标签:seo 就会 poll runner 怎么 sem class notify 解锁


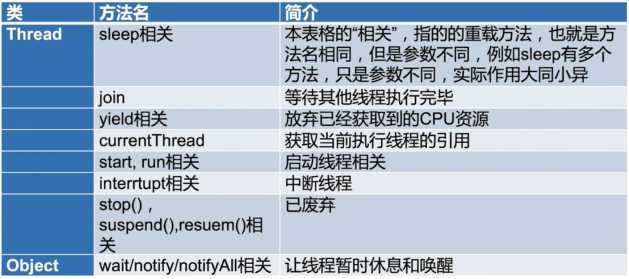
/** * 展示wait和notify的基本用法:1.研究代码执行顺序 2.证明wait释放锁 */ public class Wait { public static Object object = new Object(); static class Thread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { synchronized (object){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始执行了"); try { object.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到了锁"); } } } static class Thread2 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { synchronized (object){ object.notify(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "调用了notify()"); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(); Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(); thread1.start(); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } thread2.start(); } }
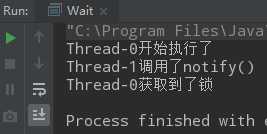
/** * notify和notifyAll区别以及start先执行不代表线程先启动 */ public class WaitNotfiyAll implements Runnable { private static final Object resourceA = new Object(); @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得锁"); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放了锁"); resourceA.wait(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行结束"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void useNotify() throws InterruptedException { WaitNotfiyAll waitNotfiyAll = new WaitNotfiyAll(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(waitNotfiyAll); Thread thread2 = new Thread(waitNotfiyAll); Thread thread3 = new Thread(()->{ synchronized (resourceA){ resourceA.notify(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了notify方法"); } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread3.start(); } public static void useNotifyAll() throws InterruptedException { WaitNotfiyAll waitNotfiyAll = new WaitNotfiyAll(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(waitNotfiyAll); Thread thread2 = new Thread(waitNotfiyAll); Thread thread3 = new Thread(()->{ synchronized (resourceA){ resourceA.notifyAll(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行了notifyAll方法"); } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); Thread.sleep(1000); thread3.start(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // useNotify(); useNotifyAll(); } }
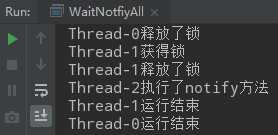
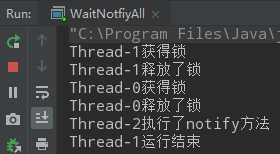
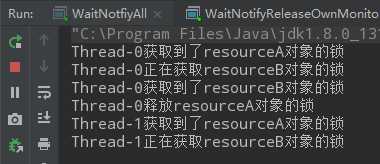
public class WaitNotifyReleaseOwnMonitor { private static volatile Object resourceA = new Object(); private static volatile Object resourceB = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{ synchronized (resourceA){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到了resourceA对象的锁"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在获取resourceB对象的锁"); synchronized (resourceB){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到了resourceB对象的锁"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放resourceA对象的锁"); try { resourceA.wait(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行结束"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{ synchronized (resourceA){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到了resourceA对象的锁"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"正在获取resourceB对象的锁"); synchronized (resourceB){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到了resourceB对象的锁"); } } }); thread1.start(); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } thread2.start(); } }
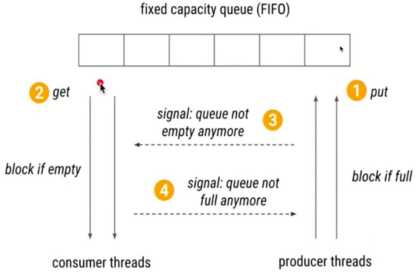
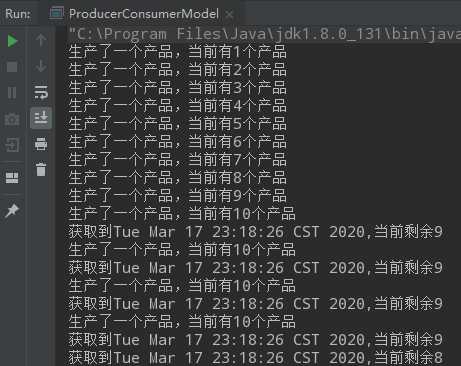
import java.util.Date; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * 用wait/notify实现生产者和消费者模式 */ public class ProducerConsumerModel { public static void main(String[] args) { EventStorage eventStorage = new EventStorage(); Producer producer = new Producer(eventStorage); Consumer consumer = new Consumer(eventStorage); new Thread(producer).start(); new Thread(consumer).start(); } } class Producer implements Runnable { private EventStorage storage; public Producer(EventStorage storage) { this.storage = storage; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { storage.put(); } } } class Consumer implements Runnable { private EventStorage storage; public Consumer(EventStorage storage) { this.storage = storage; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { storage.take(); } } } class EventStorage { private int maxSize; private LinkedList<Date> storage; public EventStorage() { this.maxSize = 10; this.storage = new LinkedList<>(); } public synchronized void put() { while (storage.size() == maxSize) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } storage.add(new Date()); System.out.println("生产了一个产品,当前有" + storage.size() + "个产品"); notify(); } public synchronized void take() { while (storage.size() == 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("获取到" + storage.poll() + ",当前剩余" + storage.size()); notify(); } }
/** * 使用两个线程交替打印0~100的奇偶数 */ public class WaitNotifyPrintOddEvenSyn { private static int count = 0; private static final Object lock = new Object(); static class TurningRunner implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (count <= 100) { synchronized (lock) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + count++); //将其他等待线程唤醒 lock.notify(); if (count <= 100) { try { //本线程休眠 lock.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { new Thread(new TurningRunner(), "偶数").start(); Thread.sleep(10); new Thread(new TurningRunner(), "奇数").start(); } }
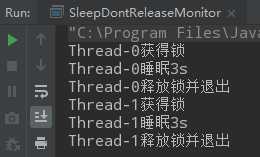
public class SleepDontReleaseMonitor implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { syn(); } private synchronized void syn(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得锁"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "睡眠3s"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放锁并退出"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SleepDontReleaseMonitor sleepDontReleaseMonitor = new SleepDontReleaseMonitor(); new Thread(sleepDontReleaseMonitor).start(); new Thread(sleepDontReleaseMonitor).start(); } }
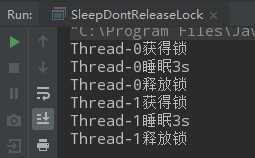
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class SleepDontReleaseLock implements Runnable { private static final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { //上锁 lock.lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁"); try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"睡眠3s"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放锁"); //解锁 lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { SleepDontReleaseLock sleepDontReleaseLock = new SleepDontReleaseLock(); new Thread(sleepDontReleaseLock).start(); new Thread(sleepDontReleaseLock).start(); } }
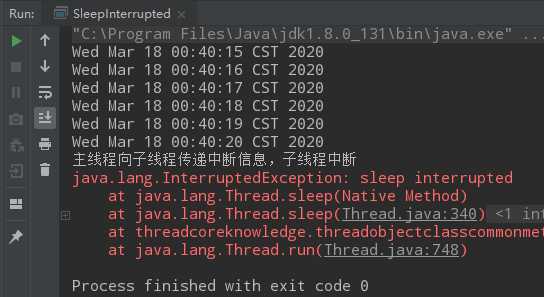
import java.util.Date; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class SleepInterrupted implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println(new Date()); try { TimeUnit.HOURS.sleep(0); TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(0); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("主线程向子线程传递中断信息,子线程中断"); e.printStackTrace(); break; } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { SleepInterrupted sleepInterrupted = new SleepInterrupted(); Thread thread = new Thread(sleepInterrupted); thread.start(); Thread.sleep(5500); thread.interrupt(); } }

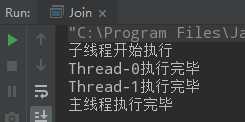
public class Join { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕"); }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行完毕"); }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); System.out.println("子线程开始执行"); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println("主线程执行完毕"); } }
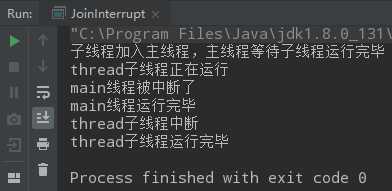
public class JoinInterrupt { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread(); Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在运行"); try { //子线程对主线程执行中断 mainThread.interrupt(); Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行完毕"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "中断"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行完毕"); } }, "thread子线程"); thread.start(); System.out.println("子线程加入主线程,主线程等待子线程运行完毕"); try { //主线程在等待子线程过程中遇到中断异常 thread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { //主线程遇到中断对子线程 也执行中断 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程被中断了"); thread.interrupt(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程运行完毕"); } }
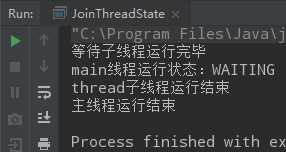
public class JoinThreadState { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread(); Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { try { Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println(mainThread.getName() + "线程运行状态:" + mainThread.getState()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "运行结束"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "thread子线程"); thread.start(); System.out.println("等待子线程运行完毕"); thread.join(); System.out.println("主线程运行结束"); } }
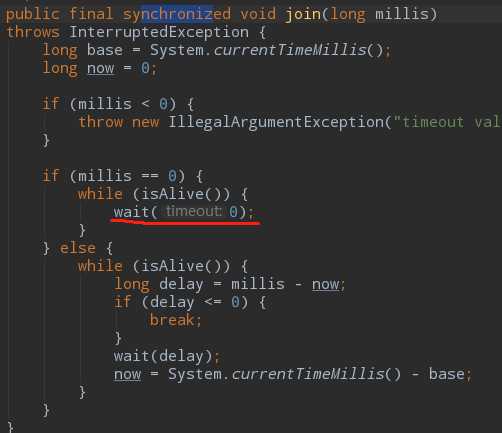

public class JoinPrinciple { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread thread = new Thread(()->{ try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行完毕"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"thread子线程"); thread.start(); System.out.println("等待子线程运行完毕"); // thread.join(); synchronized (thread){ thread.wait(); } System.out.println("所有线程都运行完毕"); } }
5.线程的八大核心基础知识之Thread和Object类中的重要方法详解
标签:seo 就会 poll runner 怎么 sem class notify 解锁
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhihaospace/p/12518969.html