标签:pre char str one rop 为什么 mic 名称 tip
6.为什么不对基本数据类型的函数参数使用const?
将const限定符用于指针,以防止指向的原始数据被修改,程序传递基本类型(int或double)时,将按值传递,以便函数使用副本,这样,原始数据将得到保护。
8.编写一个函数,将字符串中所有c1替换成c2,并返回替换次数。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 int replace(char *str, char c1, char c2);
5
6 int main()
7 {
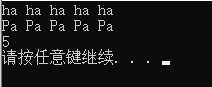
8 char a[20] = "ha ha ha ha ha";
9 cout << a << endl;
10 int count=replace(a, ‘h‘, ‘P‘);
11 cout << a << endl;
12 cout << count << endl;
13 system("pause");
14 return 0;
15 }
16
17 int replace(char *str, char c1, char c2)
18 {
19 int cnt = 0;
20 while (*str)
21 {
22 if (*str == c1)
23 {
24 *str = c2;
25 cnt++;
26 }
27 str++;
28 }
29 return cnt;
30 }
12.假设有如下结构声明:
struct applicant
{
char name[30];
int credit_ratings[3];
};
a.编写一个函数,它将application结构作为参数,并显示该结构的内容。
b.编写一个函数,它将application结构的地址作为参数,并显示该参数指向的结构的内容。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 struct applicant
5 {
6 char name[30];
7 int credit_ratings[3];
8 };
9
10 void struct_name(applicant a); //按值传递结构
11 void structin_add(applicant *app); //传递结构的地址
12
13 int main()
14 {
15 applicant a1 = { "Andy", 3,2,1 };
16 struct_name(a1);
17 structin_add(&a1);
18 system("pause");
19 return 0;
20 }
21
22 void struct_name(applicant a)
23 {
24 cout << a.name << endl;
25 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
26 cout << a.credit_ratings[i] << ‘ ‘;
27 cout << endl;
28 }
29
30 void structin_add(applicant *app)
31 {
32 cout << app->name << endl;
33 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
34 cout << app->credit_ratings[i] << ‘ ‘;
35 cout << endl;
36 }

13.假设函数f1()和f2()的原型如下:
void f1(applicant *a);
const char *f2(const applicant *a1, const applicant *a2);
请将p1和p2分别声明位指向f1和f2的指针;将ap声明为一个数组,它包含5个类型与p1相同的指针;将pa声明为一个指针,它指向的数组包含10个类型与p2相同的指针。使用typedef来帮助完成这项工作。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 struct applicant
5 {
6 char name[30];
7 int credit_ratings[3];
8 };
9
10 void f1(applicant *a);
11 const char *f2(const applicant *a1, const applicant *a2);
12
13 typedef void(*p_f1)(applicant *a);
14 typedef const char *(*p_f2)(const applicant *a1, const applicant *a2);
15
16 int main()
17 {
18 void(*p1)(applicant *a) = f1; //p_f1 p1 = f1;
19 const char *(*p2)(const applicant *a1, const applicant *a2) = f2; // p_f2 p2 = f2;
20 p_f1 ap[5]; // void(*ap[5])(app *);
21 p_f2 (*pa)[10]; // const char *(*pa[10])(const app*, const app*);
22 system("pause");
23 return 0;
24 }
1.编写一个程序,不断要求用户输入两个数,直到其中一个为0。对于每两个数,程序将使用一个函数来计算它们的调和平均数,并将结果返回给main(),而后者将报告结果。调和平均数指的是倒数平均值的倒数,计算公式如下:
调和平均数 = 2.0 * x * y / (x + y)
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 double average(int x, int y);
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int a, b;
9 cout << "Please enter 2 numbers(End with 0): " << endl;
10 while (cin>>a>>b&&a&&b)
11 {
12 double ave = average(a, b);
13 if (ave==0)
14 cout << "Please enter 2 numbers(End with 0): " << endl;
15 else
16 {
17 cout << "harmonic average = " << ave << endl;
18 cout << "Please enter 2 numbers(End with 0): " << endl;
19 }
20 }
21 system("pause");
22 return 0;
23 }
24
25 double average(int x, int y)
26 {
27 if (x == -y)
28 {
29 cout << "The sum of two Numbers cannot be 0." << endl;
30 return 0;
31 }
32 double cnt = 2.0*x*y / (x + y);
33 return cnt;
34 }

2.编写一个程序,要求用户输入最多10个高尔夫成绩,并将其存储在一个数组中。程序允许用户提早结束输入,并在 一行上显示所有成绩,然后报告平均成绩。请使用3个数组处理函数来分别进行输入、显示和计算平均成绩。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 int input(double *a);
5 void show(double *a,int);
6 double cal(double *a, int);
7
8 int main()
9 {
10 double grade[10];
11 int n=input(grade);
12 show(grade,n);
13 cout << "Average score is: " << cal(grade, n) << endl;
14 system("pause");
15 return 0;
16 }
17
18 int input(double *a)
19 {
20 int cnt = 0;
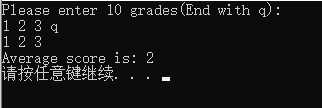
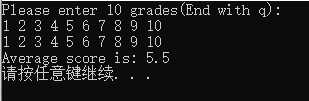
21 cout << "Please enter 10 grades(End with q): " << endl;
22 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
23 {
24 if (!(cin >> a[i]))
25 break;
26 else
27 cnt++;
28 }
29 return cnt;
30 }
31
32 void show(double *a,int n)
33 {
34 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
35 cout << a[i] << ‘ ‘;
36 cout << endl;
37 }
38
39 double cal(double *a,int n)
40 {
41 double sum = 0.0;
42 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
43 sum += a[i];
44 return sum / n;
45 }
3.下面是一个结构声明:
struct box
{
char maker[40];
float height;
float width;
float length;
float volume;
};
a.编写一个函数,按值传递box结构,并显示每个成员的值
b.编写一个函数,传递box结构的地址,并将volume成员设置为其他三维长度的乘积。
c.编写一个使用这两个函数的简单程序。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 struct box
5 {
6 char maker[40];
7 float height;
8 float width;
9 float length;
10 float volume;
11 };
12
13 void show(box b);
14 void set(box *b);
15
16 int main()
17 {
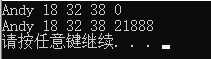
18 box b = { "Andy", 18, 32, 38 };
19 show(b);
20 set(&b);
21 system("pause");
22 return 0;
23 }
24
25 void show(box b)
26 {
27 cout << b.maker << " " << b.height << " " << b.width << " " << b.length << " " << b.volume << endl;
28 }
29
30 void set(box *b)
31 {
32 b->volume = (b->height)*(b->width)*(b->length);
33 cout << b->maker << ‘ ‘ << b->height << ‘ ‘ << b->width << ‘ ‘ << b->length << ‘ ‘ << b->volume << endl;
34 }
4.许多州的彩票发行机构都使用如程序清单7.4所示的简单彩票玩法的变体。在这些玩法中,玩家从一组被称为域号码 (field number)的号码中选择几个。例如,可以从域号码1~47中选择5个号码;还可以从第二个区间(如1~27)选择一个号码 (称为特选号码)。要赢得头奖,必须正确猜中所有的号码。中头奖的几率是选中所有域号码的几率与选中特选号码几率的乘积。 例如,在这个例子中,中头奖的几率是从47个号码中正确选取5个号码的几率与从27个号码中选择1个号码的几率的乘积。请修改程序清单7.4,以计算中得这种彩票头奖的几率。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 long double probability(long double n, unsigned p);
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 long double result1 = 1.0, result2 = 1.0;
9 result1 = probability(47, 5);
10 result2 = probability(27, 1);
11 cout << result1*result2 << endl;
12 system("pause");
13 return 0;
14 }
15
16 long double probability(long double n, unsigned p)
17 {
18 long double result = 1.0;
19 for (; p > 0; n--, p--)
20 result *= p / n;
21 return result;
22 }
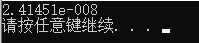
5.定义一个递归函数,接受一个整型参数,并返回该参数的阶乘。前面讲过,3的阶乘写作3!,等于3 * 2!,以此类推:而0!被定义为1.通用的计算公式是,如果n大于零 , 则n! = n * (n - 1)!。在程序中对该函数进行测试,程序使用循环让用户输入不同的值,程序将报告这些值的阶乘。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 long long factorial(int n); //阶乘
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int n;
9 long long result; //阶乘结果较大,设为long long型较好
10 cout << "Please enter an integer(End with q): ";
11 while (cin >> n)
12 {
13 result=factorial(n);
14 cout << result << endl;
15 cout << "Please enter an integer(End with q): ";
16 }
17 system("pause");
18 return 0;
19 }
20
21 long long factorial(int n)
22 {
23 if (n == 0 || n == 1)
24 return 1;
25 else
26 {
27 return n*factorial(n - 1);
28 }
29 }
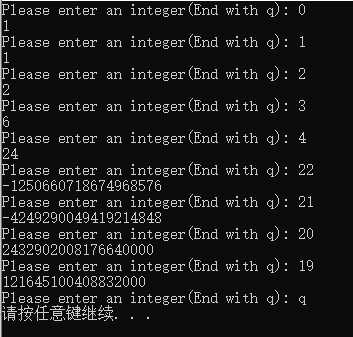
6.编写一个程序,它使用下列函数:
Fill_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数。它提示用户输入double值,并将这些值存储到数组中。当数组被填满或 用户输入了非数字时,输入将停止,并返回实际输入了多少个数字。 Show_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并显示该数组的内容。 Reverse_array()将一个double数组的名称和长度作为参数,并将存储在数组中的值的顺序反转。 程序将使用这些函数来填充数组,然后显示数组;反转数组,然后显示数组;反转数组中除第一个和最后一个元素之外的所有元素, 然后显示数组。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 const int size = 10;
5 int Fill_array(double array[], int n);
6 void Show_array(const double array[], int n);
7 void Reverse_array(double array[], int n);
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 double t;
12 double array[size];
13 int count = Fill_array(array, size);
14 cout << "Show the array: " << endl;
15 Show_array(array, count);
16 Reverse_array(array, count);
17 Show_array(array, count);
18 t = array[0];
19 array[0] = array[count - 1];
20 array[count - 1] = t;
21 Show_array(array, count);
22 system("pause");
23 return 0;
24 }
25
26 int Fill_array(double array[], int n)
27 {
28 int cnt = 0;
29 cout << "Please enter a double: " << endl;
30 while (cnt < n&&cin >> array[cnt])
31 cnt++;
32 /*for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
33 {
34 cin >> array[i];
35 if (!cin) //注:此处不能用isdigit()来判断,isdigit()只能判断char型
36 {
37 cin.clear();
38 while (cin.get() != ‘\n‘)
39 continue;
40 break;
41 }
42 cnt++;
43 }
44 */
45 return cnt;
46 }
47
48 void Show_array(const double array[], int n)
49 {
50 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
51 {
52 cout << array[i] << ‘ ‘;
53 }
54 cout << endl;
55 }
56
57 void Reverse_array(double array[], int n)
58 {
59 double t;
60 for (int i = 0,j=n-1; i <= n / 2,j>=n/2; i++,j--)
61 {
62 t = array[i];
63 array[i] = array[j];
64 array[j] = t;
65 }
66 }
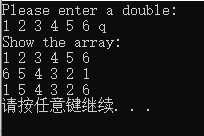
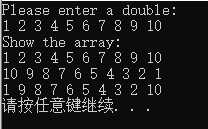
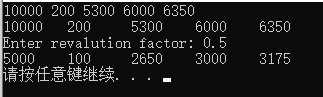
7.修改程序清单7.7中的3个数组处理函数,使之使用两个指针参数来表示区间。file_array()函数不返回实际读取了多少个数字,而是返回一个指针,该指针指向最后被填充的位置:其他的函数可以将该指针作为第二个参数,以标识数据结尾。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 const int Max = 5;
5 double * fill_array(double *a);
6 void show_array(double *a, double*b);
7 void revalue(double *a, double*b, double r);
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 double properties[Max];
12 double *last = fill_array(properties);
13 show_array(properties, last);
14 double factor;
15 cout << "Enter revalution factor: ";
16 while (!(cin >> factor))
17 {
18 cin.clear();
19 while (cin.get() != ‘\n‘)
20 continue;
21 cout << "Bad Input!" << endl;
22 }
23 revalue(properties, last, factor);
24 show_array(properties, last);
25
26 system("pause");
27 return 0;
28 }
29
30 double * fill_array(double *a)
31 {
32 int i = 0;
33 while (cin >> a[i++])
34 {
35 if (i == 5)
36 break;
37 }
38 return &a[i];
39 }
40
41 void show_array(double *a, double*b)
42 {
43 while (a != b)
44 {
45 cout << *a << "\t";
46 a++;
47 }
48 cout << endl;
49 }
50
51 void revalue(double *a, double*b, double r)
52 {
53 while (a != b)
54 {
55 (*a) *= r;
56 a++;
57 }
58 }
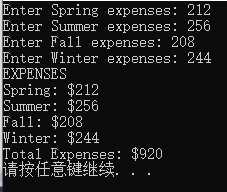
8.在不使用array类的情况下完成程序清单7.15所做的工作。编写两个这样的版本:
a.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用double数组存储开支。
b.使用const char *数组存储表示季度名称的字符串,并使用一个结构,该结构只有一个成员——一个用于存储开支的double数组。这种设计与使用array类的基本设计类似。
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 const char *season[4] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };
5 void fill(double a[]);
6 void show(double *a);
7
8 int main()
9 {
10 double expenses[4];
11 fill(expenses);
12 show(expenses);
13 system("pause");
14 return 0;
15 }
16
17 void fill(double a[])
18 {
19 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
20 {
21 cout << "Enter " << season[i] << " expenses: ";
22 cin >> a[i];
23 }
24 }
25
26 void show(double *a)
27 {
28 double total = 0.0;
29 cout << "EXPENSES" << endl;
30 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
31 {
32 cout << season[i] << ": $" << a[i] << endl;
33 total += a[i];
34 }
35 cout << "Total Expenses: $" << total << endl;
36 }
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 const char *season[4] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };
5 struct expen
6 {
7 double expenses[4];
8 };
9 void fill(expen *e);
10 void show(expen *e);
11
12 int main()
13 {
14 expen exp;
15 fill(&exp); //这里是传递结构的地址,用指针来访问结构,
16 show(&exp);
17 system("pause");
18 return 0;
19 }
20
21 void fill(expen *e)
22 {
23 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
24 {
25 cout << "Enter " << season[i] << " expenses: ";
26 cin >> e->expenses[i];
27 }
28 }
29
30 void show(expen *e)
31 {
32 double total = 0.0;
33 cout << "EXPENSES" << endl;
34 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
35 {
36 cout << season[i] << ": $" << e->expenses[i] << endl;
37 total += (e->expenses[i]);
38 }
39 cout << "Total Expenses: $" << total << endl;
40 }
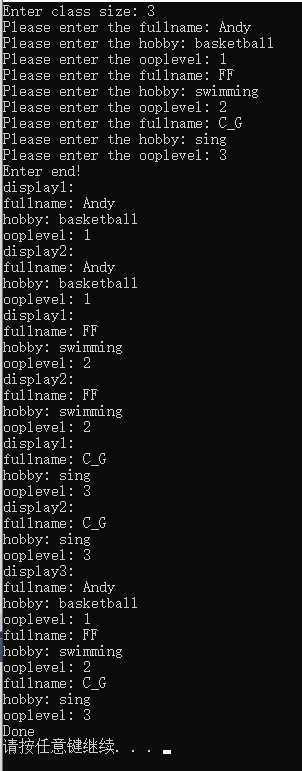
9.这个练习让您编写处理数组和结构的函数。下面是程序的框架,请提供其中描述的函数,以完成该程序。
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<string>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 const int SLEN = 30;
6 struct student
7 {
8 char fullname[SLEN];
9 char hobby[SLEN];
10 int ooplevel;
11 };
12 int getinfo(student pa[], int n);
13 void display1(student st);
14 void display2(const student *ps);
15 void display3(const student pa[], int n);
16
17 int main()
18 {
19 cout << "Enter class size: ";
20 int class_size;
21 cin >> class_size;
22 while (cin.get() != ‘\n‘)
23 continue;
24 student *ptr_stu = new student[class_size];
25 int entered = getinfo(ptr_stu, class_size);
26 for (int i = 0; i < entered; i++)
27 {
28 display1(ptr_stu[i]);
29 display2(&ptr_stu[i]);
30 }
31 display3(ptr_stu, entered);
32 delete[]ptr_stu;
33 cout << "Done\n";
34 system("pause");
35 return 0;
36 }
37
38 int getinfo(student pa[], int n)
39 {
40 int cnt = 0;
41 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
42 {
43 cout << "Please enter the fullname: ";
44 cin >> pa[i].fullname;
45 cout << "Please enter the hobby: ";
46 cin >> pa[i].hobby;
47 cout << "Please enter the ooplevel: ";
48 cin >> pa[i].ooplevel;
49 cnt++;
50 }
51 cout << "Enter end!" << endl;
52 return cnt;
53 }
54
55 void display1(student st)
56 {
57 cout << "display1:" << endl;
58 cout << "fullname: " << st.fullname << endl;
59 cout << "hobby: " << st.hobby << endl;
60 cout << "ooplevel: " << st.ooplevel << endl;
61 }
62
63 void display2(const student *ps)
64 {
65 cout << "display2:" << endl;
66 cout << "fullname: " << ps->fullname << endl;
67 cout << "hobby: " << ps->hobby << endl;
68 cout << "ooplevel: " << ps->ooplevel << endl;
69 }
70
71 void display3(const student pa[], int n)
72 {
73 cout << "display3:" << endl;
74 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
75 {
76 cout << "fullname: " << pa[i].fullname << endl;
77 cout << "hobby: " << pa[i].hobby << endl;
78 cout << "ooplevel: " << pa[i].ooplevel << endl;
79 }
80
81 }
10.设计一个名为calculate()的函数,它接受两个double值和一个指向函数的指针,而被指向的函数接受两个double参数,并返回一个double值、calculate()函数的类型也是double,并返回被指向的函数使用calculate()的两个double参数计算得到的值。例如,假如add()函数的定义如下:
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3
4 double add(double x, double y);
5 double sub(double x, double y);
6 double multiply(double x, double y);
7 double calculate(double x, double y, double (*f1)(double,double)); //f1是函数指针
8
9 int main()
10 {
11 double(*f1)(double x, double y) = add; //声明及初始化一个指向函数add的函数指针f1
12 double q = calculate(2.5, 10.4, add);
13 cout << "sum = " << q << endl << endl;
14
15 double(*pf[3]) (double, double) = { add, sub, multiply }; //函数指针数组,分别指向三个不同的函数
16 double a, b;
17 //const char(*pch[3]) = { "add", "sub", "mutiply" };
18 cout << "Enter two numbers: ";
19 while (cin >> a >> b)
20 {
21 //for (int i = 0; i<3; i++) // 这里和上面的字符串数组可代替下面的三个cont
22 //cout << pch[i] << " = " << calculate(a, b, pf[i]) << "\n";
23 cout << "add = " << calculate(a, b, pf[0]) << endl; //pf[0]换成*pf[0]也可以
24 cout << "sub = " << calculate(a, b, pf[1]) << endl;
25 cout << "multiply = " << calculate(a, b, pf[2]) << endl;
26 cout << "Enter two numbers: ";
27 }
28 system("pause");
29 return 0;
30 }
31
32 double calculate(double x, double y, double(*f1)(double, double))
33 {
34 return (*f1)(x, y);
35 }
36
37 double add(double x, double y)
38 {
39 return x + y;
40 }
41
42 double sub(double x, double y)
43 {
44 return x - y;
45 }
46
47 double multiply(double x, double y)
48 {
49 return x * y;
50 }

[C++ Primer Plus] 第7章、函数——(二)课后习题
标签:pre char str one rop 为什么 mic 名称 tip
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Fionaaa/p/12342987.html