标签:实现 ret val nim bool get 扩展 功能 string
SpringIoC容器用来容纳我们开发的各种Bean,并且我们可以从中获取各种发布在Spring IoC容器中的Bean,并通过描述来获取它。
Spring IoC容器的设计主要是基于BeanFactory和ApplicationContext两个接口,其中ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口,BeanFactory是Spring IoC容器所定义的最底层的接口,ApplicationContext是其高级接口之一,并且对BeanFactory的功能做了增强,所以我们主要使用ApplicatinContext作为Spring IoC的容器。
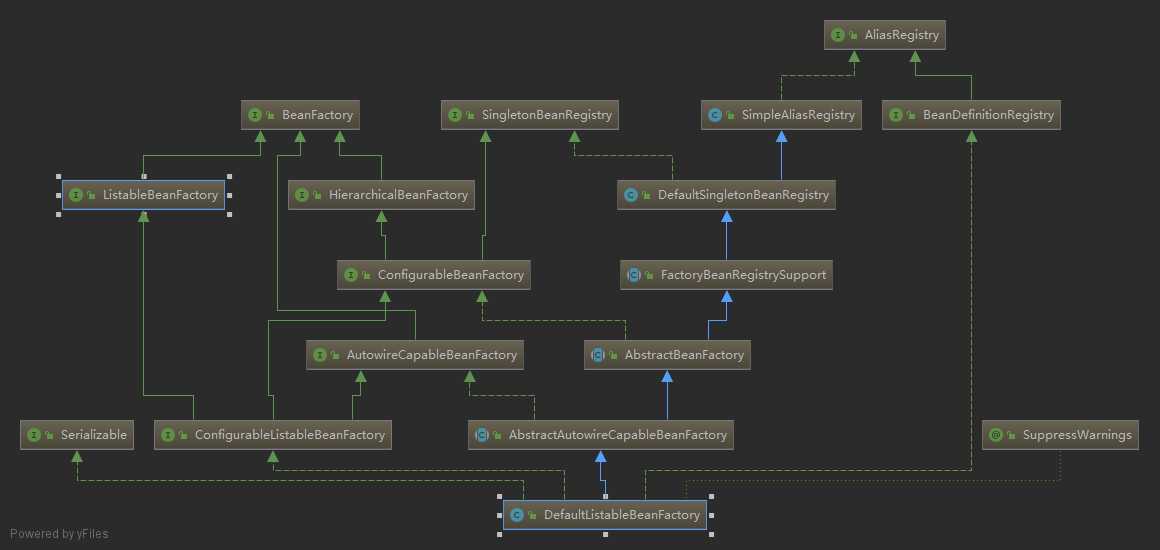
Spring为BeanFactory提供了很多的实现类,如图
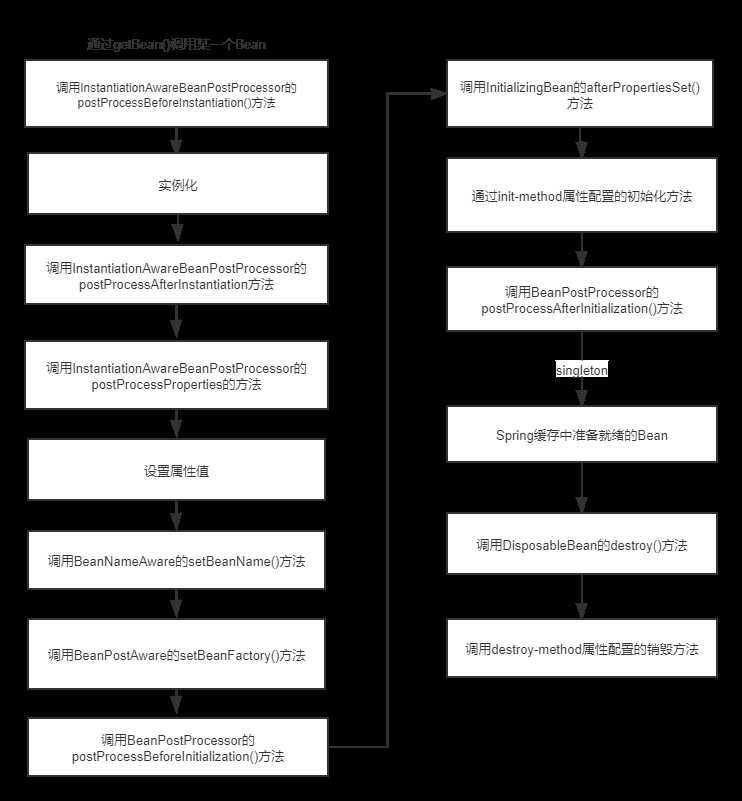
具体过程
定义一个Bean类并实现BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean接口
public class Animal implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
private int age;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
public Animal() {
System.out.println("调用Animal的构造方法");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("调用AnimalsetName设置属性");
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
System.out.println("调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()。");
this.beanName = beanName;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()。");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("调用DisposableBean.destory()。");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("调用myInit(),");
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("调用myDestroy()。");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", beanFactory=" + beanFactory +
'}';
}
}定义一个MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor并继承InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("animal".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation");
}
return super.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("animal".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation");
}
return super.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("animal".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues");
}
return pvs;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}定义一个MyBeanPostProcessor并实现BeanPostProcessor接口
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("animal")){
Animal animal=(Animal)bean;
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(): "+animal);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(beanName.equals("animal")){
Animal animal=(Animal)bean;
System.out.println("调用MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(): "+animal);
}
return bean;
}
}编写xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="animal" class="com.rookie.bigdata.factory.domain.Animal" destroy-method="myDestory" init-method="myInit">
<property name="name" value="哈士奇"></property>
<property name="age" value="3"></property>
</bean>
</beans>编写测试类
public class BeanFactoryMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourcePatternResolver resolver=new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Resource resource = resolver.getResource("classpath:beanfactory/beans.xml");
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory=new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader=new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
Person person = (Person)factory.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
}这样在运行测试类,就可以看到BeanFactory的整个运行的声明周期过程啦。
标签:实现 ret val nim bool get 扩展 功能 string
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/haizhilangzi/p/11110474.html