标签:logs 解释器 环境变量path org 我的电脑 技术 实现 如何 信息
Bison是一个语法分析器,bison和flex配合使用
可以将用户提供的语法规则转化成一个语法分析器
利用Bison,可以开发各种语言解释器
Bison的输入文件以.y作为后缀名
其语法文件的一般格式如下:
%{
Prologue
%}
Bison declarations
%%
Grammar rules
%%
Epilogue使用两个%%分隔符,将文件分为三个部分
Prologue定义动作中使用的类型和变量
Bison Declaration声明了终结符号和非终结符号的名称
还可以描述运算符的优先级以及各种符号的语义值的数据类型
Grammar rules定义了如何从各个部分构造每个非终结符
Epilogue可以包含要使用的任何代码
回归正题,windows下怎么安装Bison呢?
Bison的下载地址为http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/bison.htm
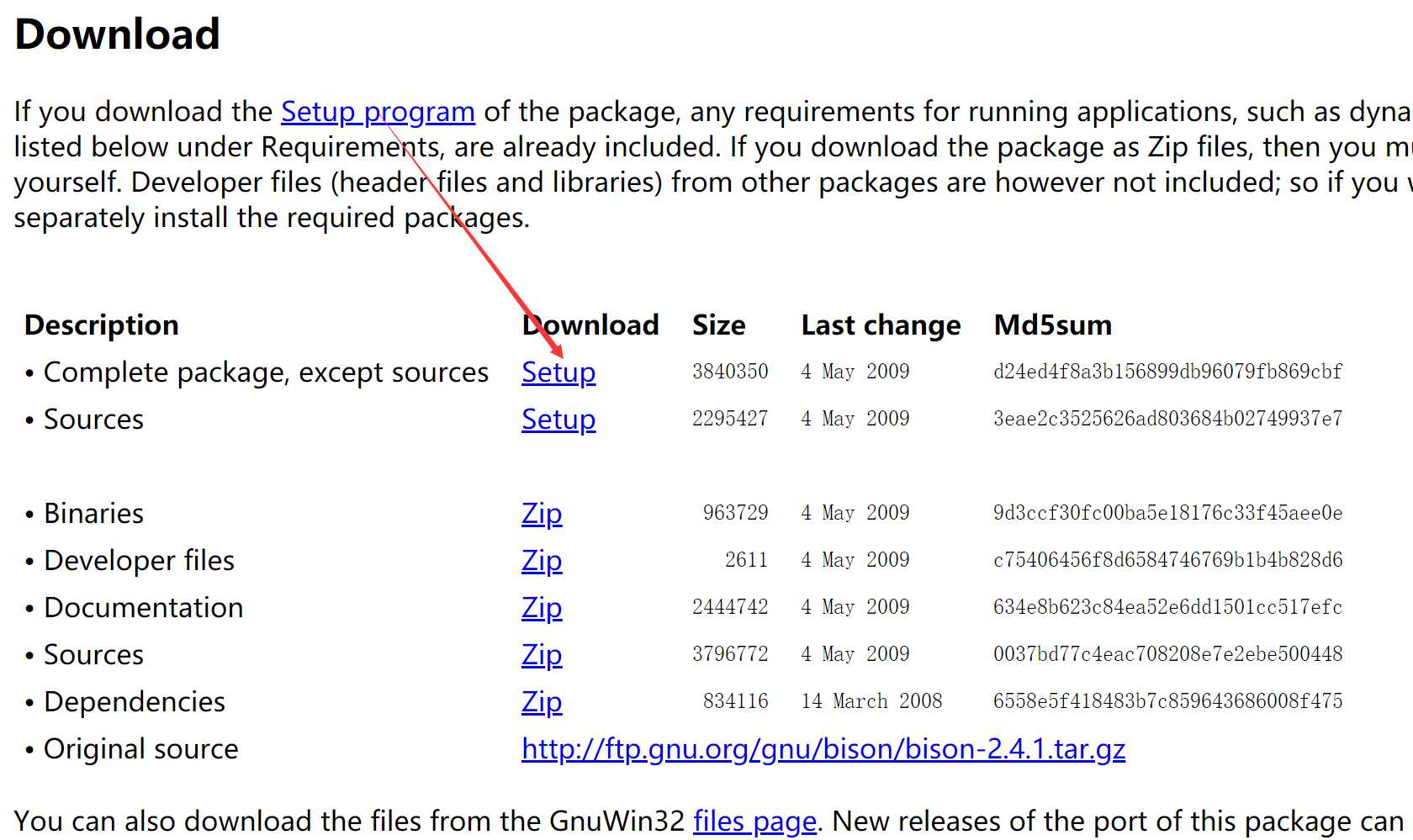
直接下载,点击安装即可
全都安装好以后还要设置一下环境变量Path,即需要将Bison的安装目录添加到Path中
打开右键->我的电脑→属性→高级系统设置->环境变量->系统变量->Path->编辑->新建->输入Bison的安装目录具体到bin目录下->确定
退出后,打开CMD,输入bison - V,记住这里的v要大写。若安装成功就会显示bison的相关信息
C:\>bison -V
bison (GNU Bison) 2.4.1
Written by Robert Corbett and Richard Stallman.
Copyright (C) 2008 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.然后结合具体的例子——四则运算来看看bison的作用
首先,准备好flex的词法文件cal.l:
另:flex的安装请见https://www.cnblogs.com/ASE265/p/12337922.html
%{
# include "y.tab.h"
%}
%%
[0-9]+ {yylval = atoi(yytext);return T_NUM;}
[-/+*()^\n] {return yytext[0];}
[ \t\r\a]+ {/*ignore all space*/}
. {return 0;}
%%
int yywrap(void){
return 1;
}然后是bison的语法分析文件cal.y文件
%{
#include <stdio.h>
int yylex();
void yyerror(const char* msg){}
%}
%token T_NUM
%left '+' '-'
%left '*' '/'
%%
S : S E '\n' {printf("ans=%d\n",$2);}
| /*enpty*/ {/*enpty*/}
;
E : E '+' E {$$ = $1+$3;}
| E '-' E {$$ = $1-$3;}
| E '*' E {$$ = $1*$3;}
| E '/' E {$$ = $1/$3;}
| T_NUM {$$ = $1;}
| '(' E ')' {$$ = $2;}
;
%%
int main(){
return yyparse();
}然后,就是执行过程
首先bison -dyv cal.y
得到y.output,y.tab.c和y.tab.h这三个文件
然后执行词法分析文件
flex cal.l
得到lex.yy.c文件
最后对c文件进行编译
gcc lex.yy.c y.tab.c -o cal
得到可执行文件cal.exe
cal.exe就是我们的小型四则运算的编译器
测试结果如下
D:\>cal.exe
2+3
ans=5
5*9
ans=45
1-5*7
ans=-34
4+(6-9)
ans=1确实,相当于实现了一个小型的四则运算的编译器
标签:logs 解释器 环境变量path org 我的电脑 技术 实现 如何 信息
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ASE265/p/12532038.html