标签:思路 基于 amp 长度 bsp oid 调用 排序 cto
个人第一眼想法是通过一个sort函数,再判断中间那数出现次数,只要出现多于n/2,就直接输出。
一般来说,最为直观的算法面试官都不会满意,那么有没有更优的算法呢?
这种算法是受快速排序算法的启发。在随机快速排序算法中,我们现在数组中随机选择一个数字,然后调整数组中数字的顺序,使得比选中的数字小的数字都排在它的左边,比选中的数字大的数字都排在它的右边。如果这个选中的数字的下标刚好是n/2,那么这个数字就是数组的中位数。如果它的下标大于n/2,那么中位数应该位于它的左边,我们可以接着在它的左边部分的数组中查找。如果它的下标小于n/2,那么中位数应该位于它的右边,我们可以接着在它的右边部分的数组中查找。这是一个典型的递归过程,实现代码如下:
1 int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int> numbers) 2 { 3 int length = numbers.size(); 4 if (numbers.empty() || length<0) 5 return 0; 6 7 int begin = 0; 8 int end = length - 1; 9 int middle = length >> 1; 10 int index = 0; 11 //利用 12 while (begin<end) 13 { 14 index = Partition(numbers, begin, end); 15 if (index == middle) 16 { 17 break; 18 } 19 else if (index > middle) 20 { 21 end = index - 1; //则值在左边部分的数组。 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 begin = index + 1;//则值在右边部分的数组。 26 } 27 } 28 //检查该值是否超过数组长度的一半 29 int cnt = 0; 30 for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) 31 { 32 if (numbers[index] == numbers[i]) 33 cnt++; 34 } 35 if (cnt * 2 > length) return numbers[index]; 36 37 return 0; 38 }
partition函数思路:
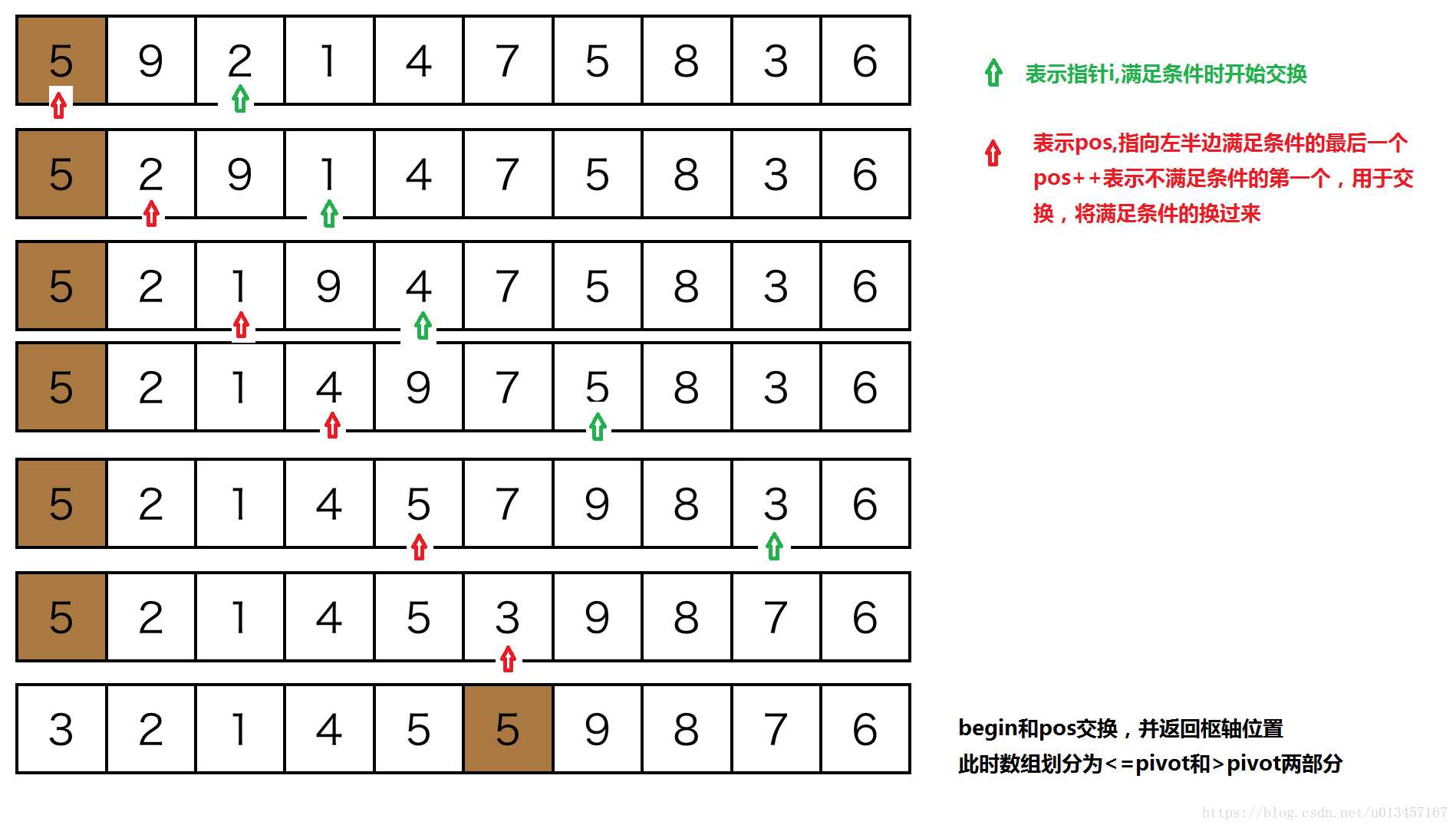
代码如下:
1 void swap(int &x, int &y) 2 { 3 int t = x; 4 x = y; 5 y = t; 6 7 } 8 int partition(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end) 9 { 10 int pivot = nums[begin];//枢轴(也可以是在begin和end之间的随机数) 11 // Last position where puts the no_larger element. 12 //凡是小于pivot的全部放到数组左端,pos指向<枢轴值的最后一个 13 //pos++指向不满足条件的(用于交换,将满足条件的换过来) 14 int pos = begin; 15 for (int i = begin + 1; i < end; ++i) 16 { 17 if (nums[i] < pivot) 18 { 19 pos++; 20 if (i != pos) //避免自身交换 21 swap(nums[pos], nums[i]); 22 } 23 24 } 25 swap(nums[pos], nums[begin]); 26 return pos; 27 }
算法分析
这种实现思路比较直观,但是其实并不高效。从直观上来分析一下,每个小于pivot的值基本上(除非到现在为止还没有遇见大于pivot的值)都需要一次交换,大于pivot的值(有可能需要被交换多次才能到达最终的位置。
算法思路
如果我们考虑用 Two Pointers 的思想,保持头尾两个指针向中间扫描,每次在头部找到大于pivot的值,同时在尾部找到小于pivot的值,然后将它们做一个交换,就可以一次把这两个数字放到最终的位置。一种比较明智的写法如下:
//Two Pointers思想的分割函数(begin为0,end为n-1) int Partition(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end) { int pivot = nums[begin];//第一个记录作为枢轴(也可是在begin和end之间的随机数) while (begin < end) { while (begin < end && nums[end] >= pivot) { end--; } nums[begin] = nums[end];//尾部找到小于pivot的值,移到低端 while (begin < end && nums[begin] <= pivot) { begin++; } nums[end] = nums[begin];//头部找到大于pivot的值,移到高端 } nums[begin] = pivot;//枢轴基准归位 return begin; }
算法分析:赋值操作不多,效率会更高
void quickSort(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end) { if (begin >= end) return; int index = partition(nums, begin, end); if (index>begin) quickSort(nums, begin, index-1); if (index<end) quickSort(nums, index+1, end); } 调用: quickSort(vec, 0, vec.size()-1); //end为n-1
标签:思路 基于 amp 长度 bsp oid 调用 排序 cto
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/knis/p/12334095.html