一、文本属性
1.text-align:cnter 文本居中
2.line heigth 垂直居中 :行高,和高度对应
3.设置图片与文本的距离:vertical-align
4.text-decoration:none 去掉超链接下划线
5.要是给a标签修改颜色的时候,就定到a标签上,用继承有时候是搞不定的
因为继承的级别是很低的,如果a标签设置了样式,是不会继承父亲的
6.首行缩进:text-indent:30px
7.font-style:oblique 或者italic....(设置字体的样式为斜体)
二、背景属性
">background-image:url(‘11.jpg‘); 背景图片链接
background-repeat:repeat-x; x轴平铺
background-repeat:no-repeat; 不重复
background-position:400px 200px 调整背景的位置(距左。距右)
background-position: center:center; 背景居中
简写:
background: url(‘11.jpg‘) no-repeat center;

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>背景处理</title> <style> .c1{ width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid red; background: url("xhr.jpg") -206px -29px; /*可在那个网页上右击点击检查,调试*/ /*background-position: center; */ /*定位*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"> </div> </body> </html> 背景调试小黄人的眼睛
三、边框属性
常用属性
简写:border :1px soild red;
deshed:虚线
只加有一个方向的:border-right :1px soild red;
四、列表属性
去掉列表前面的标志:ul li{list-style:none;}
去掉列表前面的空格:ul{padding:0}
上面两行也可写成下面一行
去掉盒子上面的间隙:*{margin:0; padding :0;}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
ul li{
font-family: 华文中宋;
list-style: none; //去掉点
/*list-style: circle;//空心圆*/
/*list-style: disc;//实心圆(默认也是实心圆)*/
}
ul{
padding: 0; //把字体移到前面
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<ul>
<li>第一章</li>
<li>第二章</li>
<li>第三章</li>
<li>第四章</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
五、display属性
display属性
1.将块级标签设置成内联标签:disply:inline;
2.将内联标签设置成块级标签:disply:block;
3.内联块级标签:像块级一样可设长宽,也可像内联一样在一行显示:display:inline-block;
4.display:none; 吧不想让用户看到的给隐藏了(很重要的一个属性)
5.visibility :hiddon; 也是隐藏
注意与visibility:hidden的区别:
visibility:hidden:可以隐藏某个元素,但隐藏的元素仍需占用与未隐藏之前一样的空间。也就是说,该元素虽然被 隐藏了,但仍然会影响布局。
display:none:可以隐藏某个元素,且隐藏的元素不会占用任何空间。也就是说,该元素不但被隐藏了,而且该元 素原本占用的空间也会从页面布局中消失

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ width: 100px; height:100px; background-color: rebeccapurple; } .c2{ width: 100px; height:100px; background-color: burlywood; } .c3{ width: 100px; height:100px; background-color: crimson; display: inline; } .c4{ width: 100px; height:100px; background-color: gray; } .s1{ display: block; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: royalblue; /*visibility: hidden;*/ //隐藏了其他的不会顶上去 display:none; //隐藏了其他的会顶上去 } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c4">div</div> <span class="s1">span</span> <div class="c1">年后</div> <div class="c2">年后</div> <div class="c3">年后</div> </body> </html> 举例
六、边距的塌陷问题
1、兄弟div:
上面div的margin-bottom和下面div的margin-top会塌陷,也就是会取上下两者margin里最大值作为显示值
2、父子div:
if 父级div中没有border,padding,inlinecontent,子级div的margin会一直向上找,直到找到某个标签包括border,padding,inline content中的其中一个,然后按此div 进行margin;

解决方法
解决方法
这两种会改变结构
1.加上padding
2.加上border
不改变结构
3.overflow:hidden

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; } .outer{ background-color: gold; width: 300px; height: 300px; /*第一种解决方法:但是改变了结构padding: 10px;*/ /*第二种方法:加个border*/ /*border: 1px solid;*/ /*第三种方法*/ overflow: hidden; } .box1{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: blue; /*如果父级标签什么都没有,那么就会找叔叔的*/ margin-top:10px; } .box2{ width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: darksalmon; /*如果这样的话就合适呢,对着就下去了*/ margin-top: 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <div style="background-color: burlywood; width:300px; height :300px"></div> <div class="outer"> <div class="box1"></div> <div class="box2"></div> </div> </body> </html> 示例
处理后的结果如图:
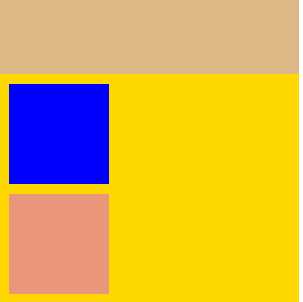
溢出问题

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>css属性操作</title> <style> .c1{ border: 1px solid; background-color: blueviolet; width: 100%; height:200px; /*text-align: center;*/ /*设置两端对齐*/ text-align: justify; line-height: 200px; /*如果你写的多了,会溢出来*/ /*第一种方法:overflow: hidden;*/ overflow: scroll; } .btn{ width: 45px; height: 70px; background-color: gray; /*设置透明度*/ opacity: 0.4; text-align: center; line-height: 70px; /*行高和高度对应*/ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1">啦啦啦啦啦绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿 啦啦啦啦啦 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿 绿绿绿绿绿绿 绿绿lllllllllllllllllllllll 绿绿绿绿绿</div> <div class="btn"> < </div> </body> </html>

解决溢出的方法
解决溢出的方法
overflow:auto;
overflow: hidden;
overflow:scoll; #加上滚动条

七、清除浮动
clear语法:
clear:none | left | right | both
1.clear:left 清除的是左边的浮动
2.clear:both :保证左右两边都没有浮动
注意:
排序的时候是一个标签一个标签的排
如果上一个是浮动的,就紧贴个上一个
如果上一个不是浮动的,就和上一个保持垂直不变
八、float父级的塌陷问题
float它不是完全脱离,它是半脱离的。像是文字环绕的就是用float实现的。float是不覆盖文字的
半脱离的,吧文字给挤过去了。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .c1{ width: 100px; height: 60px; background-color: blue; float: left; } .c2{ width: 200px; height: 30px; background-color: aqua; float: left; } .c3{ width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: crimson; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="c2"></div> <div class="c3"></div> <div class="content"> content </div> </body> </html> float塌陷

解决方案
解决方案
1.<div style=‘clear:both‘></div>
也可以不加div
2.用after
.header:after{
content:""; #内容为空
display:block; #块级标签
clear:both; #清楚浮动的功能
}
约定的名字:clearfix
.clearfix:after{
content:""; #内容为空
display:block; #块级标签
clear:both; #清楚浮动的功能(可以做到一个自动切换的功能)
}
解决问题以后的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.header{
/*height: 30px;*/
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
background-color: wheat;
float: left;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 30px;
background-color: rebeccapurple;
float: left;
}
.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
float: left;
}
.content{
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: royalblue;
}
.clearfix:after{
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header clearfix">
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</div>
<div class="content">
Content
</div>
</body>
</html>

九、position(定位)属性
position的四种属性
1.static:默认位置
2.fixed:完全脱离文档流,固定定位(以可视窗口为参照物)
3.relative:相对定位(参照的是自己本身的位置),没有脱离文档流,没有顶上去,会保持自己的位置不动。可以使用top left 进行定位
4.absolute:绝对定位:脱离了文档流(参照的是按已定位的父级标签定位,如果找不到会按body的去找)
注意:将定位标签设置为absolute,将他的父级标签设置为定位标签 (relative)
field举例(做一个返回顶部的样式。不管你拉不拉滚动条,他都会固定位置不变给它加一个)

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>固定位置</title> <style> .c1{ background-color: limegreen; width:100%; height: 1000px; } .returntop{ width: 100px; height: 40px; background-color: gray; /*透明度*/ /*opacity: 0.4;*/ color: white; text-align: center; line-height: 40px; position: fixed; bottom:50px; right: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="returntop">返回顶部>></div> </body> </html> 固定位置
相对位置,绝对位置例子

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>固定位置</title> <style> .c1{ background-color: limegreen; width:100%; height: 1000px; } .returntop{ width: 100px; height: 40px; background-color: gray; /*透明度*/ /*opacity: 0.4;*/ color: white; text-align: center; line-height: 40px; position: fixed; bottom:50px; right: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="returntop">返回顶部>></div> </body> </html> 固定位置

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>固定位置</title> <style> .c1{ background-color: limegreen; width:100%; height: 1000px; } .returntop{ width: 100px; height: 40px; background-color: gray; /*透明度*/ /*opacity: 0.4;*/ color: white; text-align: center; line-height: 40px; position: fixed; bottom:50px; right: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="c1"></div> <div class="returntop">返回顶部>></div> </body> </html> 固定位置
十、float和position的区别
float:半脱离文档流 position:全脱离文档流

