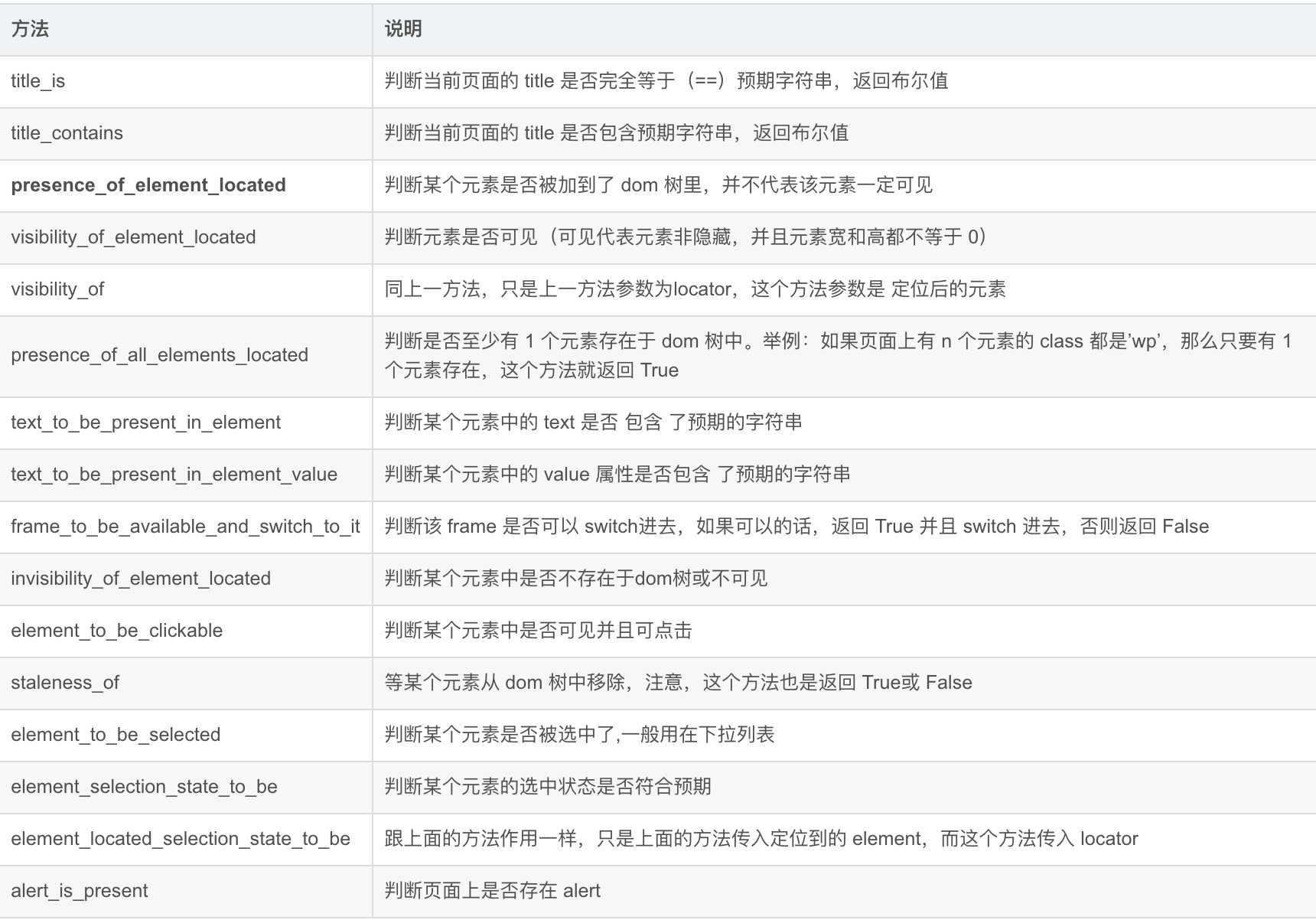
判断当前页面标题是否为title
title_is(title)
title:期望的页面标题
判断当前页面标题是否包含title
title_contains(title)
title:期望的页面标题
判断此定位的元素是否存在
presence_of_element_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断页面网址中是否包含url
url_contains(url)
url:期望的页面网址
判断页面网址是否为url
url_to_be(url)
url:期望的页面网址
判断页面网址不是url
url_changes(url)
url:期望的页面网址
判断此定位的元素是否可见
visibility_of_element_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此元素是否可见
visibility_of(element)
element:所获得的元素
判断此定位的一组元素是否至少存在一个
presence_of_all_elements_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此定位的一组元素至少有一个可见
visibility_of_any_elements_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此定位的一组元素全部可见
visibility_of_all_elements_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此定位中是否包含text_的内容
text_to_be_present_in_element(locator, text_)
locator:元素的定位信息
text_:期望的文本信息
判断此定位中的value属性中是否包含text_的内容
text_to_be_present_in_element_value(locator, text_)
locator:元素的定位信息
text_:期望的文本信息
判断定位的元素是否为frame,并直接切换到这个frame中
frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断定位的元素是否不可见
invisibility_of_element_located(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此元素是否不可见
invisibility_of_element(element)
element:所获得的元素
判断所定位的元素是否可见且可点击
element_to_be_clickable(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断此元素是否不可用
staleness_of(element)
element:所获得的元素
判断该元素是否被选中
element_to_be_selected(element)
element:所获得的元素
判断定位的元素是否被选中
element_located_to_be_selected(locator)
locator:元素的定位信息
判断该元素被选中状态是否和期望状态相同
element_selection_state_to_be(element,Boolean)
element:所获得的元素
Boolean:期望的状态(True/False)
判断定位的元素被选中状态是否和期望状态相同
element_located_selection_state_to_be(locator,Boolean)
locator:元素的定位信息
Boolean:期望的状态(True/False)
判断当前浏览器页签数量是否为num
number_of_windows_to_be(num)
num:期望的页签数量
判断此handles页签不是唯一打开的页签
new_window_is_opened(handles)
handles:页签
判断是否会出现alert窗口警报
alert_is_present()
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「许西城」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/CCGGAAG/article/details/86763952
例子:需要定位倒计时结束后的 【知道啦】按钮,并点击

上代码:
wait_element_by_xpath
from selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait def wait_element_by_xpath(driver, timeout, element_text,poll_frequency=0.5, element_by="xpath",ignored_exceptions=None): """ 等待元素出现 :param driver: :param timeout: 最长超时时间,默认以秒为单位 :param element_text: :param poll_frequency: 检测的间隔步长,默认为0.5s :param element_by: :param ignored_exceptions:超时后的抛出的异常信息,默认抛出NoSuchElementException异常。 :return: """ loc = (element_by, "//*[@text=‘%s‘]" % element_text) MyLog.logger().info(loc) e = WebDriverWait(driver, timeout, poll_frequency,ignored_exceptions).until(EC.presence_of_element_located(loc)) e.click()
调用
find_element.wait_element_by_xpath(self.driver,2,"知道啦")
七、Appium-python-UI自动化之强制等待:sleep,隐式等待:implicitly_wait,显示等待:WebDriverWait()
标签:计时 png 加载 自动 代码 获得 class 图片 val
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chushujin/p/12307746.html