标签:style blog http io color ar 使用 sp strong
本文只讨论执行"mount none /mnt/huge -t hugetlbfs"命令后,mount系统调用的执行过程(基于Linux-3.4.51),不涉及进程相关的细节。
mount系统调用的内核实现:
1 SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name, 2 char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data) 3 { 4 int ret; 5 char *kernel_type; 6 char *kernel_dir; 7 char *kernel_dev; 8 unsigned long data_page; 9 10 /* 从用户空间copy文件系统类型,文件系统类型字符串长度不能大于PAGE_SIZE,即,不能大与4K。 11 * kernel_type = "hugetlbfs" 12 */ 13 ret = copy_mount_string(type, &kernel_type); 14 if (ret < 0) 15 goto out_type; 16 17 /* 从用户空间获取挂载点, kerne_dir = "/mnt/huge" */ 18 kernel_dir = getname(dir_name); 19 if (IS_ERR(kernel_dir)) { 20 ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dir); 21 goto out_dir; 22 } 23 24 /*从用户空间获取挂载设备,kernel_dev = "none"*/ 25 ret = copy_mount_string(dev_name, &kernel_dev); 26 if (ret < 0) 27 goto out_dev; 28 29 /*获取mount命令的其它参数*/ 30 ret = copy_mount_options(data, &data_page); 31 if (ret < 0) 32 goto out_data; 33 34 /*处理具体的mount细节*/ 35 ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, kernel_dir, kernel_type, flags, 36 (void *) data_page); 37 38 free_page(data_page); 39 out_data: 40 kfree(kernel_dev); 41 out_dev: 42 putname(kernel_dir); 43 out_dir: 44 kfree(kernel_type); 45 out_type: 46 return ret; 47 }
相关参数处理完之后,具体的Mount操作由do_mount()函数实现,do_mount()主要分为两部分来实现,一是找到装载点的dentry项,二是创建hugetlbfs的super_block、vfsmount、已经挂载点dentry等相关数据结构之间的关联。

一、kern_path()查找挂载点
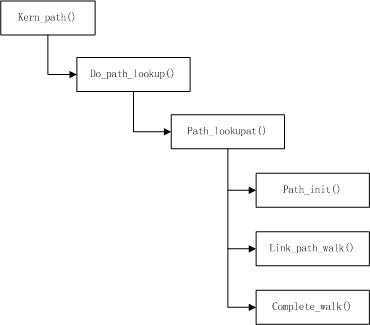
path_init():查找挂载点路径名(即,/mnt/huge)的搜索起点的根目录,保存在数据结构struct nameidata中。
nd->root = current->fs->root;
nd->path = nd->root;
nd->inode = nd->path.dentry->d_inode;
link_path_walk():该函数由一个大循环组成,逐分量处理文件名或路径名。名称在循环内分为各个分量(各分量通过一个或多个“/”分割)。每个分量表示一个目录名,最后一个分量是文件名。在每一个循环周期中,直至指定的文件名或目录名处理完毕并找到匹配的inode。
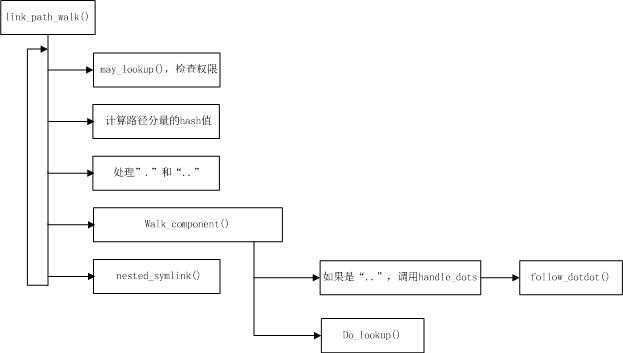
具体如下:
1、逐字符扫描路径名,斜线“/”会被跳过。
2、may_lookup()判断当前inode是否定义了permission方法,来采用不同的方法判断当前进程是否允许进入该目录。
3、判断当前分量是"."或者“..”,如果是“..”,则设置标志LAST_DOTDOT,最后调用walk_component()--->handle_dots()--->follow_dotdot()处理。如果是".",则设置标志LAST_DOT。
4、如果是普通分量,则调用walk_component()--->do_lookup()处理。do_lookup()处理实际的查找工作,查找分量对应的dentry。首先从上一级目录的dentry中查找inode,并调用d_revalidate()检查该缓存项是否有效(即,是否和实际文件系统的中的数据一致),如果有效,则返回;如果无效,则调用__lookup_hash()继续查找,首先调用lookup_dcache()查找缓存中是否存在,如果不存在,继续调用lookup_real(),调用具体的文件系统的lookup函数查找。
do_lookup()也处理跟踪挂载点的工作,也需要判断下级目录是否也挂载文件系统,__follow_mount_rcu()负责具体处理,在这里不做讨论。
5、nested_symlink()判断分量是否是符号链接。只有用于表示符号链接的inode,其inode_operations中的lookup函数指针才有具体的值,否则为NULL。
complete_walk():该函数做一些相关检查,确认是否需再次调用d_revalidate()判断缓存项是否有效。
二、do_new_mount()装载文件系统
do_new_mount()分为两个部分:do_kern_mount()和do_add_mount()。
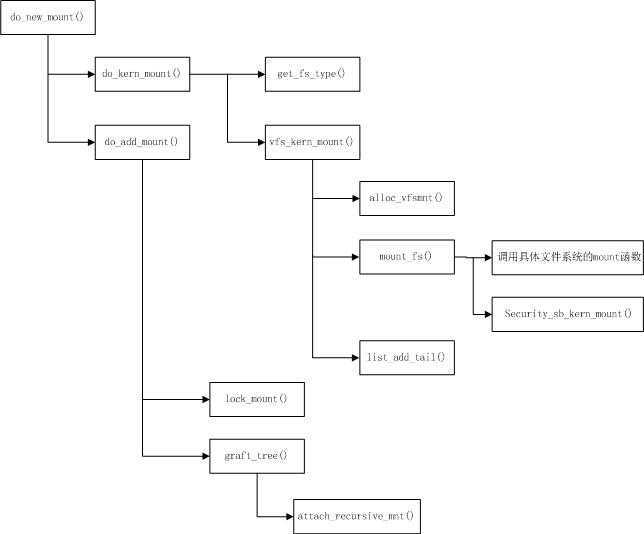
do_kern_mount():首先调用get_fs_type()获取对应的已注册的文件系统类型。对于hugetlbfs来说,对应的内核文件系统类型是hugetlbfs_fs_type。获取对应的文件系统类型后,首先调用alloc_vfsmnt()分配并初始化mount数据结构,再调用mount_fs(),进一步调用hugetlbfs_mount(),分配挂载点的super_block、dentry、inode并建立相关映射。最后建立mount、super_block、dentry之间的映射。具体的映射关系如http://www.cnblogs.com/MerlinJ/p/4053689.html文中最后的图表所示。
hugetlbfs_mount()做了如下工作:
1、申请并初始化一个super_block。
2、调用set_anon_super(),获得一个未使用的此设备号dev,然后用主设备号0和次设备号dev设置新超级块的s_dev字段。
3、将该super_block挂到全局super_blocks链表中,同时挂到hugetlbfs_fs_type->fs_supers链表中。
4、调用hugetlbfs_fill_super(),创建dentry、inode,并建立dentry、inode、super_block之间的映射。
do_add_mount():首先判断文件系统是否重复装载,相同文件系统不能挂载到相同挂载点。再调用attach_recursive_mnt(),将挂载点加入到全局目录树,即,将do_kern_mount()创建的mount数据结构,挂到全局mount_hashtable链表中,挂到命名空间的mnt_list链表中,同时挂到父挂载点的mnt_mounts链表中。
只是大体走了一下流程,很多具体细节并没有涉及到,还有待补充。
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/chenjin_zhong/article/details/8448862
http://blog.csdn.net/dndxhej/article/details/7434521
Linux Hugetlbfs内核源码简析-----(二)Hugetlbfs挂载
标签:style blog http io color ar 使用 sp strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/MerlinJ/p/4064673.html