标签:play 有一个 int insert isp 遍历 pre 方案 数据
两个数比较大小,较大的数下沉,较小的数冒起来。
过程:
时间复杂度:O(n2)
代码:
1 public static void BubbleSort(int [] arr){ 2 3 int temp;//临时变量 4 for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){ //表示趟数,一共arr.length-1次。 5 for(int j=arr.length-1; j>i; j--){ 6 7 if(arr[j] < arr[j-1]){ 8 temp = arr[j]; 9 arr[j] = arr[j-1]; 10 arr[j-1] = temp; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 }
优化:
针对问题:
数据的顺序排好之后,冒泡算法仍然会继续进行下一轮的比较,直到arr.length-1次,后面的比较没有意义的。
方案:
设置标志位flag,如果发生了交换flag设置为true;如果没有交换就设置为false。
这样当一轮比较结束后如果flag仍为false,即:这一轮没有发生交换,说明数据的顺序已经排好,没有必要继续进行下去。
1 public static void BubbleSort1(int [] arr){ 2 3 int temp;//临时变量 4 boolean flag;//是否交换的标志 5 for(int i=0; i<arr.length-1; i++){ //表示趟数,一共 arr.length-1 次 6 7 // 每次遍历标志位都要先置为false,才能判断后面的元素是否发生了交换 8 flag = false; 9 10 for(int j=arr.length-1; j>i; j--){ //选出该趟排序的最大值往后移动 11 12 if(arr[j] < arr[j-1]){ 13 temp = arr[j]; 14 arr[j] = arr[j-1]; 15 arr[j-1] = temp; 16 flag = true; //只要有发生了交换,flag就置为true 17 } 18 } 19 // 判断标志位是否为false,如果为false,说明后面的元素已经有序,就直接return 20 if(!flag) break; 21 } 22 }
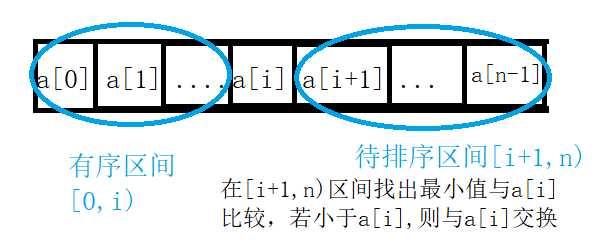
1 /* 2 * 简单选择排序 3 * */ 4 public static void selectSort(int a[],int n){ 5 //有序区间[0,i) 无序区间[i,n) 6 for (int i=0;i<n-1;i++){//遍历n-1次 7 int k=i;//最小值下标 8 for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){ //从[i+1,n)区间找出最小值和a[i]比较 9 if (a[j]<a[k]){ 10 k=j; 11 } 12 } 13 if (a[i]!=a[k]){//最小值和a[i]交换 14 int temp=a[i]; 15 a[i]=a[k]; 16 a[k]=temp; 17 } 18 19 } 20 }
基本思想:
在要排序的一组数中,根据某一增量分为若干子序列,并对子序列分别进行插入排序。
然后逐渐将增量减小,并重复上述过程。直至增量为1,此时数据序列基本有序,最后进行插入排序。
时间复杂度:O(n1.5)
1 public static void shell_sort(int array[],int lenth){ 2 3 int temp = 0; 4 int incre = lenth; 5 6 while(true){ 7 incre = incre/2; 8 9 for(int k = 0;k<incre;k++){ //根据增量分为若干子序列 10 11 for(int i=k+incre;i<lenth;i+=incre){ 12 13 for(int j=i;j>k;j-=incre){ 14 if(array[j]<array[j-incre]){ 15 temp = array[j-incre]; 16 array[j-incre] = array[j]; 17 array[j] = temp; 18 }else{ 19 break; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 if(incre == 1){ 26 break; 27 } 28 } 29 }
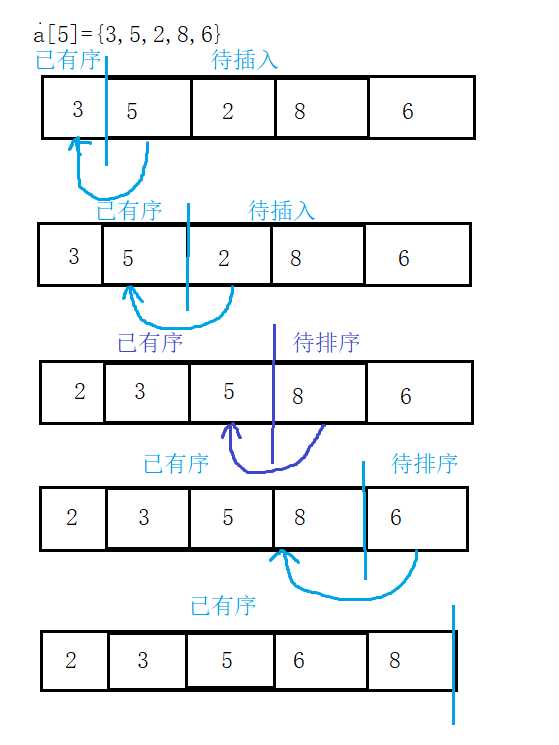
代码:
1 /* 2 * 插入排序 3 * */ 4 public static void insertSort(int a[]){ 5 for (int i=0;i<a.length-1;i++){ 6 for (int j=i+1;j>0;j--){ 7 if (a[j]<a[j-1]){ 8 int temp=a[j]; 9 a[j]=a[j-1]; 10 a[j-1]=temp; 11 } 12 else break; 13 } 14 } 15 }
代码:
/* * 快速排序 * */ //划分区间对【left,right】进行划分 public static int partition(int []a,int left,int right){ int temp=a[left];//a[left]存放至临时变量 while (left<right){//只要left和right不相遇 while (left<right&&a[right]>=temp) right--;//反复左移right a[left]=a[right]; while (left<right&&a[left]<temp) left++;//反复右移left a[right]=a[left]; } a[left]=temp;//把temp放到left和right相遇的地方 return left; } public static void quickSort(int a[],int left,int right){ if (left>=right){//当前区间长度不超过1 return; } int pos=partition(a,left,right);//将[left,right]按a[left]一分为二 quickSort(a,left,pos-1);//对左子区间递归进行快速排序 quickSort(a,pos+1,right);//对右子区间进行快速排序 }
整个过程如下图:
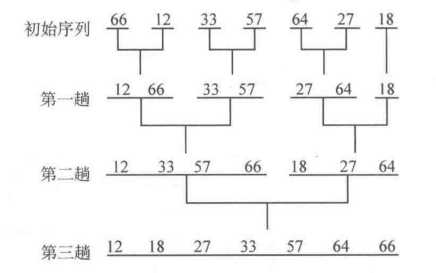
2-路归并排序的核心在于如何将两个有序序列合并为一个有序序列
代码:
1 /* 2 * 归并排序 3 * */ 4 public static void merge(int A[],int L1,int R1,int L2,int R2){ 5 /*将[L1,R1][L2,R2]合并为有序区间,L2=R1+1*/ 6 int maxn=100; 7 int i=L1,j=L2; 8 int [] temp=new int[maxn];//temp 临时数组存放合并后的数组,index为其下标 9 int index=0; 10 while(i<=R1&&j<=R2){ 11 if (A[i]<=A[j]){ 12 temp[index++]=A[i++];//将A[i]加入序列temp 13 }else{ 14 temp[index++]=A[j++];//将A[j]加入序列temp 15 } 16 } 17 while(i<=R1) temp[index++]=A[i++];//将[L1,R1]的剩余元素加入序列temp 18 while(j<=R2) temp[index++]=A[j++];//将[L2,R2]的剩余元素加入序列temp 19 for (i=0;i<index;i++){ 20 A[L1+i]=temp[i];//将合并后的序列赋值回数组A 21 } 22 } 23 public static void mergeSort(int A[],int left,int right){ 24 if (left<right){ 25 int mid=(left+right)/2;//取【left,right】的中点 26 mergeSort(A,left,mid);//递归将左子区间【left,mid】归并排序 27 mergeSort(A,mid+1,right);//递归将右子区间【mid+1,right】归并排序 28 merge(A,left,mid,mid+1,right);//将左子区间和右子区间合并 29 } 30 }
标签:play 有一个 int insert isp 遍历 pre 方案 数据
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/coderyang1/p/12411659.html